Crucially, PVD is not a material itself. It is a sophisticated coating process—Physical Vapor Deposition—used to apply an extremely thin but durable layer of a specific material onto the surface of an object. The "material" of a PVD finish is the substance being deposited, which can vary widely depending on the desired outcome.
The central misunderstanding is thinking of PVD as a substance. Instead, you should think of it as a high-tech process that bonds a separate, high-performance material (the coating) onto a base object (the substrate).
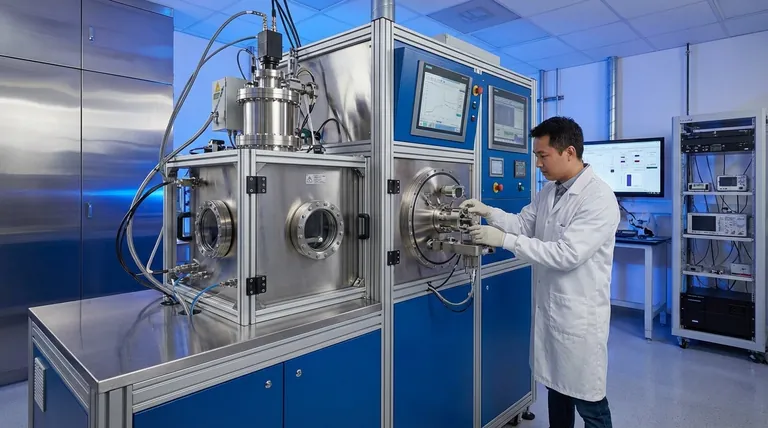

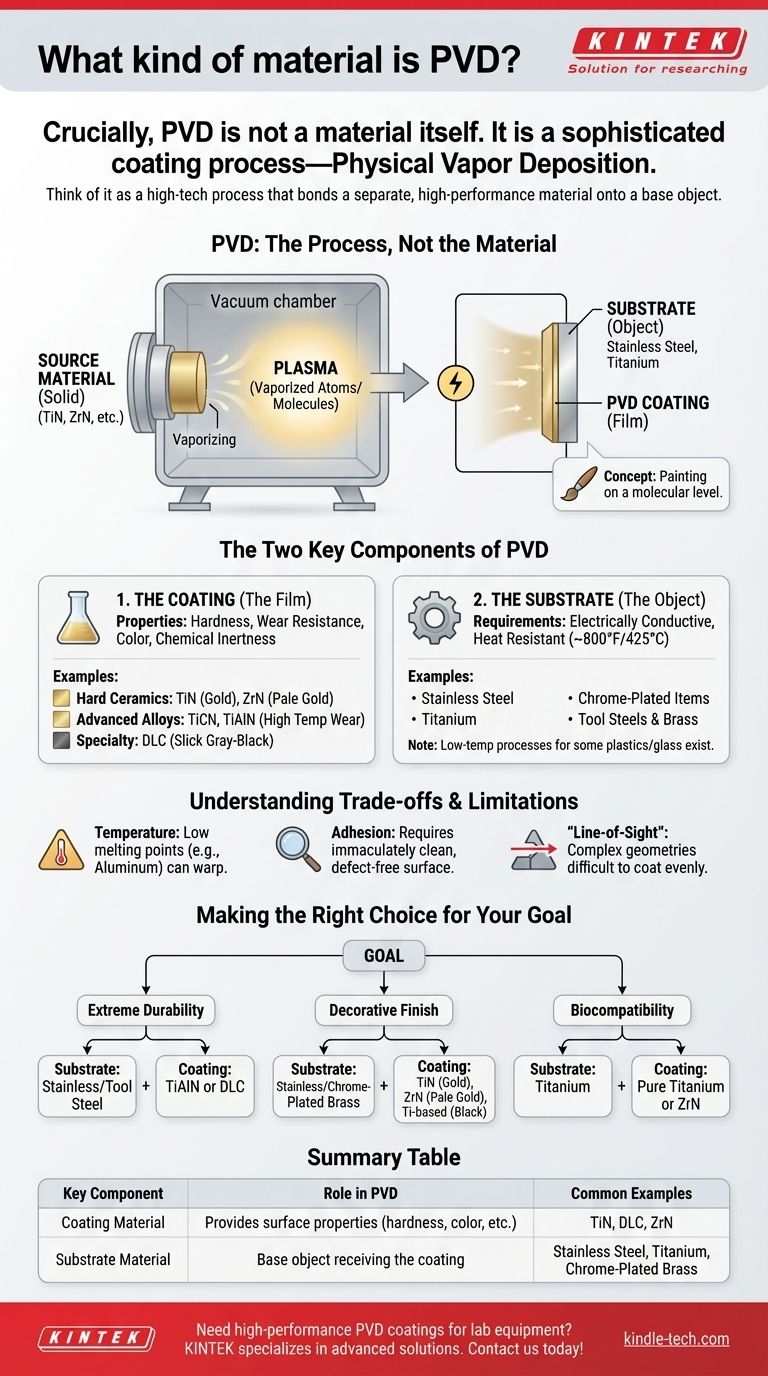
What is PVD? The Process, Not the Material
To understand PVD, you must separate the method from the materials involved. The name "Physical Vapor Deposition" describes exactly what happens.
The Core Principle: Vaporization and Deposition
In simple terms, the PVD process takes place inside a vacuum chamber. A solid source material—often a high-purity metal or ceramic—is vaporized into a plasma of atoms or molecules.
An electrical voltage is then applied to the object being coated (the substrate), which attracts these vaporized particles. They condense onto the object's surface, forming a thin, tightly bonded film. Think of it as painting on a molecular level.
Why This Distinction is Vital
Because PVD is a process, it offers incredible flexibility. Engineers can choose from a vast library of coating materials to achieve specific properties, such as enhanced hardness, different colors, or corrosion resistance, on a wide variety of substrate materials.
The Two Key Components of PVD
Every PVD application involves two distinct materials: the coating that is applied and the substrate that is being coated.
The Coating Material (The Film)
This is the material that gives the final product its unique surface properties. These materials are chosen for hardness, wear resistance, color, and chemical inertness.
Common P-VD coating materials include:
- Hard Ceramics: Such as Titanium Nitride (TiN), known for its gold color and extreme hardness, and Zirconium Nitride (ZrN), which offers a pale gold color and excellent corrosion resistance.
- Advanced Alloys: Including Titanium Carbonitride (TiCN) and Titanium Aluminum Nitride (TiAlN), which provide even greater wear resistance at high temperatures.
- Pure Metals: Precious metals like gold or titanium can be deposited for decorative or biocompatible purposes.
- Specialty Coatings: Like Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC), which creates a slick, gray-black surface with an exceptionally low coefficient of friction.
The Substrate Material (The Object)
This is the base object that receives the coating. The PVD process requires the substrate to be electrically conductive (in most cases) and able to withstand temperatures up to 800°F (425°C) without deforming.
Excellent candidates for PVD coating include:
- Stainless Steel: An ideal substrate due to its durability and ability to handle the process heat.
- Titanium: Like stainless steel, it is a perfect base for PVD.
- Chrome-Plated Items: PVD adheres exceptionally well to high-quality nickel-chrome plating.
- Some Tool Steels and Brass.
Some materials, like certain plastics (ABS, polycarbonate) and glass, can also be coated using specialized low-temperature PVD processes.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, the PVD process is not universally applicable. Understanding its constraints is key to using it effectively.
Substrate Compatibility is Key
The most significant limitation is temperature. Materials with a low melting point, such as aluminum and many zinc alloys, are typically poor candidates for standard PVD processes because they can warp or melt in the vacuum chamber.
Adhesion Requires a Perfect Surface
The PVD film is only a few microns thick. Its performance depends entirely on its bond to the substrate. The substrate surface must be immaculately clean, smooth, and free of any defects for the coating to adhere properly.
It's a "Line-of-Sight" Process
The vaporized coating material travels in a straight line inside the chamber. This means that complex internal geometries or deep, narrow holes can be very difficult to coat evenly without sophisticated rotating fixtures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of coating and substrate should be driven by your primary objective for the finished product.
- If your primary focus is extreme durability and wear resistance: Choose a substrate like stainless steel or tool steel with a ceramic coating like TiAlN or DLC.
- If your primary focus is a decorative finish: A substrate of stainless steel or high-quality chrome-plated brass with a TiN (gold), ZrN (pale gold), or Titanium-based (charcoal/black) coating is ideal.
- If your primary focus is biocompatibility for medical devices: Use a titanium substrate with either a pure titanium or a ZrN coating.
Ultimately, understanding that PVD is a versatile process empowers you to select the precise combination of materials needed to achieve your goal.
Summary Table:
| Key Component | Role in PVD | Common Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Coating Material | Provides surface properties (hardness, color, etc.) | Titanium Nitride (TiN), Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC), Zirconium Nitride (ZrN) |
| Substrate Material | Base object receiving the coating | Stainless Steel, Titanium, Chrome-Plated Brass |
Need a high-performance PVD coating for your lab equipment or components? KINTEK specializes in advanced PVD solutions for laboratory needs, offering durable, custom coatings that enhance wear resistance, reduce friction, and improve chemical inertness. Let our experts help you select the ideal coating and substrate combination for your specific application. Contact us today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Electric Heated Hydraulic Vacuum Heat Press for Lab
People Also Ask
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells



















