In essence, an induction melting furnace is a highly versatile tool that uses electromagnetic induction to heat and melt metals with remarkable speed and precision. Its applications range from melting and refining precious metals and high-tech alloys to performing specific manufacturing tasks like heat treating, forging, and welding preparation.
The true value of an induction furnace isn't just its ability to melt metal, but its capacity to do so with exceptional speed, cleanliness, and metallurgical precision, making it indispensable for producing high-quality, homogeneous alloys.

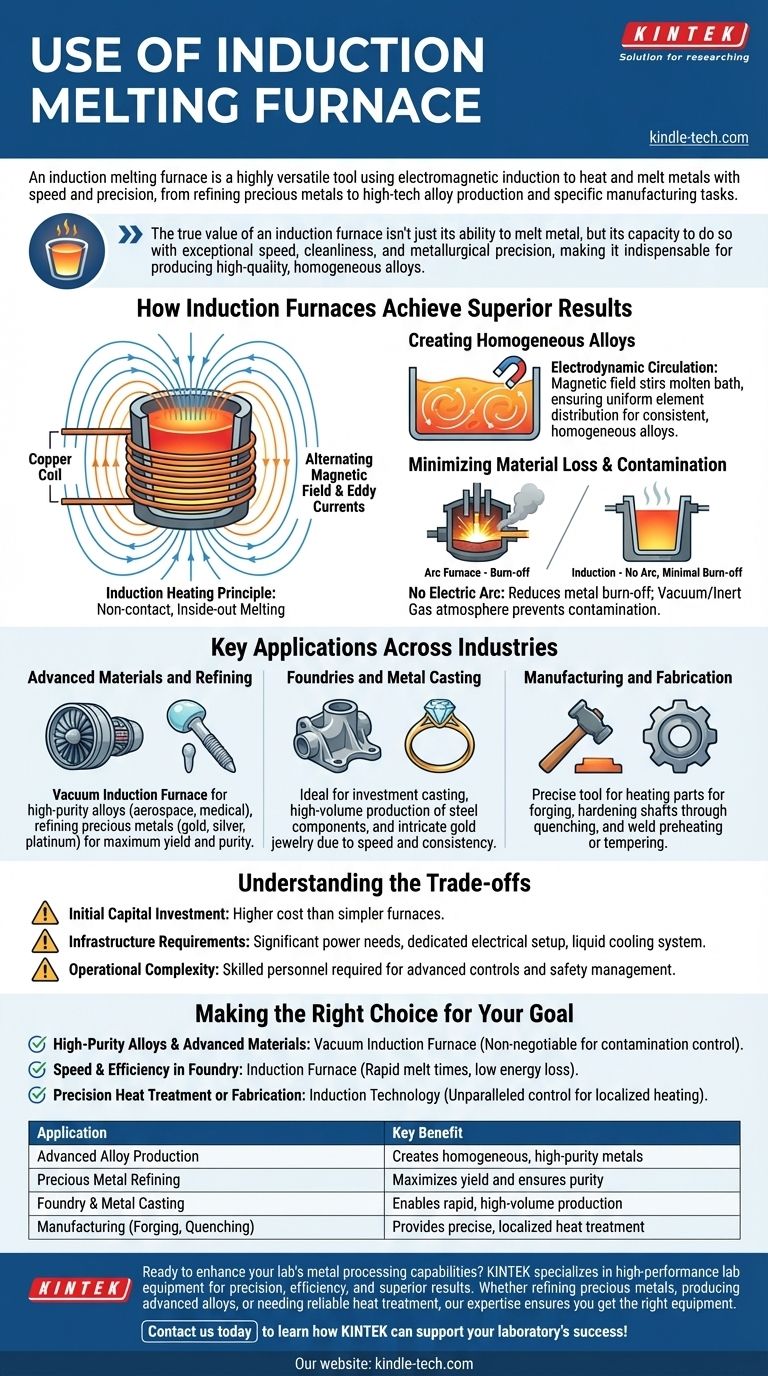
How Induction Furnaces Achieve Superior Results
The core function of an induction furnace revolves around its unique, non-contact heating method. This approach provides distinct advantages over traditional fuel-fired or arc furnaces.
The Principle of Induction Heating
An induction furnace generates a powerful, alternating magnetic field from a copper coil. When a conductive material like metal is placed within this field, it induces electrical currents (eddy currents) within the metal itself.
The metal's natural resistance to these currents generates intense, localized heat, causing it to melt rapidly from the inside out without any external flame or electric arc.
Creating Homogeneous Alloys
A key benefit of this process is the electrodynamic circulation of the liquid metal. The magnetic field naturally stirs the molten bath.
This constant motion ensures all elements are evenly distributed, resulting in a perfectly homogeneous alloy with consistent properties throughout the final product.
Minimizing Material Loss and Contamination
Traditional arc furnaces can cause significant material loss by burning away valuable alloying elements. Induction melting avoids this entirely.
Because there is no electric arc, metal burn-off is minimized. This is especially critical when working with expensive or reactive metals. The process can also be done in a vacuum or inert gas atmosphere to prevent contamination.
Key Applications Across Industries
The control and versatility of induction technology make it a cornerstone in numerous high-value sectors.
Advanced Materials and Refining
For materials where purity is paramount, the vacuum induction furnace is the standard. It is used to produce high-temperature alloys, titanium alloys, stainless steel, and other special materials for aerospace and medical applications.
It is also the preferred method for refining precious metals like gold, silver, and platinum, as it maximizes yield and ensures purity.
Foundries and Metal Casting
Induction furnaces are widely used for metal casting, including investment casting, where complex and high-quality parts are created.
Their speed and consistency are ideal for foundries producing everything from standard steel components to intricate gold jewelry.
Manufacturing and Fabrication
Beyond simple melting, induction technology is a precise tool for fabrication. It is used for heating parts for forging, hardening shafts through quenching, and for preheating or tempering welds to ensure their structural integrity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, induction technology is not a universal solution. A clear understanding of its requirements is essential for proper implementation.
Initial Capital Investment
Induction furnace systems are sophisticated pieces of equipment. The initial capital cost is typically higher than that of simpler, fuel-fired furnaces.
Infrastructure Requirements
These furnaces have significant power requirements and often necessitate dedicated electrical infrastructure. They also rely on a liquid cooling system (usually water) to protect the copper coils, which adds another layer of operational dependency.
Operational Complexity
While automation is a key advantage, operating an induction furnace requires skilled personnel. The system is equipped with advanced controls and safety alarms for voltage, current, and temperature that must be properly managed.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right heating technology depends entirely on your operational priorities and the materials you work with.
- If your primary focus is high-purity alloys and advanced materials: A vacuum induction furnace is non-negotiable for its absolute control over atmospheric contamination.
- If your primary focus is speed and efficiency in a foundry: The rapid melt times and low energy loss of an induction furnace make it ideal for high-volume casting of steel, gold, or other standard metals.
- If your primary focus is precision heat treatment or fabrication: Induction offers unparalleled control for localized heating in processes like forging, quenching, or weld preheating.
Ultimately, an induction furnace provides a level of control that transforms metal melting from a brute-force process into a precise science.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Advanced Alloy Production | Creates homogeneous, high-purity metals |
| Precious Metal Refining | Maximizes yield and ensures purity |
| Foundry & Metal Casting | Enables rapid, high-volume production |
| Manufacturing (Forging, Quenching) | Provides precise, localized heat treatment |
Ready to enhance your lab's metal processing capabilities? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including induction melting furnaces designed for precision, efficiency, and superior results. Whether you're refining precious metals, producing advanced alloys, or need reliable heat treatment solutions, our expertise ensures you get the right equipment for your needs. Contact us today to learn how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What types of metals are typically processed in a vacuum induction melting furnace? High-Purity Alloys for Critical Applications
- What principle is used to generate heat in a vacuum induction melting furnace? Achieve Clean, Efficient Metal Melting
- What is vacuum arc melting technique? Discover the Precision of Vacuum Induction Melting
- What is the vacuum induction method? Master High-Purity Metal Melting for Advanced Alloys
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity



















