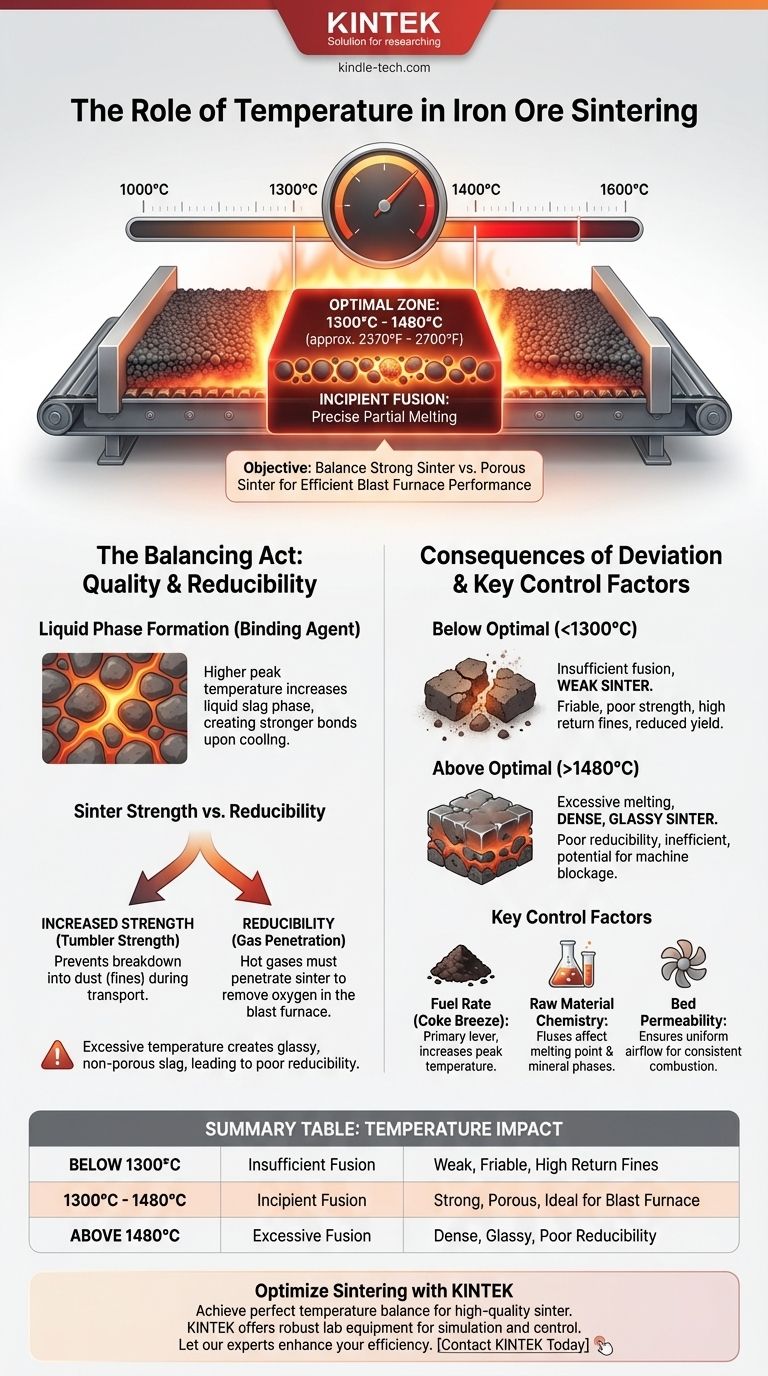
In iron ore sintering, the critical process temperature achieved within the sinter bed typically ranges from 1300°C to 1480°C (approximately 2370°F to 2700°F). This temperature is not a single target for the entire machine but rather the peak temperature reached in the narrow combustion zone as it travels down through the material bed. Achieving this specific temperature window is fundamental to producing high-quality sinter.
The objective of sintering is not simply to heat the material, but to induce incipient fusion—a precise partial melting. Controlling the temperature is a balancing act between creating sinter that is strong enough to survive handling yet porous enough to perform efficiently in the blast furnace.

The Role of Temperature in Sinter Quality
The temperature profile during sintering directly dictates the final chemical and physical properties of the product. It is the single most important variable for controlling the quality of the blast furnace feedstock.
Achieving Incipient Fusion
The primary purpose of the heat, generated by the combustion of coke breeze fuel, is to create a limited amount of a liquid slag phase. This molten material flows between the solid ore particles, acting as a binding agent. As the material cools, this liquid phase solidifies, creating a strong, porous clinker-like material called sinter.
The Impact on Sinter Strength
The amount of liquid phase formed is directly proportional to the peak temperature. A higher temperature generates more liquid, which generally results in a mechanically stronger sinter upon cooling. This strength, known as tumbler strength, is vital for preventing the sinter from breaking down into dust (fines) during transport and charging into the blast furnace.
The Effect on Reducibility
While strength is important, the sinter must also be reducible. This means the hot gases inside the blast furnace must be able to easily penetrate the sinter to remove oxygen from the iron oxides.
Temperatures that are too high can create an excessive amount of glassy, non-porous slag. This "over-fused" sinter, while very strong, has very poor reducibility. The gases cannot penetrate it, leading to major inefficiencies and increased fuel consumption in the blast furnace.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Sintering Temperature Window
The 1300°C to 1480°C range is not arbitrary; it represents a critical operational window where competing properties are balanced. Deviating from this window has significant negative consequences.
The Problem with Low Temperatures (<1300°C)
Operating below the optimal temperature range fails to generate enough liquid phase.
This results in weak sinter that is friable and has poor strength. It easily breaks apart during handling, creating an excess of "return fines" that must be re-sintered, reducing the plant's overall yield and efficiency.
The Danger of High Temperatures (>1480°C)
Exceeding the optimal temperature is often more detrimental than running too cool.
This causes excessive melting, leading to a dense, glassy, and poorly reducible sinter. Furthermore, extreme temperatures can cause the molten material to drip through and block the grate bars of the sinter machine, leading to costly operational delays and maintenance.
Key Factors That Control Sintering Temperature
Operators do not set a temperature directly. Instead, they manipulate several key inputs that collectively determine the temperature profile within the sinter bed.
Fuel Rate (Coke Breeze)
The amount of fine coke mixed into the sinter feed is the primary lever for controlling temperature. More coke provides more fuel for combustion, leading to a higher peak temperature. This is the most common and immediate adjustment operators make.
Raw Material Chemistry
The chemical composition of the iron ores and fluxes (like limestone and dolomite) significantly impacts the temperature required for fusion. Fluxes are added to lower the melting point and form specific mineral phases, like calcium ferrites, which are ideal for both strength and reducibility.
Bed Permeability
Combustion requires oxygen. Air is drawn down through the sinter bed by large fans. A highly permeable bed allows for uniform and efficient airflow, leading to stable and consistent combustion. Poor permeability starves the combustion zone of air, resulting in lower temperatures and incomplete sintering.
Optimizing Temperature for Sinter Performance
Your operational strategy for temperature control should be dictated by your specific production goals and challenges.
- If your primary focus is maximizing production throughput: You may operate at the higher end of the temperature range to ensure a fast burn-through rate, but you must constantly test sinter reducibility to avoid making an unusable product for the blast furnace.
- If your primary focus is blast furnace efficiency: You must maintain strict temperature control within the optimal window to produce sinter with the best possible balance of strength and reducibility, accepting that this may slightly limit the maximum production rate.
- If you are experiencing high rates of return fines: This is a clear signal that your average bed temperature is too low, resulting in weak agglomeration. A slight, controlled increase in the coke breeze rate is the first corrective action.
Ultimately, mastering sintering temperature is about balancing competing metallurgical properties to create the ideal feedstock for an efficient and stable blast furnace operation.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Key Outcome | Impact on Sinter Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Below 1300°C | Insufficient Fusion | Weak, friable sinter; high return fines |
| 1300°C - 1480°C (Optimal) | Incipient Fusion | Strong, porous sinter; ideal for blast furnace |
| Above 1480°C | Excessive Fusion | Dense, glassy sinter; poor reducibility |
Optimize your sintering process with precision equipment from KINTEK.
Achieving the perfect temperature balance is critical for producing high-quality sinter. KINTEK specializes in robust, reliable lab equipment and consumables for metallurgical testing and process optimization. Our solutions help you accurately simulate and control sintering conditions, ensuring your product meets the stringent strength and reducibility requirements of the modern blast furnace.
Let our experts help you enhance your sinter quality and operational efficiency. Contact KINTALK today to discuss your specific laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is sintering metallurgy? Create High-Strength Metal Parts Without Melting
- Can hydrogen be produced from biomass? A Guide to Sustainable, Low-Carbon Hydrogen
- What are the categories of heat treatment? A Guide to Softening, Hardening, and Refining Metals
- What are the two types of pyrolysis? A Guide to Fast vs. Slow Pyrolysis
- What are the methods of sintering? Choose the Right Technique for Your Materials
- Does heat transfer through a vacuum? Discover the Power of Thermal Radiation in Your Lab
- What type of brazing works at lower temperature? Silver Alloys for Heat-Sensitive Materials
- What are the four requirements of a heat treatment furnace? Ensure Precise Metallurgical Transformations



















