In high-temperature furnaces, hydrogen's primary role is to serve as a highly effective protective atmosphere. It is actively used during processes like sintering and annealing to shield sensitive materials from the damaging effects of oxygen, ensuring the final product maintains its required purity and structural integrity.
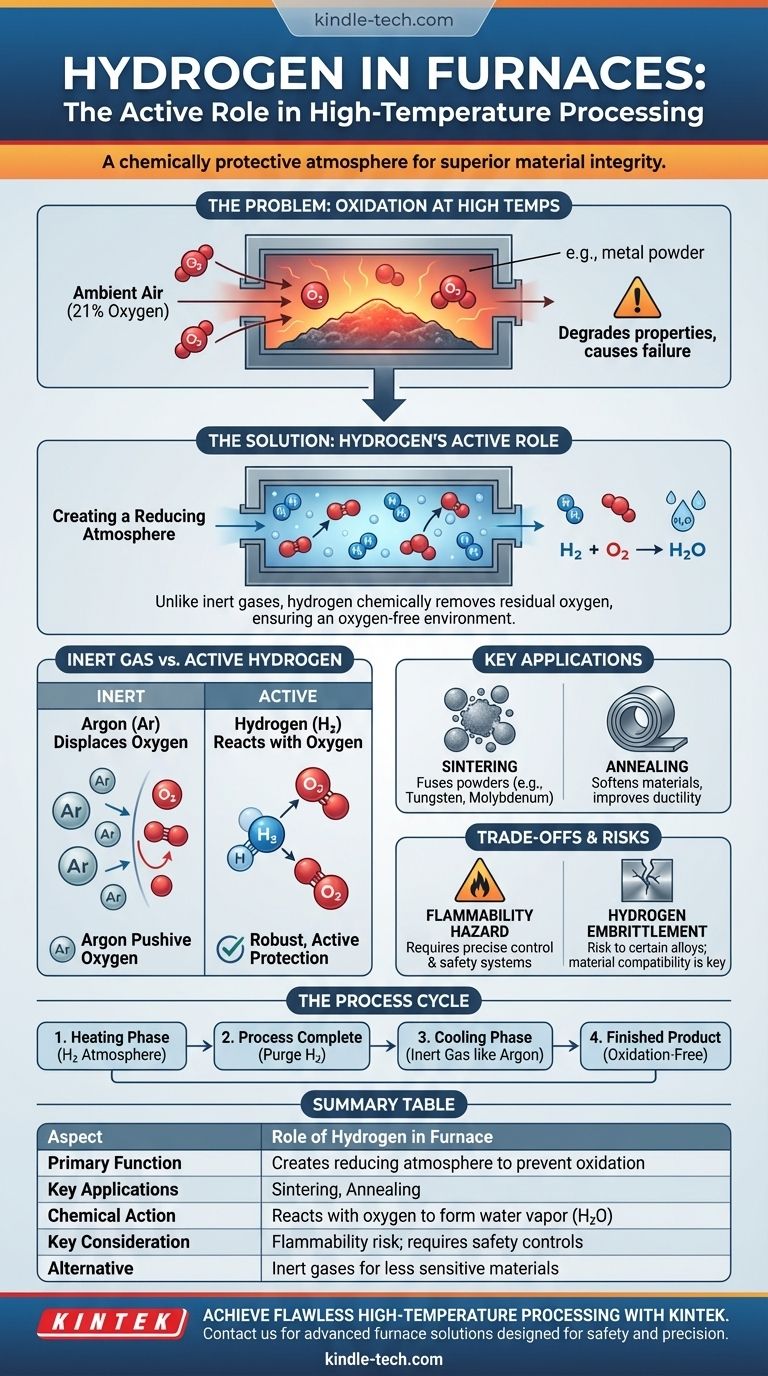
The core function of hydrogen in a furnace is to create a reducing atmosphere. Unlike inert gases that simply displace oxygen, hydrogen actively reacts with and removes any residual oxygen, chemically preventing oxidation and ensuring the integrity of materials during high-temperature processing.

The Problem: Oxygen at High Temperatures
The Challenge of Oxidation
At elevated temperatures, most metals and many ceramic materials become highly reactive with oxygen.
This reaction, known as oxidation, degrades the material's properties, can prevent proper bonding during sintering, and ultimately leads to a failed or substandard product.
Why Normal Air Is Unsuitable
Ambient air, which is approximately 21% oxygen, is the direct enemy of high-temperature material processing.
Introducing materials into a furnace full of hot air without a protective atmosphere would cause immediate and catastrophic oxidation.
Hydrogen's Role as an Active Agent
Creating a Protective Atmosphere
To solve the oxidation problem, furnaces are filled with a specific gas to create a controlled atmosphere. This is often pure hydrogen (H₂) or a hydrogen-nitrogen mixture.
This atmosphere displaces the ambient air, removing the vast majority of oxygen before the process begins.
The Chemical Advantage: Hydrogen vs. Inert Gas
While inert gases like argon simply push oxygen out of the way, hydrogen offers a more robust, active form of protection.
Hydrogen is a reducing agent, meaning it chemically seeks out and bonds with oxygen atoms. Any trace amounts of oxygen remaining in the furnace will react with the hydrogen to form water vapor (H₂O), which is then vented.
This chemical "scrubbing" action ensures a virtually oxygen-free environment, which is critical for the most sensitive materials.
Key Applications: Sintering and Annealing
This process is essential for applications like the sintering of tungsten and molybdenum powders, where particles must fuse together cleanly.
It is also vital for annealing, a heat treatment used to soften materials and improve their ductility. Without a hydrogen atmosphere, these processes would fail due to surface oxidation.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
The Flammability Hazard
Hydrogen's primary drawback is that it is highly flammable and explosive when mixed with air.
This risk mandates sophisticated furnace designs with precise pressure control systems, safety interlocks, and purge cycles that use an inert gas to safely remove hydrogen before opening the furnace.
The Need for Precise Control
The concentration of hydrogen, furnace temperature, and processing time must be meticulously controlled.
Modern hydrogen furnaces use advanced automatic controllers with extreme temperature precision (±1℃) to manage these variables, ensuring both product quality and operational safety.
Hydrogen Embrittlement
While beneficial for many materials, hydrogen can be detrimental to certain ferrous alloys and steels.
At high temperatures, hydrogen atoms can diffuse into the metal's crystal structure, causing a phenomenon known as hydrogen embrittlement, which makes the material brittle and prone to fracture. This makes material compatibility a critical consideration.
The System in Practice
The Heating and Cooling Cycle
During the heating phase, the furnace is filled with hydrogen to protect the material.
Once the process is complete, the hydrogen is safely purged and replaced with an inert gas, such as argon. This inert gas is then circulated through a heat exchanger to cool the material down rapidly without re-introducing oxygen while it is still at a reactive temperature.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
- If your primary focus is processing highly oxygen-sensitive materials like tungsten or refractory metals: A hydrogen atmosphere is essential to chemically guarantee an oxygen-free environment for successful sintering or annealing.
- If your primary focus is general heat treating of less sensitive materials: A less expensive and non-flammable inert gas like nitrogen or argon may provide sufficient protection by simply displacing oxygen.
- If you are working with specific steel alloys: You must first investigate the material's susceptibility to hydrogen embrittlement, as a hydrogen atmosphere could be damaging.
Ultimately, understanding the unique chemical role of hydrogen empowers you to select the precise atmospheric conditions required to achieve flawless integrity in your high-temperature applications.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Role of Hydrogen in Furnace |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Creates a reducing atmosphere to prevent oxidation |
| Key Applications | Sintering (e.g., tungsten, molybdenum), Annealing |
| Chemical Action | Reacts with oxygen to form water vapor (H₂O) |
| Key Consideration | Flammability risk; requires precise safety controls |
| Alternative for Less Sensitive Materials | Inert gases (e.g., Nitrogen, Argon) |
Achieve Flawless High-Temperature Processing with KINTEK
Does your lab work with oxygen-sensitive materials like tungsten or molybdenum? The precise, chemically active protection of a hydrogen atmosphere is essential for successful sintering and annealing, ensuring material integrity and purity.
KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory furnaces and atmosphere systems designed for safety and precision. Our experts can help you select the right equipment to master your high-temperature processes.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific application and ensure optimal results for your materials.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the use of inert gas in reaction? Control Your Process and Ensure Safety
- What is the primary purpose of using atmospheres in heat treating? Protect Surfaces and Enhance Metal Quality
- What is an integral quench furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Sealed Atmosphere Heat Treating
- Why is it necessary to use an atmosphere furnace for NaFePO4 precursors? Ensure Stable Maricite Phase Formation
- What gases are used in brazing welding? Key Insights for Strong, Clean Joints
- What advantages does a high-temperature atmosphere sintering furnace offer for UO2? Precision Fuel Densification
- Why are high-vacuum or atmospheric high-temperature furnaces required for phosphate glass matrices? Expert Guide
- What role does an atmosphere furnace play in catalyst calcination? Ensure High Performance for Denitration Catalysts



















