In materials science, vacuum hot pressing is a sophisticated manufacturing process that simultaneously applies high temperature and mechanical pressure to a powdered material inside a vacuum. This combination of forces causes the powder particles to consolidate and bond, forming a solid component with exceptionally high density and a refined internal structure. It is a powerful method for producing high-performance materials that cannot be made effectively through other means.
The central advantage of vacuum hot pressing lies in its synergistic approach. By combining heat, pressure, and a vacuum, the process creates materials with near-perfect density and fine-grained microstructures at lower temperatures and in less time than conventional methods.

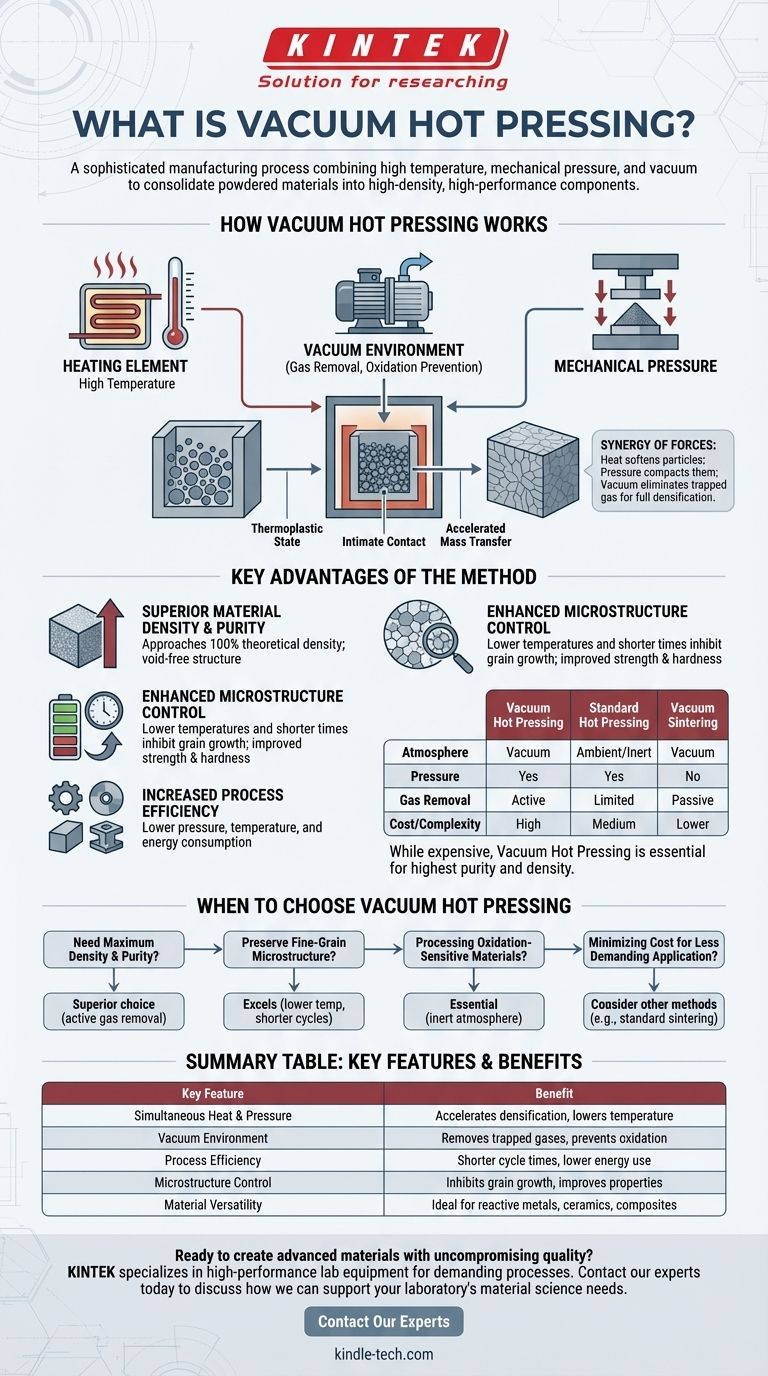
How Vacuum Hot Pressing Works
To understand the value of this technique, it's essential to break down how each component—heat, pressure, and vacuum—contributes to the final product. The process is a carefully controlled synergy of these three elements.
The Core Principle: A Synergy of Forces
The foundation of the process is the simultaneous application of heat and uniaxial pressure. The heat brings the powdered material into a thermoplastic state, making the individual particles more malleable and reducing their resistance to deformation. At the same time, mechanical pressure forces these softened particles into intimate contact, closing the gaps between them.
The Critical Role of the Vacuum
Creating a vacuum within the furnace chamber is what elevates this technique. The vacuum serves two primary purposes:
- It removes atmospheric gases (like oxygen and nitrogen) from between the powder particles before consolidation begins.
- It prevents oxidation and other chemical reactions that could occur at high temperatures, which is crucial for sensitive materials.
By eliminating trapped gases, the vacuum removes a major obstacle to achieving full densification. In other methods, these gases can become trapped in microscopic pores, creating internal defects and limiting the material's final density and strength.
The Sintering and Densification Process
As heat and pressure are applied in the vacuum, mass transfer processes like diffusion and particle flow are greatly accelerated. Atoms move across the boundaries of the contacting particles, forming strong metallurgical or ceramic bonds.
This entire process—heating, pressing, and sintering—is often managed by advanced control systems. This allows for precise manipulation of the process curve to control the densification and ensure the final material meets exacting quality standards.
Key Advantages of the Method
The unique combination of process variables gives vacuum hot pressing several distinct advantages over other consolidation techniques.
Superior Material Density and Purity
The primary benefit is the ability to produce components that approach 100% of their theoretical density. By effectively removing gas from micro-pores, the process creates a solid, void-free structure with superior mechanical properties.
Enhanced Microstructure Control
The process allows for lower sintering temperatures and significantly shorter processing times compared to pressureless sintering. This is critical because it effectively inhibits grain growth, resulting in a fine-grained microstructure that often translates to improved strength, hardness, and electrical performance.
Increased Process Efficiency
Because the powder is in a thermoplastic state, the pressure required is only a fraction (often just one-tenth) of that needed for cold pressing. This, combined with lower temperatures and shorter cycles, leads to a reduction in overall energy consumption.
Versatility in Production
Vacuum hot pressing is capable of producing not only simple shapes but also complex components with accurate dimensions. The process can also be scaled to prepare large-diameter materials, making it suitable for a wide range of industrial applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single process is perfect for every application. To make an informed decision, it's vital to understand where vacuum hot pressing fits in the broader landscape of materials processing.
Vacuum Hot Pressing vs. Standard Hot Pressing
Standard hot pressing also uses heat and pressure but operates in an ambient or inert gas atmosphere. While effective, it cannot remove gases already adsorbed to the powder surfaces, which can lead to residual porosity. The addition of a vacuum adds complexity but is essential for achieving the highest levels of purity and density.
Vacuum Hot Pressing vs. Vacuum Sintering
Vacuum sintering involves heating a material in a vacuum without the simultaneous application of mechanical pressure. Densification relies solely on atomic diffusion driven by heat. Vacuum hot pressing is a more aggressive and efficient process because the external pressure actively forces the particles together, accelerating densification and closing pores that sintering alone cannot.
Equipment and Cost Considerations
The combination of a high-temperature furnace, a hydraulic press, and a high-vacuum system makes the equipment for vacuum hot pressing inherently complex and expensive. While the process is efficient in terms of energy and time, the initial capital investment is significant compared to conventional furnaces.
When to Choose Vacuum Hot Pressing
Your choice of manufacturing process should be driven by the final properties your component requires.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum theoretical density and purity: Vacuum hot pressing is the superior choice, as it actively removes the trapped gases that inhibit full consolidation in other methods.
- If your primary focus is preserving a fine-grain microstructure for superior mechanical or electrical properties: This method excels by enabling lower temperatures and shorter cycle times, which directly prevents unwanted grain growth.
- If your primary focus is processing advanced materials sensitive to oxidation: The vacuum environment provides an essential inert atmosphere, making it ideal for non-oxide ceramics, reactive alloys, and advanced composites.
- If your primary focus is minimizing cost for a less-demanding application: A simpler method like conventional sintering or standard hot pressing may be more economical, provided the resulting material properties are sufficient for your needs.
Ultimately, understanding the interplay of heat, pressure, and vacuum empowers you to select the precise manufacturing path for creating materials with uncompromising quality.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Simultaneous Heat & Pressure | Accelerates densification, lowers required temperature. |
| Vacuum Environment | Removes trapped gases, prevents oxidation for superior purity. |
| Process Efficiency | Shorter cycle times and lower energy consumption. |
| Microstructure Control | Inhibits grain growth for improved strength and hardness. |
| Material Versatility | Ideal for reactive metals, non-oxide ceramics, and composites. |
Ready to create advanced materials with uncompromising quality?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including solutions for demanding processes like vacuum hot pressing. Our expertise helps you achieve superior material density, purity, and microstructure control for your most critical applications.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's material science and research needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Electric Heated Hydraulic Vacuum Heat Press for Lab
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot press sintering furnace? Achieve 99.1% Density in CuW30 Composites
- Why is precise temperature control necessary for SiC/Cu Vacuum Hot Pressing? Mastering the Cu9Si Interface Phase
- What is the significance of precise temperature control in melt infiltration? Achieve High-Performance Li-Alloy Electrodes
- What advantages does hot pressing sintering equipment provide for NASICON? Achieve 100% Dense Solid Electrolyte Plates
- What conditions does a Vacuum Hot Pressing Furnace provide for Copper-MoS2-Mo composites? Achieve Peak Densification



















