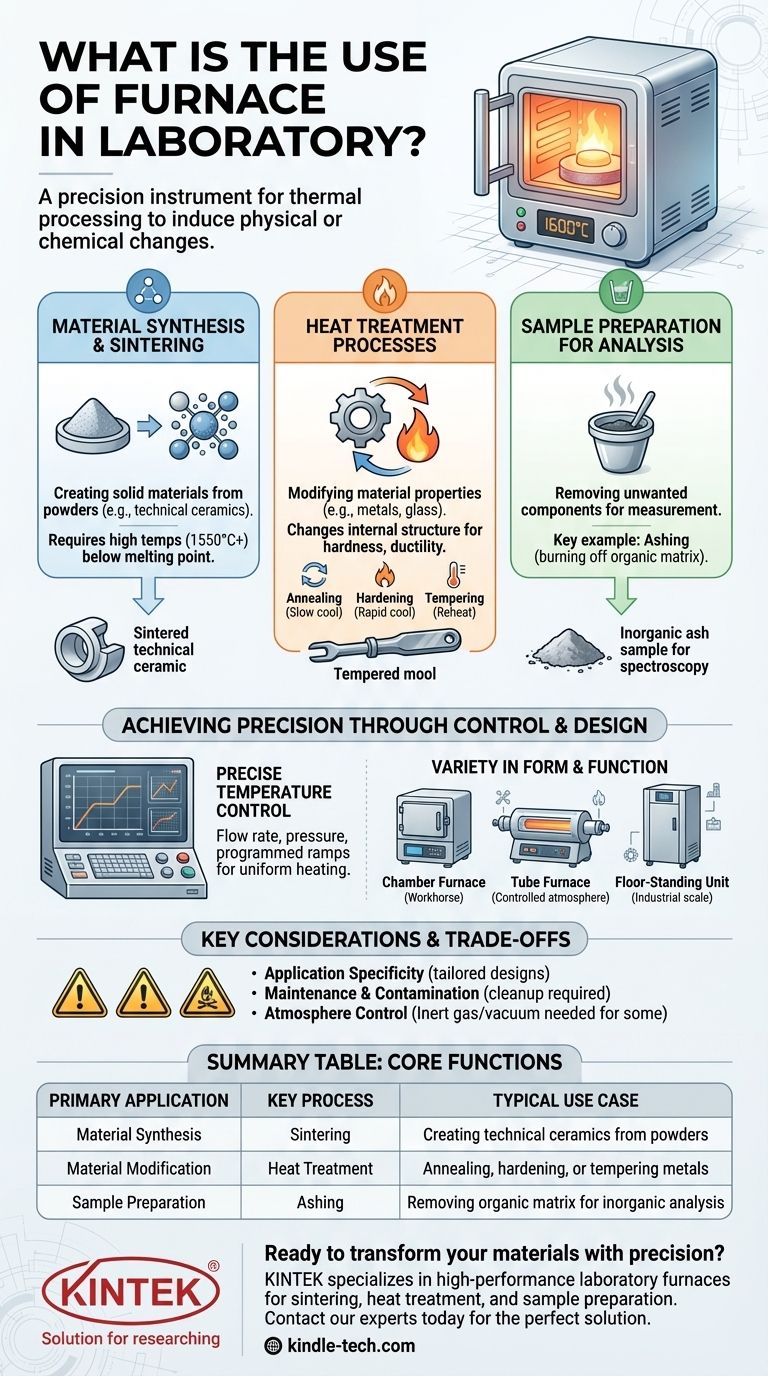
In short, a laboratory furnace is a high-temperature oven used for thermal processing. Its primary role is to subject materials to precisely controlled, extreme temperatures to induce physical or chemical changes. This includes creating new materials through sintering, altering the properties of existing ones via heat treatment, or preparing samples for analysis.
The core purpose of a laboratory furnace is not simply to heat things up, but to fundamentally transform materials. It is a precision instrument for altering a substance's structure, composition, or properties using controlled thermal energy.
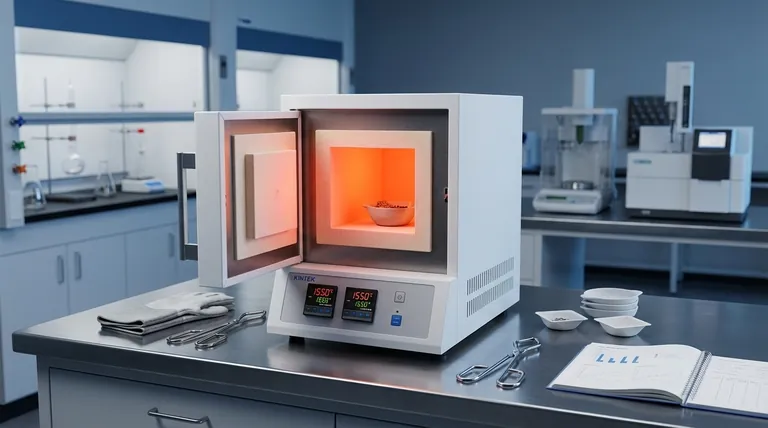

The Core Function: High-Temperature Material Transformation
A laboratory furnace's applications can be broadly categorized into three main areas: creating materials, modifying them, or preparing them for further analysis. Each requires precise control over the thermal environment.
Material Synthesis and Sintering
One of the most common uses is creating solid materials from powders. Sintering involves heating a powdered compact to a high temperature (below its melting point) until its particles bond together.
This process is critical in fields like metallurgy and materials science for producing technical ceramics, which may require working temperatures of 1550° C or higher.
Heat Treatment Processes
Furnaces are essential for modifying the properties of materials like metals and glass. These processes change a material's internal structure, affecting its hardness, ductility, or strength.
Common heat treatments include:
- Annealing: Heating and then slowly cooling a material to remove internal stresses and make it less brittle.
- Hardening: Heating and then rapidly cooling a material to increase its hardness.
- Tempering: A secondary, lower-temperature heating process used to reduce the brittleness that can result from hardening.
Sample Preparation for Analysis
In analytical chemistry, furnaces are used to prepare samples by removing unwanted components.
Ashing, also known as charring, is a key example. This process uses the furnace to burn off the organic matrix of a sample, leaving behind only the inorganic analytes for measurement, often as a preparatory step for techniques like atomic absorption (AA) spectroscopy.
How a Laboratory Furnace Achieves Precision
The value of a furnace lies in its ability to reliably create and hold specific thermal conditions. This is accomplished through sophisticated control systems and designs tailored to specific tasks.
Precise Temperature Control
Simple furnaces may use a basic thermostat for on/off regulation to maintain a set temperature.
More advanced systems offer greater precision by controlling the flow rate and pressure of the medium being heated. This ensures uniform temperature distribution and allows for programmed temperature ramps—critical for complex processes like annealing.
Variety in Form and Function
Furnaces are not one-size-fits-all. Their design reflects their intended purpose.
- Chamber Furnaces: These are general-purpose "workhorses" suitable for frequent, repetitive tasks like sterilization or basic heat treatments.
- Tube Furnaces: These are ideal for processing small samples or for applications requiring a controlled atmosphere, such as degassing or coating.
- Large Floor-Standing Units: Built for industrial-scale lab work, these can accommodate entire trolleys of material for larger batch processing.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, selecting and using a laboratory furnace requires careful thought. The instrument must match the application to be effective and safe.
Application Specificity is Crucial
A furnace designed for ashing small samples will be fundamentally different from one built to sinter large ceramic components. The heating elements, chamber size, and control systems are all tailored for specific temperature ranges and sample sizes.
Maintenance and Contamination
High-temperature equipment can be delicate and require significant maintenance. Cross-contamination between different materials heated in the same furnace is a serious risk, often necessitating rigorous cleanup procedures between uses.
Atmosphere Control
Many advanced material processes require not just high temperatures but also a controlled atmosphere (e.g., inert gas or a vacuum). A standard furnace that only heats in ambient air is unsuitable for these applications. This capability represents a significant difference in complexity and cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the right thermal process, you must first define your objective.
- If your primary focus is creating new materials: You need a high-temperature furnace capable of sintering processes, often with specialized features for technical ceramics or metallurgy.
- If your primary focus is modifying existing materials: Look for a furnace that excels at programmable heat treatments like annealing, hardening, or tempering, with an emphasis on precise temperature control.
- If your primary focus is preparing samples for analysis: A specialized tube or muffle furnace designed for ashing or residue analysis is your most reliable choice.
Understanding these core functions allows you to select the precise thermal process required to advance your research or production goals.
Summary Table:
| Primary Application | Key Process | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Material Synthesis | Sintering | Creating technical ceramics from powders |
| Material Modification | Heat Treatment | Annealing, hardening, or tempering metals |
| Sample Preparation | Ashing | Removing organic matrix for inorganic analysis |
Ready to transform your materials with precision?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance laboratory furnaces designed for sintering, heat treatment, and sample preparation. Whether you're developing new materials in R&D or ensuring quality control in production, our equipment delivers the precise temperature control and reliability you need.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect furnace solution for your specific application and achieve superior results in your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- Do you need to heat the clean crucible before using it? Prevent Thermal Shock and Ensure Process Accuracy
- How do you choose calcination temperature? A Guide to Optimizing Material Properties
- How is the ash content determined in a muffle furnace? Master the Gravimetric Analysis Method
- How long is the calcination process? Optimize Your Process Time for Maximum Efficiency
- What is the yield of biochar in slow pyrolysis? Maximize Your Output Up to 30%



















