In a laboratory, a muffle furnace is a high-temperature chamber oven used for processes that demand thermal transformation or analysis in a controlled, isolated environment. Unlike a standard oven used for simple drying, a muffle furnace reaches extreme temperatures to fundamentally alter or decompose a material, such as turning organic matter to ash or changing the crystalline structure of a metal.
The core purpose of a muffle furnace is to provide extremely high, uniform heat (often up to 1200°C) within a chamber that isolates the sample from the heating elements. This design prevents contamination and is essential for precise analytical procedures and advanced materials development.
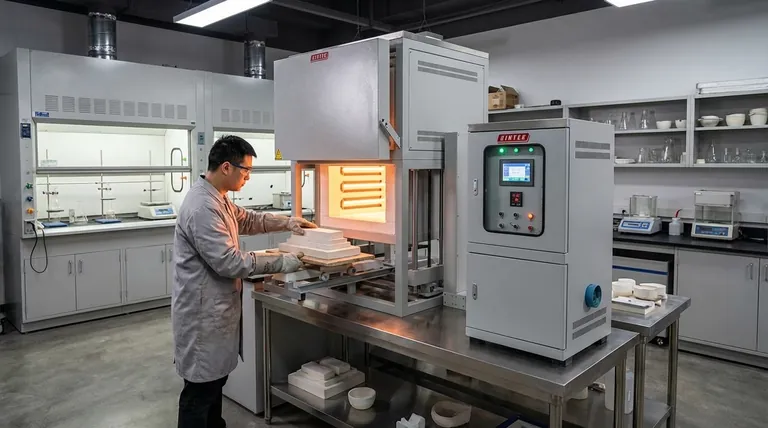

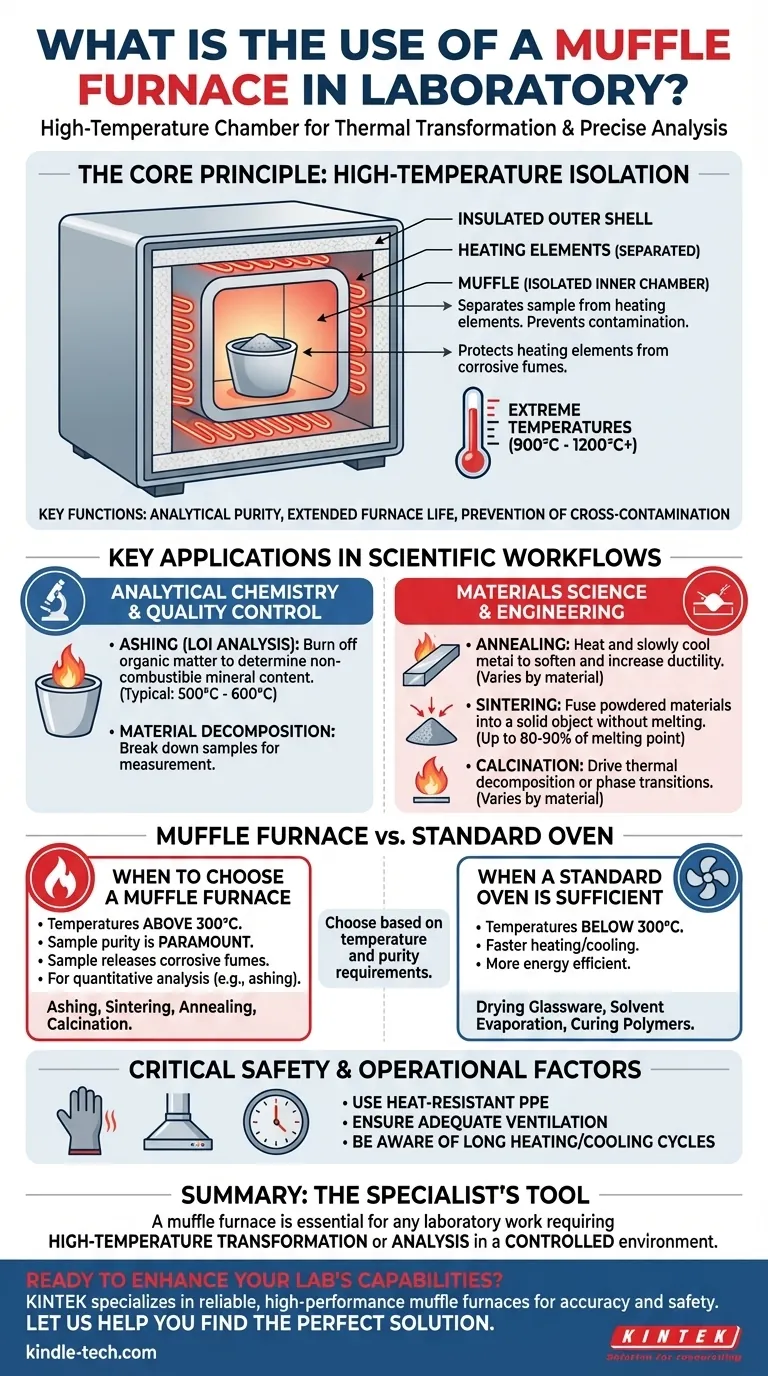
The Core Principle: High-Temperature Isolation
A muffle furnace's unique capabilities stem from its specific design, which separates it from other types of laboratory ovens.
What "Muffle" Means
The term "muffle" refers to the insulated inner chamber of the furnace, which contains the sample. This chamber is a separate enclosure from the heating elements themselves.
This separation is the key design feature. It protects the sample from direct infrared radiation and any potential contaminants (like flakes) from the heating coils.
Achieving Extreme Temperatures
Muffle furnaces are engineered for high-temperature applications. While a typical lab oven might reach 250-300°C, a muffle furnace routinely operates in the range of 900°C to 1200°C (1650°F to 2200°F), with some models going even higher.
This capability is necessary for processes like melting glass, sintering ceramics, or completely combusting organic samples.
Preventing Cross-Contamination
The muffle design serves two critical functions. First, it ensures analytical purity by preventing anything but thermal energy from reaching the sample.
Second, it protects the heating elements from any corrosive fumes or volatile compounds released by the sample during heating, which extends the life of the furnace.
Key Applications in Scientific Workflows
The applications of a muffle furnace fall into two main categories: decomposing materials for analysis and transforming materials to create new properties.
For Analytical Chemistry & Quality Control
In this context, the furnace is used to break down a sample to measure its components.
Key uses include ashing, where a sample is burned at high temperatures to determine its non-combustible mineral content. This is also known as Loss-On-Ignition (LOI) analysis. It is a standard procedure in environmental science, materials research, and quality control for coal and other raw materials.
For Materials Science & Engineering
Here, the goal is to use heat to purposefully change a material's physical properties.
This includes processes like annealing, which heats and slowly cools metal to make it more ductile, and sintering, which uses heat to fuse powdered materials (like ceramics or metals) into a solid object without melting them. It is also essential for creating technical ceramics, enamel coatings, and melting glass.
For High-Temperature Synthesis & Reactions
A muffle furnace provides the energy needed to drive chemical reactions that only occur at high temperatures.
This includes calcination, a process that uses heat to cause thermal decomposition or a phase transition in a material, which is critical in the manufacturing of cement and certain catalysts.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Muffle Furnace vs. Standard Oven
Choosing the right heating instrument depends entirely on your goal. Using a muffle furnace for a low-temperature task is inefficient and unnecessary.
When to Choose a Muffle Furnace
A muffle furnace is the correct tool when your process involves temperatures above 300°C or when the purity of the sample is paramount.
If your sample may release corrosive fumes or if you are performing quantitative analysis like ashing, a muffle furnace is required.
When a Standard Laboratory Oven is Sufficient
For low-temperature tasks like drying glassware, simple solvent evaporation, or curing polymers below 300°C, a standard lab oven is the more efficient and cost-effective choice.
These ovens heat up and cool down much faster and consume significantly less energy.
Critical Safety and Operational Factors
Due to the extreme temperatures, operating a muffle furnace requires strict safety protocols. This includes using heat-resistant personal protective equipment (PPE), ensuring adequate ventilation for fumes, and being aware of the very long heating and cooling cycles.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your application's temperature and purity requirements dictate the right tool for the job.
- If your primary focus is quantitative analysis (like ashing): A muffle furnace is essential for complete combustion to obtain an accurate, non-volatile residue.
- If your primary focus is materials transformation (like annealing or sintering): A muffle furnace provides the necessary high temperatures and controlled environment to alter the material's microstructure.
- If your primary focus is simple drying or sterilization: A standard laboratory oven is the more efficient and appropriate choice.
Ultimately, a muffle furnace is the specialist's tool for any laboratory work that requires not just heating, but fundamentally transforming or analyzing a substance at extreme temperatures.
Summary Table:
| Application | Purpose | Typical Temperature Range |
|---|---|---|
| Ashing / LOI Analysis | Determine mineral content by burning off organic matter | 500°C - 600°C |
| Annealing | Soften metals by heating and slow cooling | Varies by material |
| Sintering | Fuse powdered materials into a solid mass | Up to 80-90% of melting point |
| Calcination | Drive thermal decomposition or phase transitions | Varies by material |
Ready to enhance your lab's high-temperature capabilities?
A muffle furnace is critical for achieving precise results in applications like ashing, sintering, and materials testing. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable laboratory equipment, including high-performance muffle furnaces designed for accuracy, safety, and durability.
Let us help you find the perfect solution for your specific needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss your application and get a personalized recommendation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature range of a laboratory muffle furnace? Find the Right Model for Your Application
- How do you cool down a muffle furnace? Ensure Longevity and Safety with the Correct Procedure
- What is the meaning of muffle furnace? The Key to Pure, High-Temperature Processing
- What is the temperature verification of muffle furnace? Ensure Accurate Thermal Processing
- What is the precaution for muffle furnace? Essential Safety Protocols for Lab Excellence



















