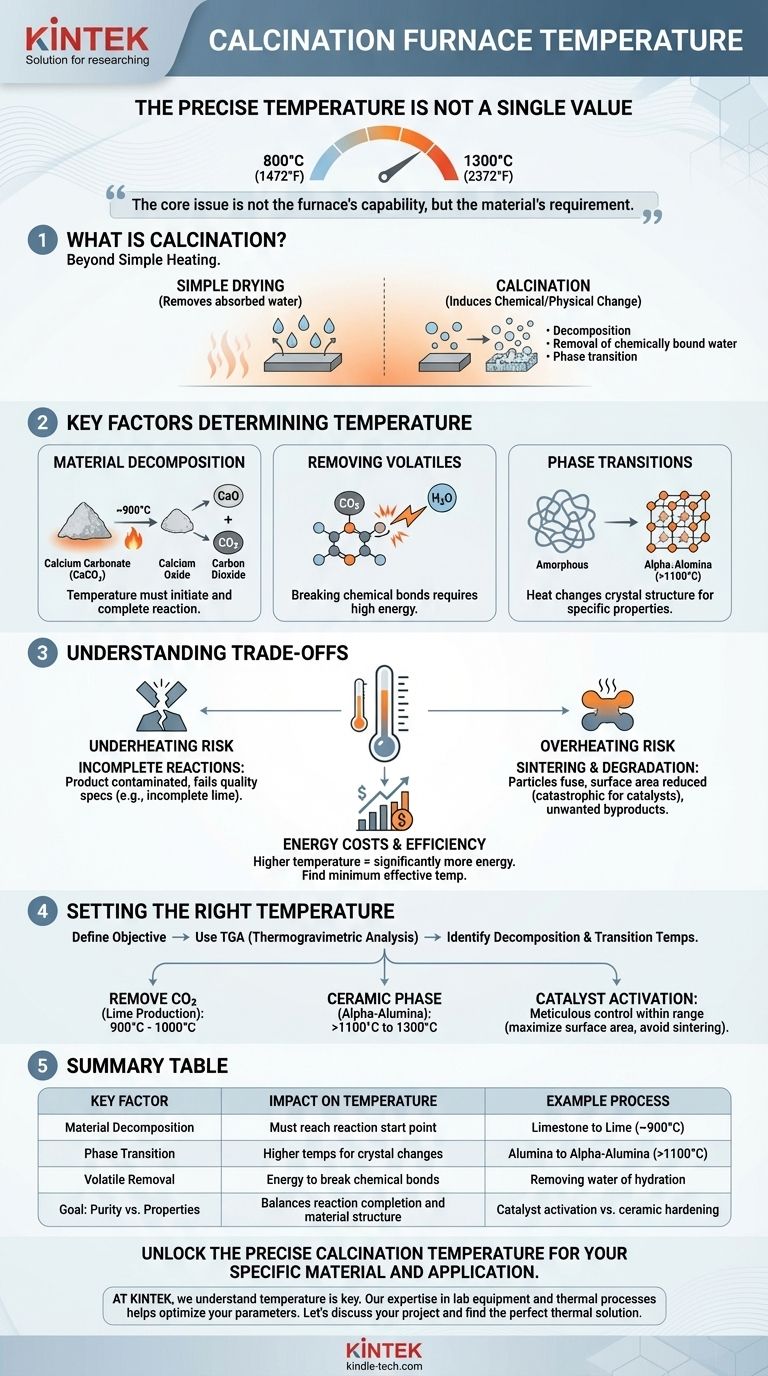
The precise temperature of a calcination furnace is not a single value but a carefully controlled range, typically between 800°C and 1300°C (1472°F to 2372°F). This wide variation exists because the exact temperature is a critical process parameter dictated by the specific material being treated and the desired chemical or physical transformation.
The core issue is not the furnace's capability, but the material's requirement. The question is not "What is the temperature of the furnace?" but rather, "What is the correct temperature needed to achieve my specific process goal for my specific material?"

What is Calcination? A Primer
Beyond Simple Heating
Calcination is a thermal treatment process applied to solids to induce a chemical reaction or physical change. It is fundamentally different from drying, which only removes absorbed water.
Calcination aims to cause a specific transformation, such as thermal decomposition, the removal of chemically bound water (water of hydration), or the transition from one crystalline phase to another.
The Goal Dictates the Process
The end goal of the process determines all operating parameters, most critically the temperature. Whether you are creating cement from limestone, preparing a catalyst, or producing a ceramic powder, the target properties of the final product dictate the required thermal conditions.
Key Factors Determining Calcination Temperature
Material Decomposition Temperature
Every material has a temperature at which it will thermally decompose. The calcination temperature must be high enough to initiate and complete this reaction.
For example, calcium carbonate (limestone) decomposes into calcium oxide (lime) and carbon dioxide. This reaction begins around 825°C and is typically carried out commercially near 900°C to ensure a complete and efficient conversion.
Removing Volatiles
Calcination is often used to remove volatile substances that are chemically bonded within a material's structure, such as carbon dioxide (CO₂) or water of hydration (H₂O).
Breaking these chemical bonds requires significantly more energy than simple drying. The temperature must be sufficient to supply the activation energy for these decomposition reactions to proceed.
Phase Transitions and Crystallinity
Heat can be used to change the crystal structure of a material, which in turn alters its physical and chemical properties.
For instance, certain alumina (aluminum oxide) precursors are calcined at temperatures exceeding 1100°C to convert them into the stable, hard alpha-alumina phase required for abrasives and ceramics. Lower temperatures would result in a different, less stable crystalline phase.
Understanding the Trade-offs of Temperature Control
The Risk of Overheating: Sintering and Degradation
Exceeding the optimal temperature can be as detrimental as not reaching it. Excessively high temperatures can cause unwanted sintering, where individual particles begin to fuse together.
This fusion reduces the material's surface area, which can be catastrophic for applications like catalysts or adsorbents. In other cases, overheating can lead to melting or decomposition into undesirable byproducts.
The Problem of Underheating: Incomplete Reactions
If the temperature is too low or the holding time is too short, the calcination reaction will be incomplete.
This results in a final product contaminated with unreacted starting material, failing to meet the required chemical purity or physical properties. For example, incompletely calcined limestone will still contain calcium carbonate, reducing the quality of the resulting lime.
Energy Costs and Efficiency
There is a direct and significant relationship between operating temperature and energy consumption. Running a furnace at 1200°C requires substantially more energy than running it at 900°C.
Therefore, finding the minimum effective temperature for a complete reaction is not just a matter of process quality but also a critical factor in managing operational costs.
Setting the Right Temperature for Your Goal
To select the correct temperature, you must first define your objective. A laboratory technique called Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA) is often used to precisely identify the decomposition and transition temperatures of a material before scaling up the process.
- If your primary focus is removing CO₂ from limestone to produce lime: You will operate in the lower end of the range, typically between 900°C and 1000°C.
- If your primary focus is producing a specific ceramic phase like alpha-alumina: You will need much higher temperatures, often exceeding 1100°C and approaching 1300°C, to drive the required phase transformation.
- If your primary focus is activating a catalyst support: The temperature must be meticulously controlled to maximize surface area and porosity without initiating sintering, often requiring a very precise temperature within the broader range.
Ultimately, the ideal calcination temperature is not a fixed number, but a carefully determined parameter that unlocks the specific material properties your process requires.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Impact on Temperature | Example Process |
|---|---|---|
| Material Decomposition | Must reach reaction start point | Limestone to Lime (~900°C) |
| Phase Transition | Higher temps for crystal changes | Alumina to Alpha-Alumina (>1100°C) |
| Volatile Removal | Energy to break chemical bonds | Removing water of hydration |
| Goal: Purity vs. Properties | Balances reaction completion and material structure | Catalyst activation vs. ceramic hardening |
Unlock the precise calcination temperature for your specific material and application.
At KINTEK, we understand that the correct temperature is the key to achieving your desired material properties, whether you are developing catalysts, producing ceramics, or processing minerals. Our expertise in lab equipment and thermal processes can help you optimize your calcination parameters for maximum efficiency, purity, and performance.
Let's discuss your project and find the perfect thermal solution for your lab. Contact our experts today to ensure your process is a success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a quartz tube in the preparation of Mo2Ga2C powder precursors? Essential Synthesis Benefits
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.



















