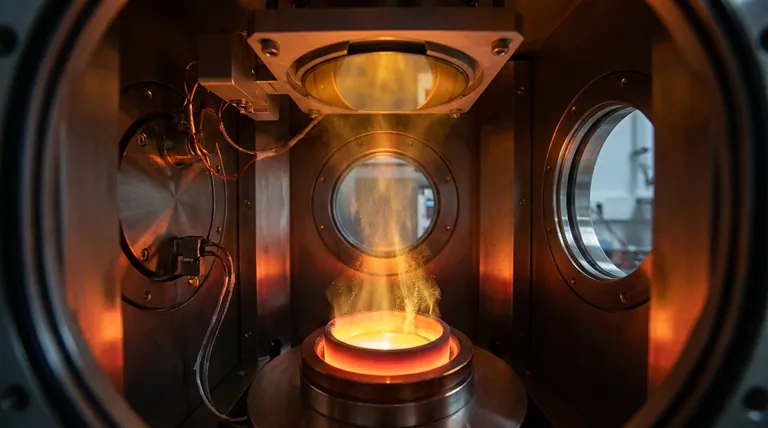
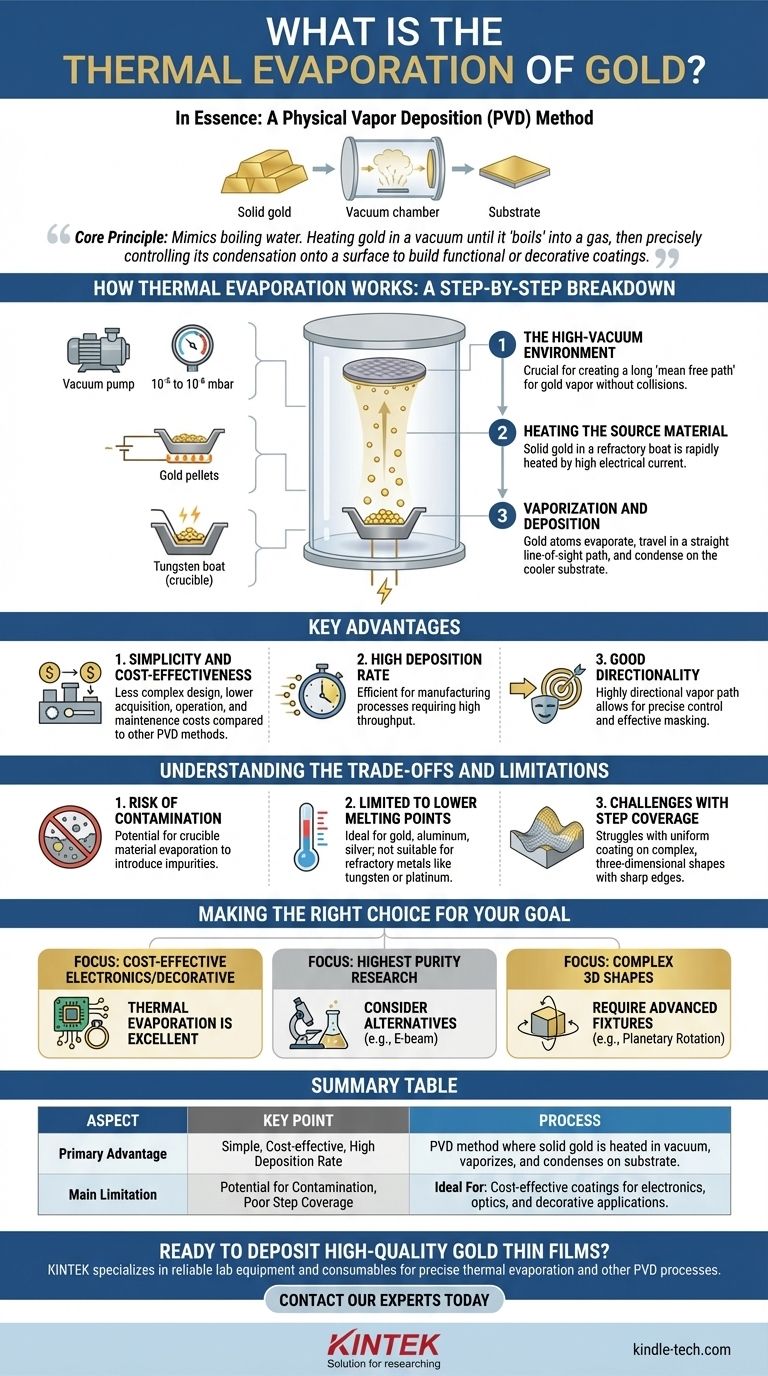
In essence, thermal evaporation of gold is a physical vapor deposition (PVD) method used to create a thin, uniform layer of gold on a surface. The process works by heating a piece of solid gold in a high-vacuum chamber until it turns into a vapor. These gold vapor atoms then travel through the vacuum and condense onto a cooler target object, known as a substrate, forming the desired thin film.
At its core, thermal evaporation is a straightforward and cost-effective technique that mimics the process of boiling water. By heating gold in a vacuum until it "boils" into a gas, we can precisely control its condensation onto a surface to build functional or decorative coatings atom by atom.

How Thermal Evaporation Works: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
The entire process occurs inside a sealed vacuum chamber, and each step is critical for producing a high-quality film. The principle is fundamentally simple, relying on basic physics to move material from a source to a substrate.
The High-Vacuum Environment
The first and most crucial element is the high-vacuum environment, typically at a pressure of 10⁻⁵ to 10⁻⁶ mbar. This vacuum removes air and other gas molecules from the chamber.
This step is essential because it creates a clear, unobstructed path—often called a long "mean free path"—for the gold vapor to travel from the source to the substrate without colliding with other particles.
Heating the Source Material
The solid gold, often in the form of pellets or wire, is placed in a small container called a crucible or "boat." This boat is typically made from a refractory material like tungsten.
A very high electrical current is passed through the boat, causing it to heat up rapidly due to its electrical resistance. This heat is transferred directly to the gold.
Vaporization and Deposition
As the gold reaches its evaporation temperature (well below its boiling point, thanks to the vacuum), its atoms gain enough thermal energy to escape the surface and become a vapor.
This stream of gold vapor travels in a straight, line-of-sight path until it strikes the cooler substrate (such as a silicon wafer, glass, or plastic part) positioned above it. Upon contact, the vapor atoms rapidly cool, condense back into a solid state, and build up to form a thin, solid film.
Key Advantages of Using Thermal Evaporation for Gold
This method remains popular because it offers a practical balance of performance, cost, and simplicity, making it an ideal choice for many applications.
Simplicity and Cost-Effectiveness
Compared to more complex deposition techniques like sputtering or electron-beam evaporation, thermal evaporation systems are relatively simple in design and operation. This makes them less expensive to acquire, operate, and maintain.
High Deposition Rate
Thermal evaporation can deposit material quickly, making it efficient for manufacturing processes where throughput is a key consideration.
Good Directionality
Because the vapor travels in a straight line, the coating is highly directional. This provides excellent control over where the material is deposited, which is useful for techniques that involve masking off certain areas of the substrate.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly effective, thermal evaporation is not the right solution for every scenario. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
The Risk of Contamination
The primary drawback is the potential for crucible contamination. The boat holding the gold is heated to extreme temperatures, and atoms from the boat material itself can evaporate along with the gold. This can introduce impurities into the final gold film, which may be unacceptable for high-purity applications.
Limited to Lower Melting Points
This method works exceptionally well for materials with relatively low melting points, like gold, aluminum, and silver. However, it is not suitable for refractory metals like tungsten or platinum, which require far too much energy to evaporate thermally.
Challenges with Step Coverage
The line-of-sight nature of the process means it can struggle to uniformly coat complex, three-dimensional surfaces with sharp edges or deep trenches. Areas that are not in the direct path of the vapor stream will receive little to no coating.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right deposition method depends entirely on the requirements of your final product, from cost and speed to purity and uniformity.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective coating for electronics or decorative parts: Thermal evaporation is an excellent and highly efficient choice for depositing gold.
- If your primary focus is achieving the absolute highest film purity for sensitive research: You should consider alternative methods like electron-beam evaporation to mitigate crucible contamination.
- If your primary focus is coating complex 3D shapes uniformly: You will need to invest in advanced substrate fixtures, such as planetary rotation systems, to overcome line-of-sight limitations.
By understanding these core principles and trade-offs, you can effectively determine if thermal evaporation is the optimal technique for creating your high-quality gold thin film.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Point |
|---|---|
| Process | A PVD method where solid gold is heated in a vacuum until it vaporizes and condenses on a substrate. |
| Primary Advantage | Simple, cost-effective, and offers high deposition rates. |
| Main Limitation | Potential for crucible contamination and poor step coverage on complex 3D shapes. |
| Ideal For | Cost-effective coatings for electronics, optics, and decorative applications. |
Ready to Deposit High-Quality Gold Thin Films?
KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables for precise thermal evaporation and other PVD processes. Whether you're in R&D or manufacturing, our solutions help you achieve consistent, high-performance coatings.
Let's discuss your project requirements and find the perfect equipment for your lab's needs.
Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Conductive Boron Nitride Crucible BN Crucible
People Also Ask
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What are the components of PECVD? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition Systems
- What is the speed of PECVD? Achieve High-Speed, Low-Temperature Deposition for Your Lab



















