In dental technology, a porcelain furnace is far more than a simple oven. It is a highly specialized piece of equipment designed to fire dental ceramics under precisely controlled conditions. Its core function is to transform powdered, paste, or milled ceramic materials—used for crowns, veneers, bridges, and other restorations—into a hard, dense, and aesthetically pleasing final form through a carefully managed thermal process.
The true purpose of a porcelain furnace is to provide an immaculate and perfectly repeatable thermal environment. Mastering its use is not about simply pressing a button, but about understanding how to calibrate and maintain this environment to achieve consistently superior clinical and aesthetic results.
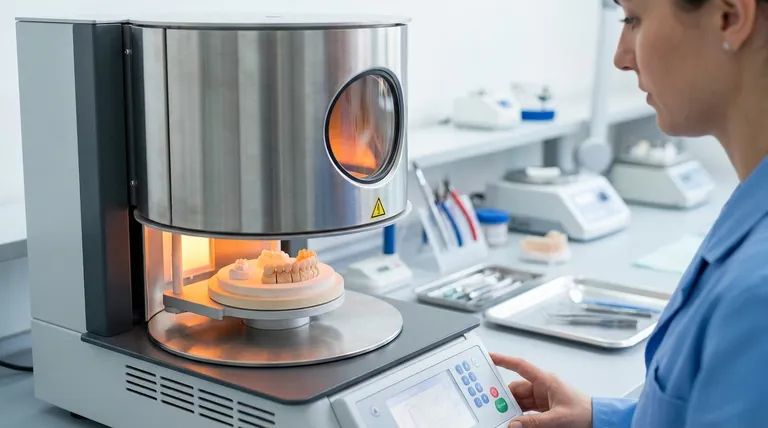

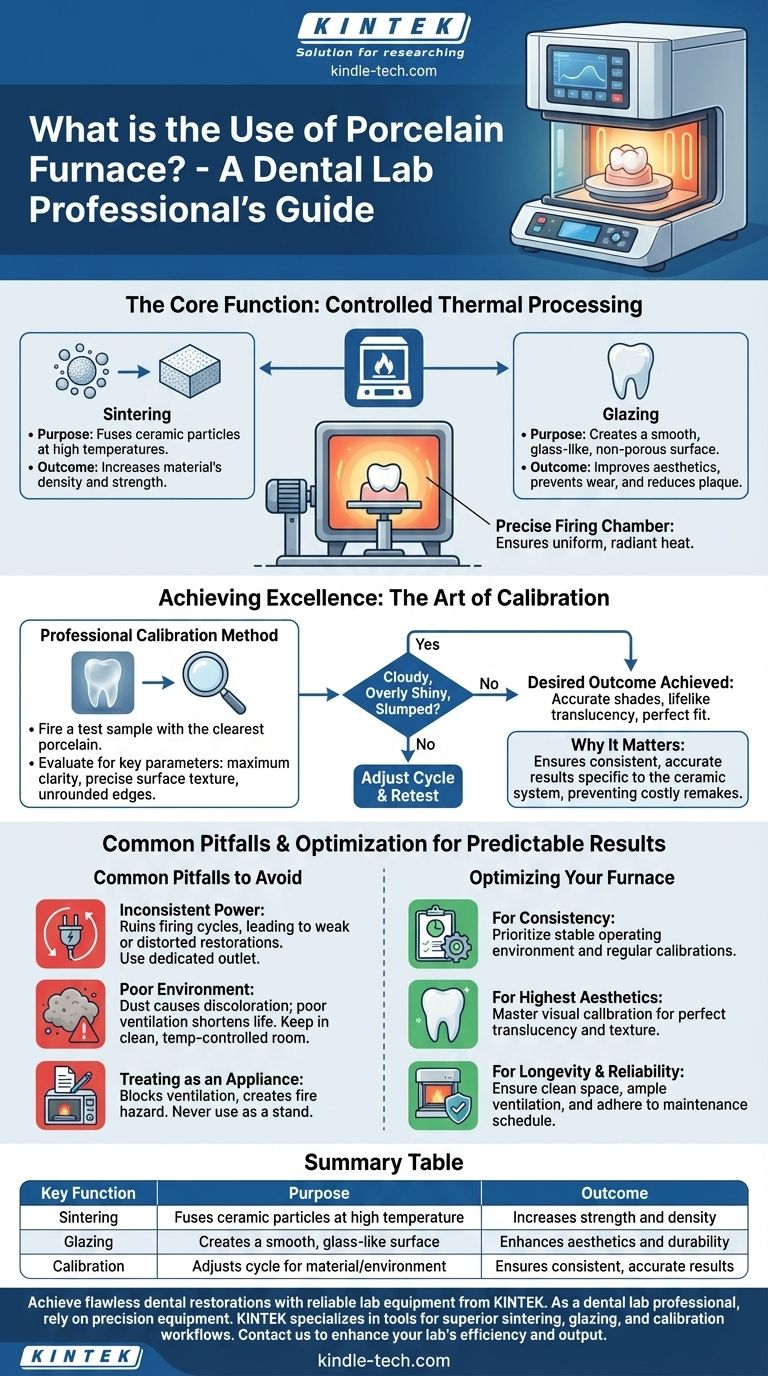
The Core Function: Controlled Thermal Processing
A porcelain furnace executes a programmed heating and cooling cycle to fundamentally change the properties of dental ceramic material. This process is what gives a restoration its final strength, color, and fit.
How It Works: The Firing Chamber
At the heart of the furnace is a firing chamber containing high-purity heating coils. These coils are typically arranged concentrically around a firing platform where the restoration is placed.
A motor-driven mechanism then seals the chamber, either by raising the platform into the heated upper housing or by lowering the housing over the platform. This design ensures uniform, radiant heat is applied to the entire surface of the restoration.
The Goal: Sintering and Glazing
The primary purpose of the heating cycle is sintering. This is the process where individual ceramic particles fuse together at high temperatures, reducing porosity and dramatically increasing the material's density and strength.
Subsequent or final cycles are often for glazing, which creates a smooth, glass-like, non-porous surface on the restoration. This glaze improves aesthetics, prevents wear on opposing teeth, and reduces plaque accumulation.
Achieving Excellence: The Art of Calibration
While furnaces come with manufacturer-programmed cycles, experienced technicians know that achieving optimal results requires custom calibration. Environmental factors and furnace age can cause a furnace's actual temperature to drift from its setpoint.
The Professional's Calibration Method
Expert ceramists rarely trust the factory settings alone. They calibrate their furnace by firing a test sample, often using the clearest porcelain powder from a specific system they work with.
They then critically evaluate the fired sample for key parameters: maximum clarity, precise surface texture, and sharply defined, unrounded edges. If the sample is cloudy, overly shiny, or slumped, the firing cycle is adjusted and re-tested until the desired outcome is achieved.
Why Meticulous Calibration Matters
This hands-on calibration ensures that the furnace is producing the exact thermal effect required by the specific ceramic system. It is the key to achieving accurate shades, lifelike translucency, and a perfect fit, preventing the costly and time-consuming need for remakes.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
A porcelain furnace is a precision instrument, and its performance is directly tied to its environment and power supply. Neglecting these factors will inevitably compromise the quality of your work.
The Risk of Inconsistent Power
A furnace must execute its heating and cooling program without interruption. It should be connected to a dedicated electrical outlet to avoid power fluctuations or circuit overloads from other equipment.
A momentary power dip can ruin an entire firing cycle, resulting in an under-fired restoration that is weak and opaque, or a power surge could cause over-firing, leading to distortion and a glassy, unnatural appearance.
The Hidden Danger of a Poor Environment
The furnace must be kept in a clean, temperature-controlled room with proper airflow. Placing it in the corner of a casting or grinding room exposes it to airborne contaminants.
Dust and debris can be drawn into the chamber and permanently baked into the porcelain, causing discoloration and surface defects. Poor ventilation can also cause the furnace's electronic components to overheat, shortening its operational life.
Treating It Like an Appliance, Not an Instrument
Never use the furnace as a stand for papers, models, or other items. This not only creates a fire hazard but also blocks ventilation ports, leading to overheating. The vibrations from placing or removing objects can also damage the delicate internal mechanisms.
Optimizing Your Furnace for Predictable Results
Your approach to using and maintaining your furnace should be dictated by your specific goals for quality, consistency, and longevity.
- If your primary focus is consistency across all cases: Prioritize a stable operating environment with a dedicated power source and perform regular, documented calibrations.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest level of aesthetics: Master the art of visual calibration using test samples to perfectly dial in the translucency and surface texture for each specific porcelain system you use.
- If your primary focus is operational longevity and reliability: Ensure the furnace is in a clean, dust-free space with ample ventilation and adhere strictly to the manufacturer's maintenance schedule.
Ultimately, mastering the porcelain furnace is about transforming a simple heating process into a predictable and artistic outcome.
Summary Table:
| Key Function | Purpose | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Sintering | Fuses ceramic particles at high temperature | Increases strength and density |
| Glazing | Creates a smooth, glass-like surface | Enhances aesthetics and durability |
| Calibration | Adjusts cycle for material/environment | Ensures consistent, accurate results |
Achieve flawless dental restorations with reliable lab equipment from KINTEK.
As a dental lab professional, you understand that consistent, high-quality results depend on precision equipment. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing dental technicians with the tools needed for superior sintering, glazing, and calibration workflows.
Let us help you enhance your lab's efficiency and output. Contact us today to explore our range of porcelain furnaces and accessories tailored to your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- Horizontal High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is in a dental laboratory? Discover the High-Tech Hub Creating Your Perfect Smile
- What is low fusing porcelain? Achieve Superior Esthetics and Metal Integrity in PFM Restorations
- Are ceramic veneers stain-resistant? Yes, Porcelain Veneers Offer Superior Stain Resistance
- What is the furnace in which ceramics are fired? A Guide to Choosing the Right Kiln for Your Project
- What physical changes occur to ceramic materials like zirconia during sintering? Maximize Density and Strength
- What are the components of dental porcelain? A Guide to Engineered Strength and Beauty
- What is the burnout cycle on a furnace? Stop This Destructive Overheating Pattern Now
- How much heat is needed to make porcelain? It's More Than Just Temperature















