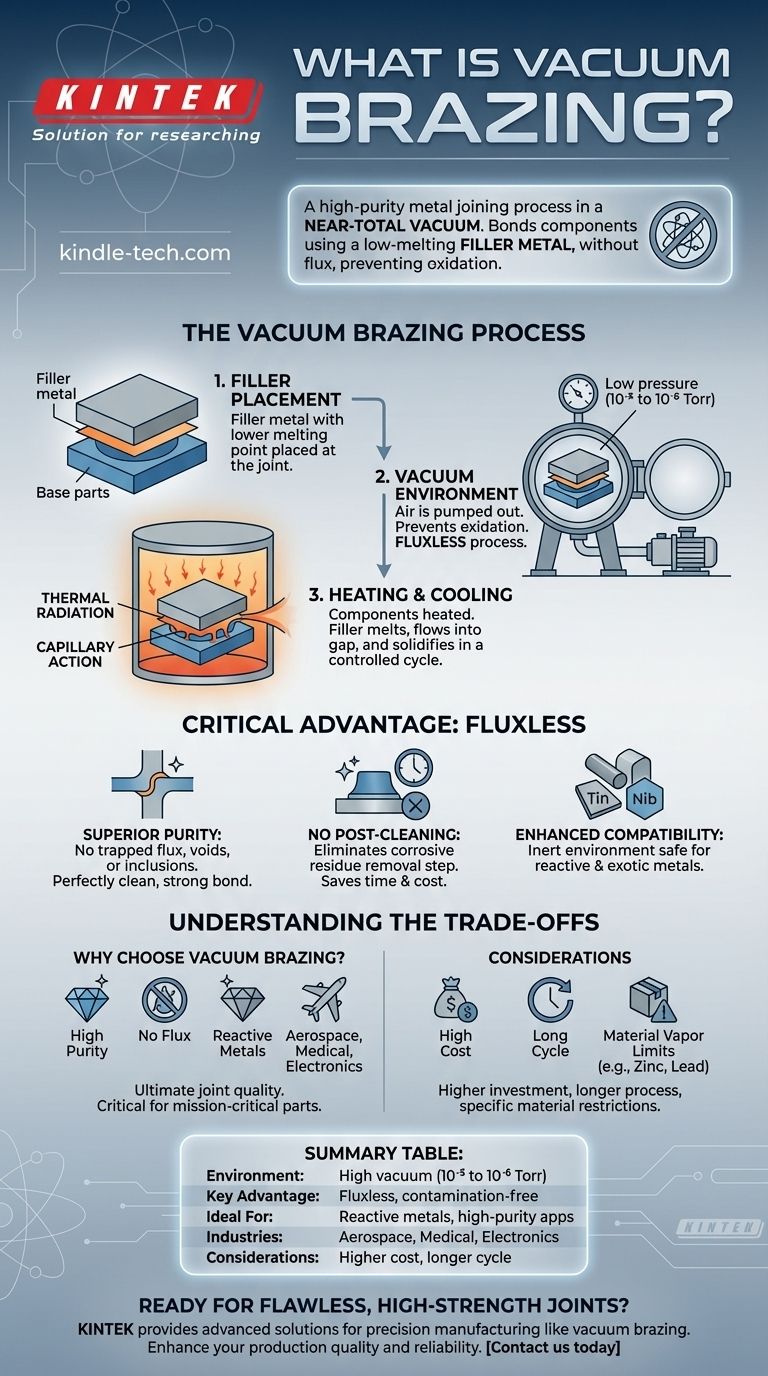
In essence, vacuum brazing is a high-purity metal joining process where two or more components are bonded together using a filler metal in a near-total vacuum. The key is that the filler metal has a lower melting point than the base materials, allowing it to melt and flow into the joint without melting the components themselves. The vacuum environment is the critical element that prevents oxidation and eliminates the need for chemical fluxes.
By removing the atmosphere, vacuum brazing creates exceptionally clean, strong, and flux-free joints. This makes it the preferred method for high-performance applications in industries like aerospace, medical, and electronics, where joint integrity and purity are non-negotiable.

How Vacuum Brazing Fundamentally Works
The process is more than just heating parts in a vacuum; it's a precisely controlled metallurgical operation that relies on the unique properties of a vacuum environment.
The Role of the Filler Metal
The process begins with a filler metal, often in the form of a foil, paste, or wire, placed at the joint of the base metal components.
This filler has a carefully selected melting point that is lower than the base metals. When heated, only the filler becomes liquid.
Through capillary action, the molten filler is drawn into the tight gap between the workpieces, ensuring complete and uniform coverage of the joint interface.
The Power of the Vacuum
The entire assembly is placed inside a vacuum furnace, where the air is pumped out to a very low pressure, typically in the range of 10⁻⁵ to 10⁻⁶ Torr.
This vacuum environment is inherently active. It prevents the formation of oxides on the metal surfaces that would otherwise interfere with the bond. In many cases, it can even remove existing light oxides.
Crucially, this makes the process fluxless. Traditional brazing requires a chemical flux to clean the surfaces, but the vacuum accomplishes this task cleanly and without leaving any residue.
The Heating and Cooling Cycle
Inside the vacuum, heating cannot occur through convection. Instead, the components are heated by thermal radiation.
Once the furnace reaches the target temperature, the filler metal melts, flows, and diffuses into the base metals, forming a strong, permanent metallurgical bond.
The assembly is then cooled in a controlled manner within the vacuum, ensuring the joint solidifies properly without thermal stress or contamination.
The Critical Advantage: A Fluxless Process
Eliminating flux is the single most important benefit of vacuum brazing, leading to significant improvements in quality and reliability.
Superior Joint Purity
Flux can become trapped within a joint, creating voids or inclusions that compromise its structural integrity. A fluxless process results in a perfectly clean, solid metal bond.
No Post-Brazing Cleaning
Parts brazed with flux require extensive post-process cleaning to remove corrosive residues. Vacuum brazing eliminates this entire step, saving time and preventing potential damage from cleaning agents.
Enhanced Material Compatibility
Flux can react negatively with certain base metals, especially reactive metals like titanium. A vacuum is an inert environment that is compatible with a much wider range of materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum brazing is not the universal solution. Its specialized nature comes with specific considerations.
High Initial Investment
Vacuum furnaces and the associated pumping equipment represent a significant capital expense compared to standard atmospheric brazing equipment.
Longer Cycle Times
The process of pumping down the chamber to a deep vacuum, followed by a controlled heating and cooling cycle, can be more time-consuming than other brazing methods.
Material Vapor Pressure Limitations
Materials with high vapor pressures, such as zinc, lead, or cadmium, are generally unsuitable for vacuum brazing. At high temperatures and low pressures, these elements can "outgas" and contaminate the furnace and the workpiece itself.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right brazing method depends entirely on the technical requirements and economic constraints of your project.
- If your primary focus is ultimate joint quality and purity: Vacuum brazing is the unparalleled choice, especially for mission-critical components in aerospace, medical implants, or semiconductor equipment.
- If your primary focus is joining reactive or exotic metals: The inert nature of the vacuum is essential for materials like titanium, niobium, and certain superalloys that cannot tolerate oxygen.
- If your primary focus is cost-sensitive, high-volume production of simple parts: Traditional flux or controlled-atmosphere brazing often provides a more economical solution for less demanding applications.
Choosing the correct joining process is a crucial step in ensuring the performance and reliability of your final product.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Feature |
|---|---|
| Environment | High vacuum (10⁻⁵ to 10⁻⁶ Torr) |
| Key Advantage | Fluxless process, eliminating contamination |
| Ideal For | Reactive metals, high-purity applications |
| Primary Industries | Aerospace, Medical, Electronics |
| Considerations | Higher initial cost, longer cycle times |
Ready to achieve flawless, high-strength metal joints for your critical components? KINTEK specializes in providing advanced laboratory equipment and consumables for precision manufacturing processes like vacuum brazing. Our expertise ensures you have the right tools for joining reactive metals and producing contamination-free parts for aerospace, medical, and electronics applications. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your production quality and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a vacuum oven necessary for treating SiOx anodes? Ensure Battery Stability and Prevent Copper Oxidation
- How is the sintering temperature related to the melting temperature? A Guide to Solid-State Bonding
- What is the temperature range of a vacuum furnace? From 500°C to 2200°C for Your Specific Process
- What is the role of Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) furnaces in Ti-Nb-Zr alloys? Precision Engineering for Implants
- What is a high temperature furnace? A Guide to Precision Heat Treatment & Sintering
- How do high-temperature reaction furnaces control in-situ MMCs? Master Material Precision and Structural Integrity
- How does high-temperature heating equipment facilitate corrosion research? Replicating Nuclear Reactor Environments
- What is the precaution of furnace? Essential Safety Steps to Protect Operators and Equipment



















