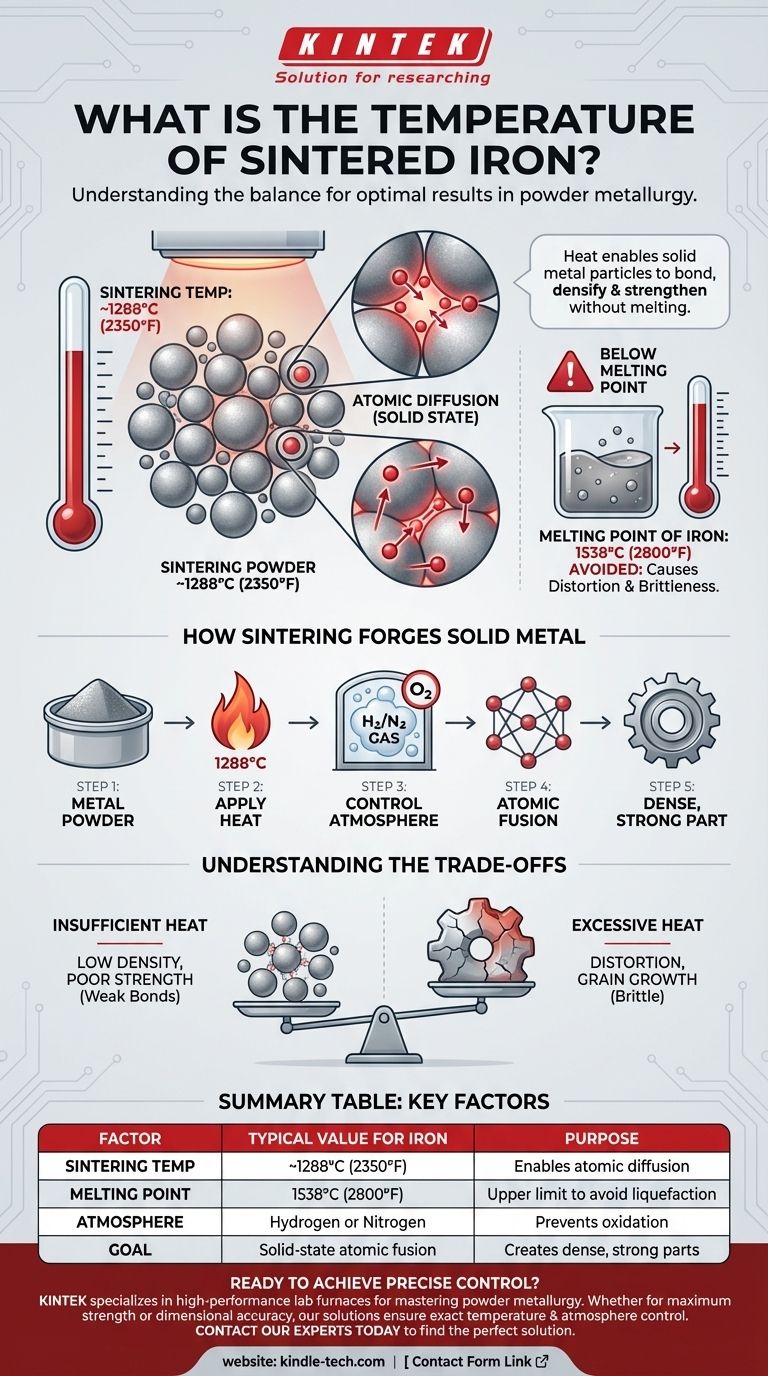
In practice, iron is typically sintered at temperatures approaching 1288°C (2350°F). This high temperature is crucial for the process, but it is intentionally kept below the actual melting point of iron, which is 1538°C (2800°F). The goal is not to liquefy the metal, but to give the metal powder particles enough energy to fuse together into a solid, functional part.
The key to understanding sintering temperature is recognizing that the process is about atomic fusion, not melting. The heat allows solid metal particles to bond and densify, creating a strong component without ever turning it into a liquid.

How Sintering Forges Solid Metal from Powder
Sintering is a cornerstone of powder metallurgy, a process that transforms fine metal powders into strong, net-shape parts. It relies on a careful balance of temperature, atmosphere, and time.
The Fundamental Role of Heat
The primary purpose of the high temperature is to enable atomic diffusion. At around 1288°C, the iron atoms become highly agitated. This energy allows them to move across the boundaries of individual powder particles, creating strong metallic bonds where the particles touch.
Think of it like pressing a handful of snowflakes together to form a solid snowball. The heat in sintering is the "pressure" that fuses the individual particles into a single, dense mass.
The Critical Importance of Atmosphere
This process does not happen in open air. Sintering furnaces are filled with a tightly controlled atmosphere, typically a reducing gas like hydrogen or an inert gas like nitrogen.
This is essential to prevent oxidation. If oxygen were present at these high temperatures, the iron would rapidly form iron oxide (rust), compromising the integrity and strength of the final component.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the precise sintering temperature is a critical engineering decision that involves balancing competing factors. It is not a single, fixed number but a variable controlled to achieve a desired outcome.
The Risk of Insufficient Heat
If the temperature is too low, atomic diffusion will be slow and incomplete. This results in weak bonds between particles. The final part will suffer from low density and poor mechanical strength, making it unsuitable for most applications.
The Danger of Excessive Heat
If the temperature gets too close to iron's melting point, you risk distortion and unwanted grain growth. The part can lose its precise shape, and large crystal grains can form within the metal, often making it more brittle. This defeats the purpose of creating a strong, dimensionally accurate component.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal sintering temperature is determined entirely by the objectives of the manufacturing process and the specific material alloy being used.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and density: You will operate at the higher end of the sintering range, close to 1288°C, to ensure the most complete particle bonding possible.
- If your primary focus is dimensional accuracy for complex shapes: You may use a slightly lower temperature or a more controlled heating cycle to minimize the risk of any part distortion.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency for non-critical parts: Lower temperatures may be used to reduce energy consumption, provided the resulting mechanical properties are still acceptable for the application.
Ultimately, mastering the sintering process is about precisely controlling temperature to produce a final part with the exact properties required.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Typical Value for Iron | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Sintering Temperature | ~1288°C (2350°F) | Enables atomic diffusion to bond particles |
| Melting Point of Iron | 1538°C (2800°F) | Upper limit to avoid liquefaction |
| Atmosphere | Hydrogen or Nitrogen | Prevents oxidation during heating |
| Goal | Solid-state atomic fusion | Creates dense, strong parts from powder |
Ready to achieve precise control over your sintering process?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the high-performance lab furnaces and consumables you need to master powder metallurgy. Whether you're sintering iron for maximum strength or dimensional accuracy, our equipment ensures the exact temperature and atmosphere control critical for success.
Let's discuss your project. Contact our experts today to find the perfect sintering solution for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why would you braze instead of solder? For Superior Joint Strength and High-Temperature Performance
- What are the methods of brazing heating? Choose the Right Method for Your Production Needs
- What are the advantages of vacuum sintering? Achieve Superior Purity, Strength, and Performance
- Why is environmental control within a vacuum furnace important for diffusion bonding? Master Titanium Alloy Laminates
- What is sintering reaction? Transform Powders into Dense Solids Without Melting



















