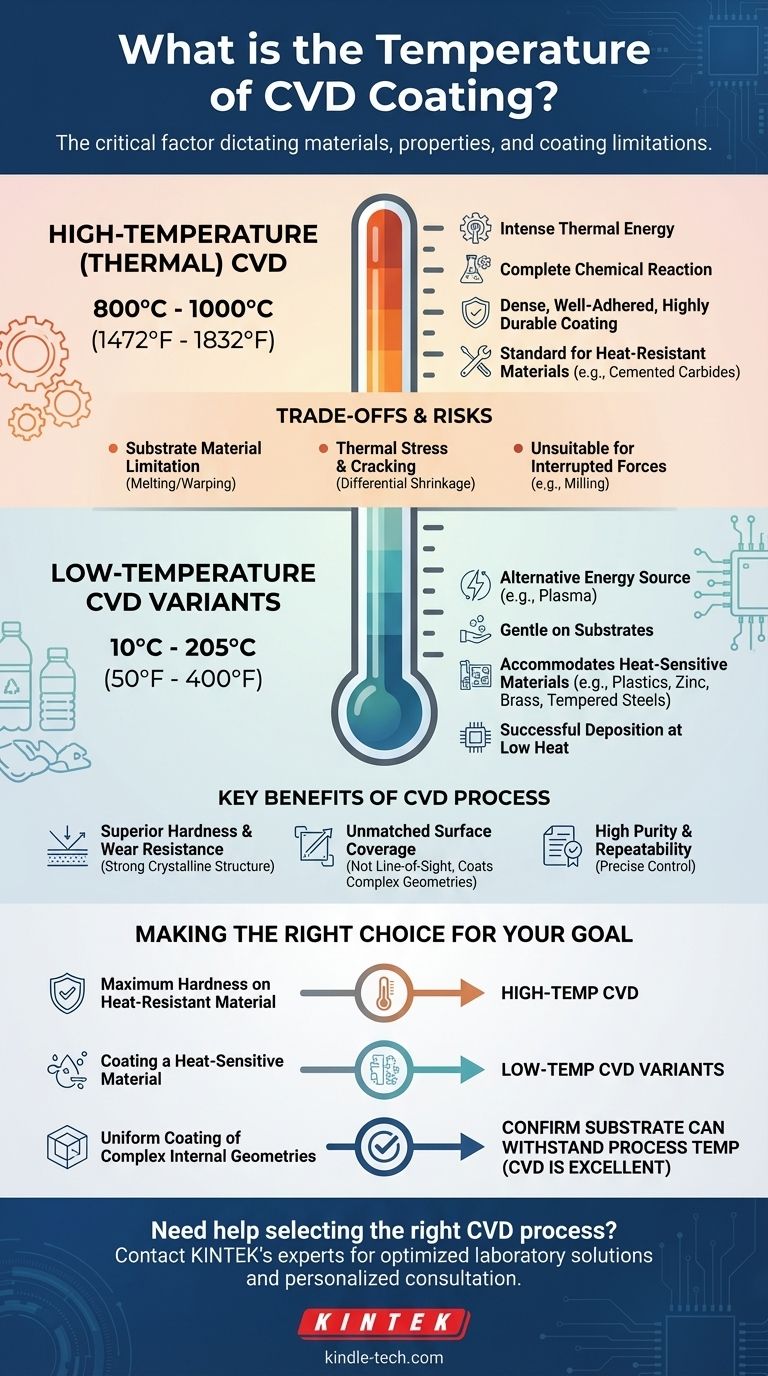
The temperature of a Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) process is not a single value, but rather a range that depends entirely on the specific type of CVD and the material being coated. Traditional thermal CVD operates at extremely high temperatures, typically between 800°C and 1000°C (1472°F and 1832°F). However, specialized low-temperature CVD variants exist that can operate at much lower temperatures, from approximately 10°C to 205°C (50°F to 400°F), to accommodate heat-sensitive materials.
The core principle to understand is that the process temperature is the single most critical factor in CVD. It dictates not only the materials you can coat but also the final properties—and potential weaknesses—of the coating itself.
The Defining Role of Temperature in CVD
Temperature in a CVD process is the primary catalyst. It provides the necessary thermal energy to initiate chemical reactions between precursor gases, allowing them to decompose and deposit a solid, high-purity film onto a substrate's surface.
High-Temperature (Thermal) CVD
The most common form of CVD relies on high heat, typically in the 800°C to 1000°C range. This intense thermal energy ensures a complete chemical reaction.
This results in a very dense, well-adhered, and highly durable coating. It is the standard process for materials that can withstand extreme heat, such as cemented carbides used in cutting tools.
Low-Temperature CVD Variants
For substrates that would be damaged or destroyed by high heat—such as plastics, zinc, brass, or certain steels—specialized CVD processes are required.
These methods use an alternative energy source, such as an electrical plasma, to drive the chemical reaction. This allows for successful deposition at much lower temperatures, sometimes as low as 10°C to 205°C.
Understanding the Trade-offs of High-Temperature CVD
While high-temperature CVD produces exceptionally hard coatings, the heat itself introduces significant limitations and risks that you must consider.
Substrate Material Limitation
This is the most significant constraint. The 800-1000°C process window immediately excludes any material that melts, warps, or has its fundamental properties altered by such high temperatures.
Risk of Thermal Stress and Cracking
During the cooling phase, the substrate and the new coating shrink at different rates. This differential creates immense tensile stress within the coating.
In thicker coatings (10-20μm), this stress can lead to the formation of fine cracks. While not always visible, these micro-cracks can become points of failure under physical impact.
Unsuitability for Certain Applications
The potential for micro-cracks makes high-temperature CVD less suitable for applications involving interrupted or inconsistent forces, such as milling. Each impact can propagate the cracks, eventually causing the coating to peel or chip away.
Key Benefits of the CVD Process
Despite the challenges posed by temperature, CVD offers unique advantages that make it the ideal choice for many applications.
Superior Hardness and Wear Resistance
The high-energy environment of thermal CVD creates a coating with a strong crystalline structure and excellent bonding to the substrate. This results in superior resistance to abrasion and wear compared to many other processes.
Unmatched Surface Coverage
Because the process uses reactive gases within a chamber, CVD is not a "line-of-sight" process. It can uniformly coat all exposed surfaces of an object, including complex internal channels, blind holes, and threads.
High Purity and Repeatability
The highly controlled nature of the chemical reaction allows for the creation of exceptionally pure films. This, combined with precise environmental control, ensures the process has excellent repeatability, which is critical for industries like semiconductors.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of process temperature is fundamentally a choice about your material and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness on a heat-resistant material (like cemented carbide): Traditional high-temperature CVD (800-1000°C) is the superior choice for its exceptional wear resistance.
- If your primary focus is coating a heat-sensitive material (like plastic, zinc, or tempered steel): You must specify a specialized low-temperature CVD variant that operates below the material's tolerance threshold.
- If your primary focus is uniform coating of complex internal geometries: CVD is an excellent option, but you must first confirm that your substrate material can withstand the thermal requirements of the process.
Ultimately, matching the process temperature to your substrate's limitations is the key to successfully leveraging the power of CVD technology.
Summary Table:
| CVD Process Type | Typical Temperature Range | Key Characteristics | Suitable Substrates |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-Temperature (Thermal) CVD | 800°C - 1000°C (1472°F - 1832°F) | Superior hardness, dense coating, excellent wear resistance | Cemented carbides, heat-resistant materials |
| Low-Temperature CVD Variants | 10°C - 205°C (50°F - 400°F) | Plasma-assisted, minimal thermal stress, gentle on substrates | Plastics, zinc, brass, tempered steels |
Need help selecting the right CVD process for your specific application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in laboratory equipment and consumables for advanced coating technologies. Our experts understand the critical balance between temperature requirements and substrate limitations. Whether you're working with heat-resistant materials requiring maximum hardness or delicate substrates needing low-temperature solutions, we can help you optimize your CVD process for superior results.
Contact us today to discuss your specific coating challenges and discover how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities. Get in touch with our specialists for personalized consultation and support.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the process capabilities of ICPCVD systems? Achieve Low-Damage Film Deposition at Ultra-Low Temperatures
- What is the process of PECVD in semiconductor? Enabling Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- Can plasma enhanced CVD deposit metals? Why PECVD is rarely used for metal deposition
- What is the difference between PECVD and APCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application
- How do PECVD systems improve DLC coatings on implants? Superior Durability and Biocompatibility Explained



















