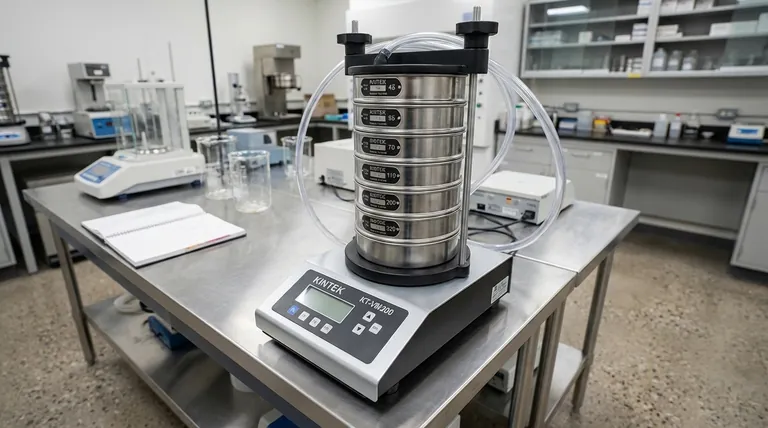
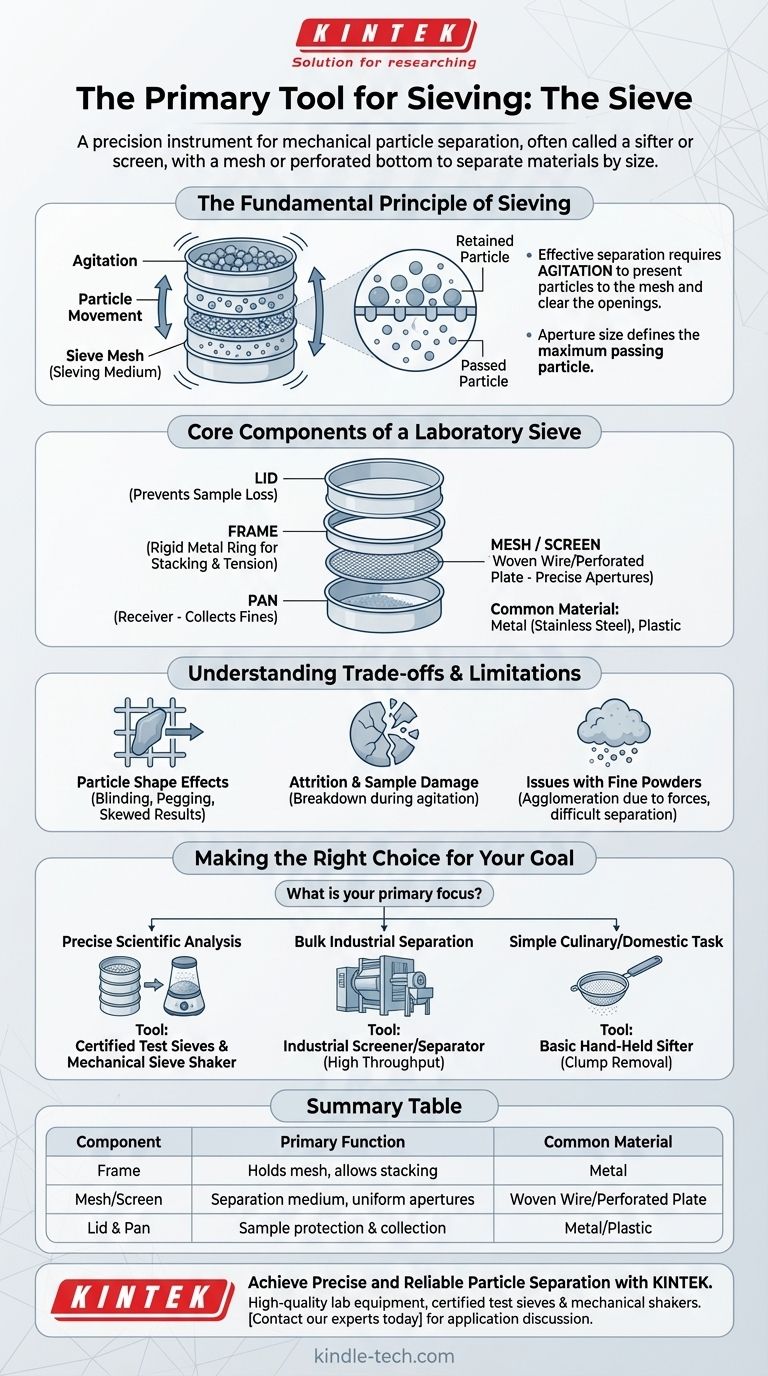
The primary tool used in the process of sieving is called a sieve. Often referred to as a sifter or screen, a sieve is a device with a mesh or perforated bottom used to separate wanted elements from unwanted material or to characterize the particle size distribution of a sample.
At its core, a sieve is a precision instrument for mechanical particle separation. It operates on the simple principle that agitation allows particles smaller than the mesh openings to pass through, while retaining those that are larger.

The Fundamental Principle of Sieving
The effectiveness of any sieving operation hinges on a single, clear mechanical principle: creating relative movement between the particles and the sieve mesh. This agitation is critical for ensuring an accurate and efficient separation.
The Role of Agitation
A static pile of material on a sieve will result in poor separation. Motion is required to continuously present new particles to the mesh openings and to clear away particles that have already passed through. This is why sieving involves shaking, vibrating, or tapping.
The Sieve Mesh (Sieving Medium)
The heart of the sieve is its mesh, also known as the sieving medium or screen. This surface contains a series of uniform apertures or holes of a specific size.
The aperture size is the defining characteristic of a sieve, dictating the maximum particle size that can pass through.
Particle vs. Aperture Interaction
During agitation, each particle is tested against the mesh openings numerous times. If a particle's dimensions are smaller than the aperture in at least two directions, it will likely fall through. Particles larger than the aperture are retained on the mesh surface.
Core Components of a Laboratory Sieve
While the concept is simple, a laboratory-grade sieve is a precisely manufactured tool. It is often used in a stack, from coarsest mesh on top to finest on the bottom, to perform a particle size distribution analysis.
The Frame
The frame is a rigid, typically cylindrical, metal ring that holds the sieving mesh under tension. Its primary job is to provide structural integrity and allow for stacking.
The Mesh
This is the functional component, most commonly made of woven stainless steel wire or a perforated plate. Meshes are manufactured to strict standards (like ASTM or ISO) to ensure the aperture sizes are highly accurate and consistent.
The Lid and Pan (Receiver)
When sieves are used in a stack, a lid is placed on the top sieve to prevent any loss of the sample during agitation. A solid pan, also called a receiver, is placed at the very bottom of the stack to collect the finest particles that pass through all the sieves.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Sieving is a powerful and widely used technique, but it is not without its limitations. Understanding these challenges is key to generating reliable results.
Particle Shape Effects
Sieving assumes particles are roughly spherical. Elongated or flat particles can present a problem by either passing through the mesh end-on (skewing results) or getting stuck in the apertures, a phenomenon known as blinding or pegging.
Attrition and Sample Damage
The mechanical agitation required for sieving can damage friable or brittle particles. This process, called attrition, breaks down larger particles into smaller ones during the test, which can lead to an inaccurate analysis of the original sample.
Issues with Fine Powders
Very fine powders (typically below 45 microns) are difficult to separate using standard dry sieving. Cohesive forces, static electricity, and moisture can cause particles to agglomerate, preventing them from passing through the mesh effectively.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The term "sieve" can apply to a simple kitchen tool or a calibrated scientific instrument. The right tool depends entirely on your objective.
- If your primary focus is precise scientific analysis: You require a set of certified test sieves with documented aperture sizes and a mechanical sieve shaker to ensure repeatable, consistent agitation.
- If your primary focus is bulk industrial separation: Your tool is an industrial screener or separator, designed for high throughput and durability rather than analytical precision.
- If your primary focus is a simple culinary or domestic task: A basic hand-held sifter or strainer is perfectly sufficient for tasks like removing clumps from flour.
Ultimately, understanding the mechanics of the sieve allows you to select the right tool to achieve reliable and accurate particle separation for any application.
Summary Table:
| Sieve Component | Primary Function | Common Material |
|---|---|---|
| Frame | Holds the mesh under tension; allows for stacking | Metal (e.g., Stainless Steel) |
| Mesh / Screen | The sieving medium with uniform apertures for separation | Woven Wire or Perforated Plate |
| Lid & Pan (Receiver) | Prevents sample loss (lid) and collects fine particles (pan) | Metal or Plastic |
Achieve precise and reliable particle separation with KINTEK.
Whether you are performing precise particle size distribution analysis in your laboratory or require robust equipment for industrial screening, the right sieve is critical for accurate results. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including certified test sieves and mechanical sieve shakers, designed for durability, consistency, and adherence to ASTM/ISO standards.
Let our expertise help you select the perfect sieving solution for your specific needs. Contact our experts today to discuss your application and enhance your separation processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Dry Three-Dimensional Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Vortex Mixer Orbital Shaker Multifunctional Rotation Oscillation Mixer
People Also Ask
- What is sieve analysis of raw materials? Control Quality with Particle Size Data
- Why is a 100 µm standard test sieve required for LGVO powder? Ensure Smooth Aerosol Deposition and Coating Uniformity
- What are the different methods of sieving? Choose the Right Technique for Your Material
- How do I choose a sieve size? A Step-by-Step Guide to Building the Perfect Sieve Stack
- What is the sieving method of separation? A Guide to Efficient Particle Size Classification
- What is a sieve used for in a lab? Ensure Material Consistency with Precise Particle Size Analysis
- Why use a standard sieve for Prosopis juliflora pretreatment? Ensure Precision in Particle Size Control
- Role of Mechanical Disassembly and Sieving in Recycling Lithium Battery Anodes? Achieve 99%+ Purity Feedstock



















