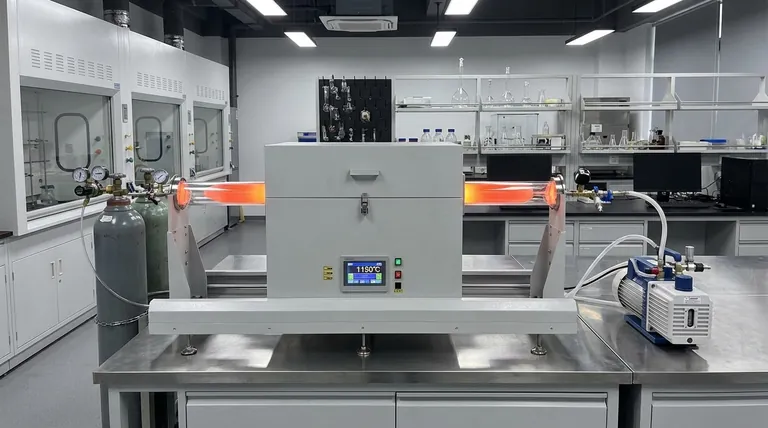
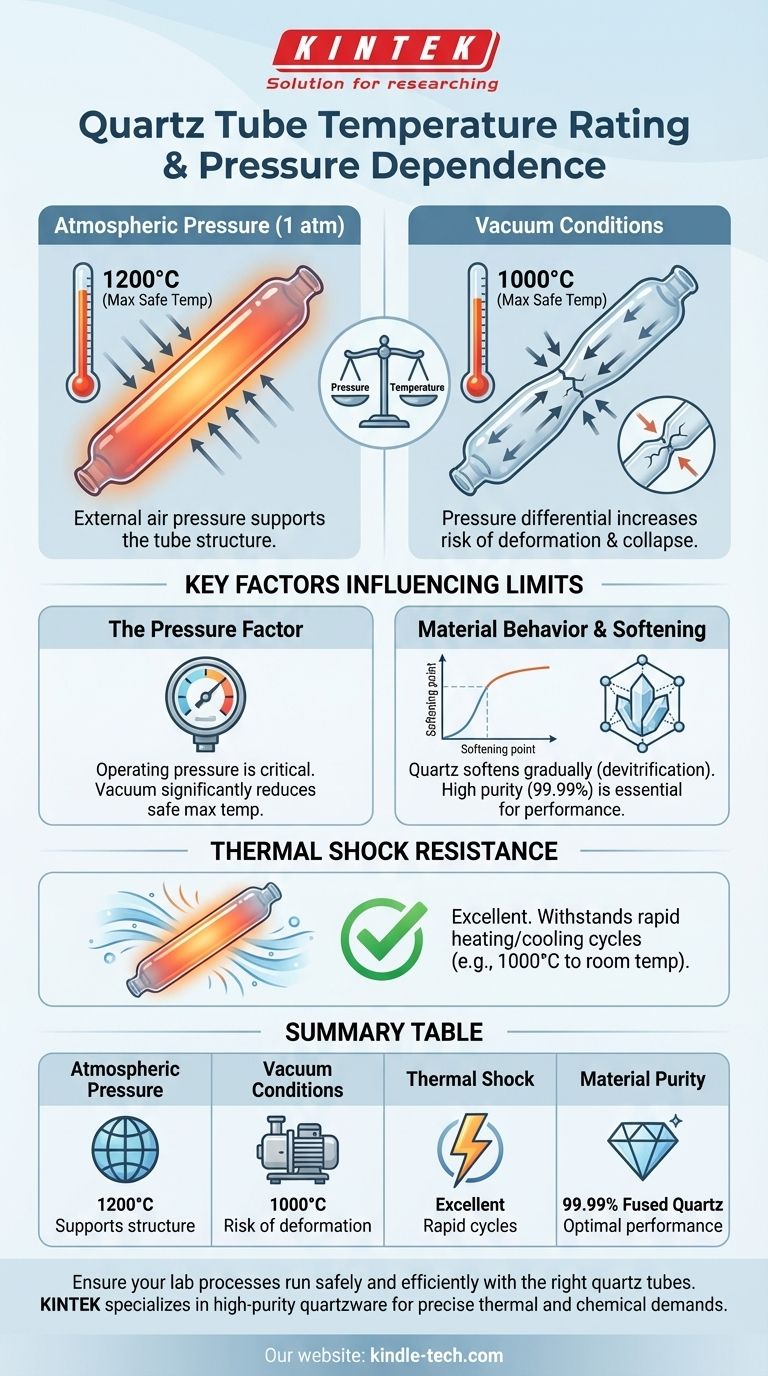
In short, a quartz tube's maximum operating temperature is typically between 1000°C and 1200°C. This rating is not a single number but depends critically on the operating pressure. Under a standard atmosphere, the limit is around 1200°C, but this drops to approximately 1000°C when operating under vacuum conditions.
The most critical factor determining a quartz tube's temperature rating is not just the heat itself, but the pressure environment. Operating under vacuum significantly reduces the safe maximum temperature compared to operating at atmospheric pressure.

Key Factors Influencing Temperature Limits
The material properties of high-purity quartz make it ideal for high-temperature applications, but its performance is governed by the physical stresses placed upon it. Understanding these factors is crucial for safe and effective operation.
The Impact of Atmospheric Pressure
At standard atmospheric pressure (1 atm), a quartz tube can typically be used continuously at temperatures up to 1200°C. The external air pressure helps support the tube's structure, preventing it from deforming as the material approaches its softening point.
The Challenge of Vacuum Conditions
When a vacuum is pulled inside the tube, the situation changes. The pressure differential between the outside (atmosphere) and the inside (vacuum) creates significant stress on the tube walls. This stress lowers the safe operating limit to approximately 1000°C to prevent the tube from softening and potentially collapsing.
Exceptional Thermal Shock Resistance
Beyond its high-temperature ceiling, quartz has remarkable resistance to thermal shock. This means it can withstand rapid and extreme temperature changes without cracking. A quartz tube can be heated to 1000°C and then safely exposed to room temperature air, a property that many other materials lack.
Understanding the Material's Behavior
A material's temperature "rating" is often a guideline for its service limit, not an absolute breaking point. For quartz, the primary concern at high temperatures is not shattering but a gradual loss of structural integrity.
The Softening Point
As quartz approaches its maximum temperature limit, it doesn't melt suddenly. Instead, it begins to soften and lose its rigidity. This process, known as devitrification, makes it susceptible to deformation, especially under the physical stress of a vacuum.
The Role of Purity
High-quality quartz tubes are made from 99.99% pure fused quartz. This high purity is essential for achieving excellent high-temperature performance and chemical resistance. Impurities can create weak points in the material, lowering its effective softening point and overall reliability.
How to Apply This to Your Process
Choosing the correct operating parameters is essential for safety and the longevity of your equipment. Use these guidelines to determine your limits.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature processing at atmospheric pressure: You can safely operate your system at up to 1200°C.
- If your primary focus is working under vacuum: You must restrict your maximum temperature to 1000°C to avoid tube deformation and failure.
- If your primary focus is rapid heating and cooling cycles: The superior thermal shock resistance of quartz makes it an ideal choice for your application.
Understanding these operational limits ensures you can leverage the unique properties of quartz safely and effectively.
Summary Table:
| Operating Condition | Maximum Safe Temperature | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Atmospheric Pressure | 1200°C | External air pressure supports tube structure. |
| Vacuum Conditions | 1000°C | Pressure differential increases risk of deformation. |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Excellent | Can withstand rapid heating/cooling cycles. |
| Material Purity | 99.99% Fused Quartz | High purity ensures optimal performance and chemical resistance. |
Ensure your lab processes run safely and efficiently with the right quartz tubes.
KINTEK specializes in high-purity quartz tubes and lab equipment, designed to meet the precise thermal and chemical demands of your research or production. Our products help you achieve reliable results while maximizing equipment longevity.
Contact us today to discuss your specific application requirements and get expert guidance on selecting the ideal quartzware for your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a tube furnace work? Master Precise Thermal and Atmospheric Control
- What is the role of high-precision laboratory tube furnaces in the development of heterojunction photocatalysts?
- What can you use glass tubes for? Essential Applications in Labs, Industry, and Design
- What is the pyrolysis method of plastic recycling? Turn Waste Plastic into Fuel and Chemicals
- What are the primary applications of tube or muffle furnaces in the study of phase transformations? Reverting Martensite
- What functions does a laboratory high-temperature tube furnace perform? Master Catalyst Synthesis & Carbonization
- Why is a high-precision atmosphere tube furnace necessary? Ensure Stability in Carbon Catalyst Calcination
- What is the range of a TF tube furnace? Maximize Your Process with the Right Temperature & Uniformity



















