In essence, induction heating is a precise and rapid non-contact heating method used for a vast range of industrial and technical processes. Its primary applications include the heat treatment of metals (like surface hardening), melting and brazing, the manufacturing of high-purity semiconductors, and even common household induction cooktops. The process excels where speed, efficiency, and precise temperature control are critical.
The true value of induction heating lies not in its diverse applications, but in its fundamental principle: generating heat directly within the material itself. This provides a level of speed, localization, and clean efficiency that conventional furnaces or flame heating cannot achieve.
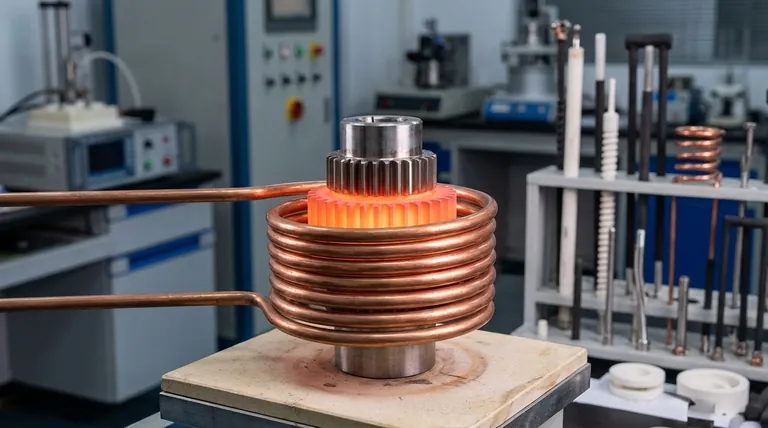

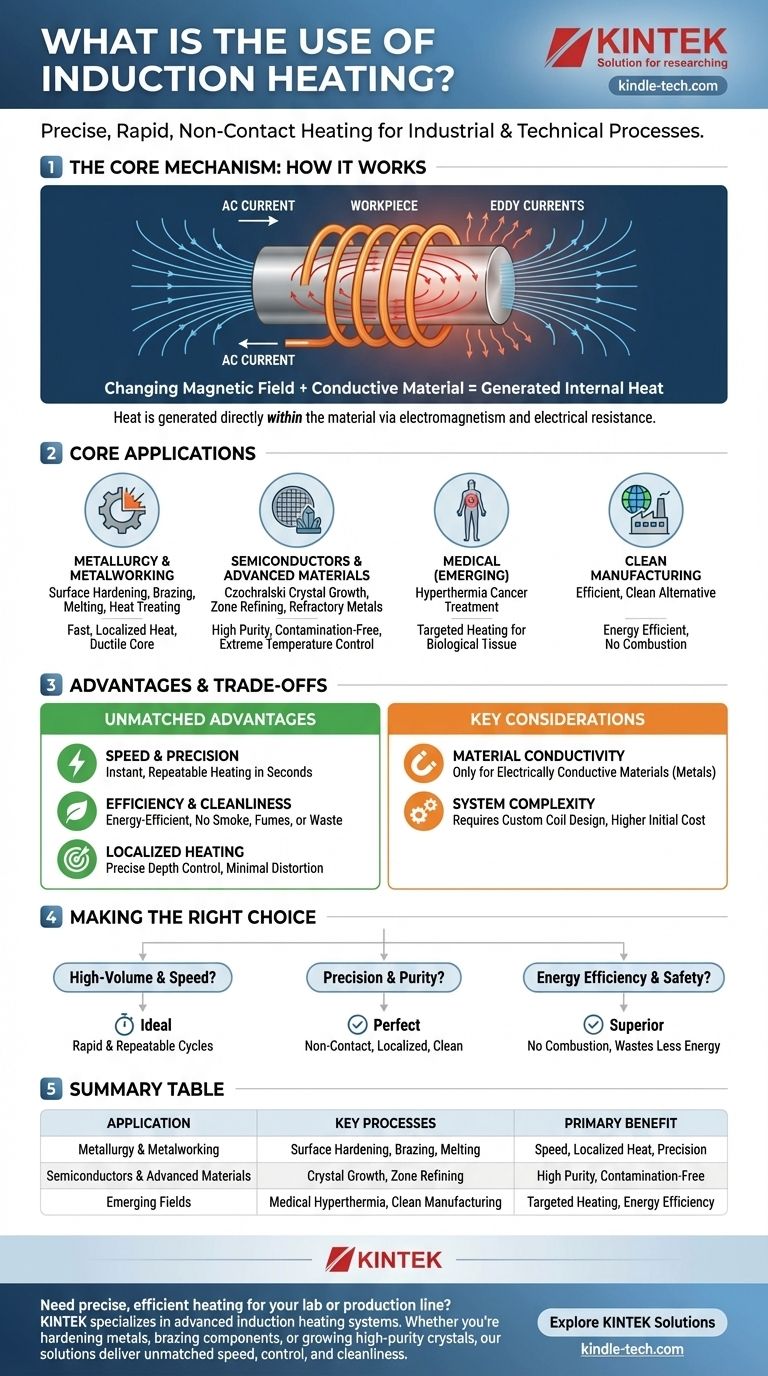
How Induction Heating Fundamentally Works
To understand its uses, you must first understand its mechanism. The process is based on two core physics principles working together: electromagnetism and electrical resistance.
The Role of the Changing Magnetic Field
For induction heating to occur, a powerful, rapidly changing magnetic field is required. This is created by passing a high-frequency alternating current (AC) through a specifically designed induction coil.
The coil itself does not get hot. It acts as the source of the magnetic field that will transfer energy to the workpiece without any physical contact.
The Response of the Conductive Workpiece
When an electrically conductive material, or workpiece, is placed inside this magnetic field, the field induces circular electrical currents within the metal. These are known as eddy currents.
The material's natural resistance to the flow of these eddy currents generates precise and instantaneous heat. Think of it like a transformer where the induction coil is the primary winding and the workpiece is a single-turn secondary winding that is short-circuited.
Core Industrial and Technical Applications
The unique properties of induction heating make it the superior choice for many demanding processes.
Metallurgy and Metalworking
This is the largest area of application. Induction heating is used for surface hardening gears and shafts, where only the outer layer needs to be durable while the core remains ductile. It is also used for brazing and soldering, providing fast, localized heat to join components without distorting the entire assembly.
Other common uses include melting metals in clean, controlled environments and heat treating parts to alter their metallurgical properties.
Advanced Materials and Semiconductors
In the semiconductor industry, induction heating is critical for processes like Czochralski crystal growth and zone refining. Because the heating is non-contact, it prevents contamination and allows for the extreme temperature control needed to create high-purity single crystals.
It is also used for melting refractory metals that have extremely high melting points, which would be difficult or impossible to achieve cleanly with conventional furnaces.
Emerging and Specialized Fields
The principles of induction heating are being applied in new ways. In medicine, research is exploring its use for hyperthermia cancer treatment, where it can heat biological tissues in a targeted way.
It is also central to empowering developing nations with modern manufacturing capabilities, offering an efficient and clean alternative to traditional, fuel-intensive methods.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Advantages
No technology is perfect for every scenario. Understanding the pros and cons of induction heating is key to using it effectively.
The Advantage: Unmatched Speed and Precision
Heat is generated instantly and only where the magnetic field is strongest. This allows for heating cycles that take seconds instead of the minutes or hours required by a furnace. The depth of heating can be precisely controlled by adjusting the frequency of the AC current.
The Advantage: High Efficiency and Cleanliness
Since heat is generated inside the part, very little energy is wasted heating the surrounding air or equipment. This makes the process highly energy-efficient.
Furthermore, as a non-contact method with no combustion, it is an extremely clean process, producing no smoke, fumes, or waste gases.
The Primary Limitation: Material Conductivity
Induction heating only works on materials that are electrically conductive. It cannot be used to directly heat insulators like most plastics, ceramics, or glass. The workpiece itself must be able to support the flow of eddy currents.
The Consideration: System Complexity
Induction heating systems are sophisticated. The induction coil often needs to be specifically designed and shaped for the part being heated to ensure the magnetic field is applied correctly. This can result in higher initial equipment costs compared to a simple torch or oven.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting induction heating depends entirely on your process requirements and material properties.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production and speed: Induction heating is ideal due to its extremely rapid and repeatable heating cycles.
- If your primary focus is precision and material quality: The localized, non-contact nature is perfect for surface hardening, semiconductor growth, or clean melting.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency and workplace safety: Induction is a superior choice, as it wastes less energy and produces no combustion byproducts.
- If you are working with non-conductive materials: You must use a different heating method or employ an intermediate conductive vessel (a susceptor) to transfer heat.
Ultimately, choosing induction heating is about recognizing when direct, internal heat generation provides an unparalleled advantage in control and efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Processes | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Metallurgy & Metalworking | Surface Hardening, Brazing, Melting | Speed, Localized Heat, Precision |
| Semiconductors & Advanced Materials | Crystal Growth, Zone Refining | High Purity, Contamination-Free |
| Emerging Fields | Medical Hyperthermia, Clean Manufacturing | Targeted Heating, Energy Efficiency |
Need precise, efficient heating for your lab or production line? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including induction heating systems, to meet your specific industrial and research needs. Whether you're hardening metals, brazing components, or growing high-purity crystals, our solutions deliver unmatched speed, control, and cleanliness. Contact us today to explore how KINTEK's expertise can enhance your process efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Metal Disc Electrode Electrochemical Electrode
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What material is used for making heating element? Choose the Right Alloy for Your Application
- What are the uses of silicon carbide rod? The Ultimate Heating Solution for Extreme Temperatures
- What is the maximum temperature for silicon carbide heating element? The Real Limit for Your High-Temp Furnace
- What are silicon carbide heating elements used for? Reliable High-Temp Heating for Industrial Processes
- What is SiC elements? The Ultimate High-Temperature Heating Solution



















