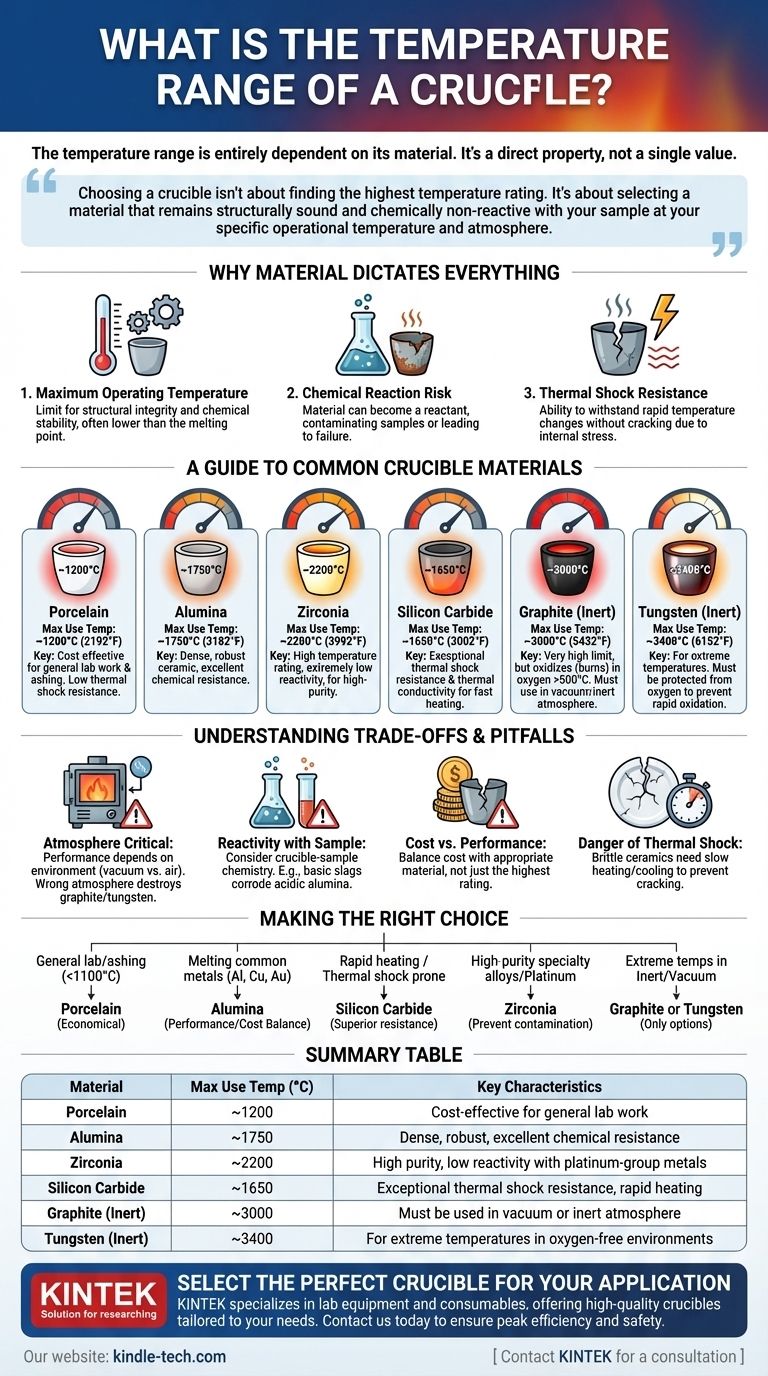
The temperature range of a crucible is entirely dependent on its material. A common porcelain crucible may only withstand temperatures up to 1200°C (2192°F), while a specialized tungsten crucible can be used at over 3000°C (5432°F). There is no single temperature range; the rating is a direct property of the material from which the crucible is made.
Choosing a crucible isn't about finding the one with the highest temperature rating. It's about selecting a material that remains structurally sound and chemically non-reactive with your sample at your specific operational temperature and atmosphere.

Why Material Dictates Everything
The question of temperature range goes far deeper than a simple melting point. The suitability of a crucible is determined by a combination of thermal and chemical properties that must match the intended application.
The Concept of Maximum Operating Temperature
A crucible's "maximum use temperature" is often lower than the material's actual melting point. It represents the highest temperature at which the crucible maintains its structural integrity and chemical stability without degrading or deforming under load.
The Risk of Chemical Reaction
At high temperatures, the crucible itself can become a reactant. The wrong material can contaminate your sample, or your sample can actively corrode and destroy the crucible, leading to catastrophic failure.
Thermal Shock Resistance
Materials expand when heated and contract when cooled. If this happens too quickly, the resulting internal stress can crack a brittle ceramic crucible. This property, known as thermal shock resistance, is a critical factor for applications requiring rapid temperature cycles.
A Guide to Common Crucible Materials
Each material offers a unique profile of temperature resistance, chemical inertness, and cost. Understanding these options is the key to making an informed choice.
Porcelain
Porcelain is a cost-effective choice for general laboratory work like ashing organic materials. It has a relatively low thermal shock resistance and should be heated and cooled slowly.
- Maximum Use Temperature: ~1200°C (2192°F)
Alumina (Aluminum Oxide)
High-purity alumina is a dense, robust ceramic, making it one of the most versatile and widely used crucible materials. It has excellent chemical resistance against many metals and slags.
- Maximum Use Temperature: ~1750°C (3182°F)
Zirconia (Zirconium Dioxide)
Zirconia offers a higher temperature rating than alumina and has extremely low reactivity, especially with platinum-group metals. It is an excellent choice for high-purity applications where contamination is a primary concern.
- Maximum Use Temperature: ~2200°C (3992°F)
Silicon Carbide (SiC)
The defining characteristic of silicon carbide is its exceptional thermal conductivity and resistance to thermal shock. This makes it ideal for applications that require very fast heating rates.
- Maximum Use Temperature: ~1650°C (3002°F)
Graphite
Graphite boasts a very high temperature limit but comes with a critical caveat: it readily oxidizes (burns) in the presence of oxygen above 500°C. It must be used in a vacuum or an inert (oxygen-free) atmosphere to reach its full potential.
- Maximum Use Temperature (Inert): ~3000°C (5432°F)
Refractory Metals (Tungsten, Molybdenum)
For the most extreme temperature requirements, crucibles made from refractory metals are the only option. Like graphite, they must be protected from oxygen at high temperatures to prevent rapid oxidation and failure.
- Maximum Use Temperature (Tungsten, Inert): ~3400°C (6152°F)
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
Selecting the wrong crucible can be a costly mistake, leading to failed experiments, damaged equipment, and contaminated results.
Atmosphere is Critical
A crucible's performance is inseparable from its environment. A graphite or tungsten crucible is a top performer in a vacuum furnace but will be destroyed quickly in an air-atmosphere furnace operating at high temperatures.
Reactivity with Your Sample
Always consider the chemistry between your crucible and the material you are heating. For example, melting highly basic slags in an acidic alumina crucible can lead to rapid corrosion and failure.
Cost vs. Performance
There is a significant cost difference between a common porcelain crucible and a high-purity zirconia one. The goal is not to choose the highest-rated material, but the most appropriate and cost-effective one for the specific task.
The Danger of Thermal Shock
Brittle ceramics like porcelain and alumina do not tolerate rapid temperature changes. Always pre-heat them and allow for controlled cooling to prevent cracking and extend their service life.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by your specific experimental or process conditions.
- If your primary focus is general lab work or ashing below 1100°C: A standard porcelain crucible is the most economical and practical choice.
- If your primary focus is melting common metals like aluminum, copper, or gold: An alumina crucible offers an excellent balance of performance and cost.
- If your primary focus is rapid heating cycles or materials prone to causing cracks: A silicon carbide crucible is superior due to its excellent thermal shock resistance.
- If your primary focus is melting high-purity specialty alloys or platinum: A zirconia crucible is necessary to prevent contamination at very high temperatures.
- If your primary focus is achieving extreme temperatures in an inert atmosphere or vacuum: Graphite or a refractory metal like tungsten are your only viable options.
Ultimately, selecting the correct crucible requires matching its material properties to your specific temperature, atmosphere, and chemical requirements.
Summary Table:
| Material | Maximum Use Temperature (°C) | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Porcelain | ~1200°C | Cost-effective for general lab work (e.g., ashing) |
| Alumina | ~1750°C | Dense, robust, excellent chemical resistance |
| Zirconia | ~2200°C | High purity, low reactivity with platinum-group metals |
| Silicon Carbide | ~1650°C | Exceptional thermal shock resistance, rapid heating |
| Graphite (Inert) | ~3000°C | Must be used in vacuum or inert atmosphere |
| Tungsten (Inert) | ~3400°C | For extreme temperatures in oxygen-free environments |
Select the Perfect Crucible for Your Application
Choosing the right crucible is critical for the success and safety of your lab work. The wrong material can lead to contamination, equipment damage, or even failure of your experiment.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, offering a wide range of high-quality crucibles tailored to your specific needs—whether you're working with common metals, high-purity alloys, or extreme-temperature processes.
Let our experts help you match the ideal crucible material to your temperature, atmosphere, and chemical requirements. Contact us today to ensure your lab operates at peak efficiency and safety.
Contact KINTEK for a consultation
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Tungsten Crucible and Molybdenum Crucible for High Temperature Applications
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
People Also Ask
- What is the container that holds the metal source material called in e-beam evaporation? Ensure Purity and Quality in Your Thin-Film Deposition
- What affects melting point chemistry? A Guide to Molecular Forces and Lattice Energy
- Why are high-temperature crucibles required for Li_xScCl_{3+x} electrolytes? Ensure Purity & Ionic Conductivity
- What are 4 disadvantages of brazing? Understanding the Critical Limitations of This Joining Method
- What three factors cause melting? Understand Temperature, Pressure, and Impurities



















