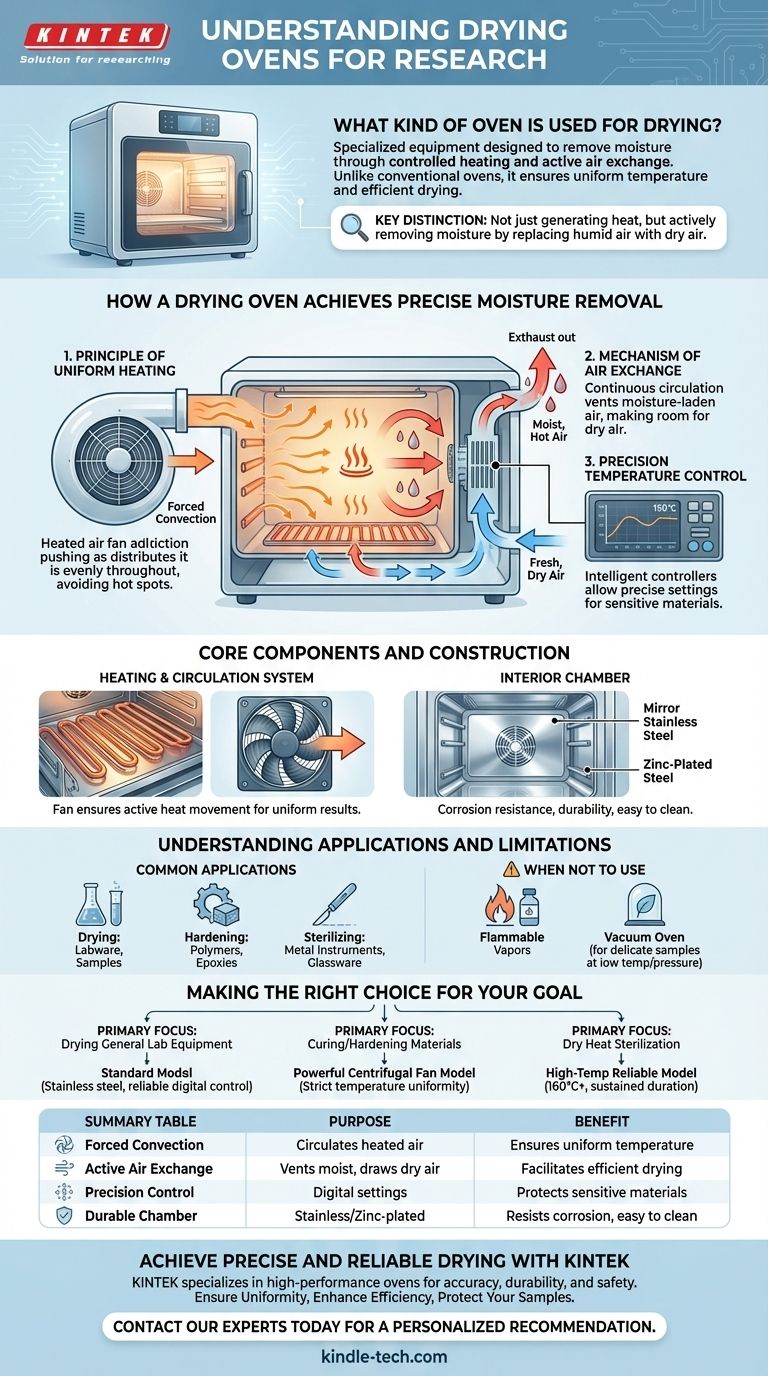
The specialized equipment used for this purpose is known as a drying oven. Unlike a conventional oven, its primary design function is to remove moisture from objects and materials through a process of controlled heating and active air exchange. It ensures a uniform temperature throughout its chamber by circulating heated air, which is critical for consistent results in laboratory and industrial settings.
The key distinction of a drying oven is not just its ability to generate heat, but its mechanism for active moisture removal. It systematically replaces the moist, hot air inside the chamber with fresh, dry air to facilitate efficient and uniform drying.

How a Drying Oven Achieves Precise Moisture Removal
A drying oven operates on a simple but effective principle: heated air can hold more moisture. By continuously circulating hot air and venting the moisture-laden air, it effectively dehydrates the items inside.
The Principle of Uniform Heating
To prevent hot spots and ensure the entire object dries at the same rate, a drying oven uses a forced convection system. A large-diameter centrifugal fan or wind wheel actively pushes air across the heating elements and distributes it evenly throughout the chamber.
This constant dissipation of hot air is what maintains a stable and uniform internal temperature.
The Mechanism of Air Exchange
A drying oven is not a sealed system. Fresh, ambient air is drawn into the oven, typically near the heating elements. As this air is heated, it circulates around the items, absorbing moisture.
This now-humid air is then vented out of the chamber, making room for a new cycle of fresh, dry air. This active exchange is the core of the drying process.
Precision Temperature Control
These ovens are equipped with intelligent temperature controllers, often featuring a digital display. This allows for precise settings and stability, which is vital when working with sensitive materials that could be damaged by temperature fluctuations.
Core Components and Construction
The design of a drying oven is optimized for durability, performance, and ease of use in a professional environment.
The Heating and Circulation System
The primary components are the electrical heating elements and the fan. The fan ensures that the heat generated by the elements is not static but is actively moved throughout the oven, creating the uniform environment necessary for reliable results.
The Interior Chamber
The internal chamber is typically constructed from high-grade materials like mirror stainless steel or zinc-plated steel. These materials are chosen for their corrosion resistance, durability, and how easy they are to clean and decontaminate.
Understanding the Applications and Limitations
While its name implies a single function, a drying oven is a versatile tool used for several thermal processes. However, it's important to know when it is—and is not—the right choice.
Common Applications
The main functions of a drying oven include:
- Drying: Removing moisture from laboratory glassware, parts, or material samples.
- Hardening: Curing polymers, epoxies, or other materials that require thermal processing to achieve their final strength.
- Sterilizing: Using sustained dry heat to sterilize metal instruments or certain types of glassware.
When Not to Use a Drying Oven
A standard drying oven is not suitable for all tasks. It should not be used for materials that release flammable vapors unless the oven is specifically rated for that purpose. It is also distinct from a vacuum oven, which dries delicate samples at lower temperatures by reducing pressure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the appropriate equipment, match the oven's features to your specific application.
- If your primary focus is drying general lab equipment: A standard model with a stainless steel interior and reliable digital temperature control will be sufficient.
- If your primary focus is curing materials or hardening parts: Prioritize an oven with a powerful centrifugal fan to guarantee strict temperature uniformity across the entire product.
- If your primary focus is dry heat sterilization: Ensure the oven can reliably achieve and hold the necessary sterilization temperatures (typically 160°C or higher) for the required duration.
Understanding these core principles ensures you select and use the right tool for precise and repeatable results.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Purpose | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Forced Convection | Circulates heated air | Ensures uniform temperature and drying |
| Active Air Exchange | Vents moist air, draws in dry air | Facilitates efficient moisture removal |
| Precision Control | Digital temperature settings | Protects sensitive materials, ensures repeatability |
| Durable Chamber | Stainless or zinc-plated steel interior | Resists corrosion, easy to clean and decontaminate |
Achieve Precise and Reliable Drying with KINTEK
Whether your primary focus is drying labware, curing materials, or dry heat sterilization, selecting the right equipment is critical for your results. KINTEK specializes in high-performance laboratory drying ovens designed for accuracy, durability, and safety.
We provide solutions that help you:
- Ensure Uniformity: Prevent hot spots and achieve consistent results with our ovens' advanced forced convection systems.
- Enhance Efficiency: Speed up your processes with reliable and efficient moisture removal.
- Protect Your Samples: Rely on precise digital temperature control to handle sensitive materials confidently.
Ready to find the perfect drying oven for your laboratory's needs?
Contact our experts today to discuss your application and get a personalized recommendation. Let KINTEK be your partner in precision.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Scientific Electric Heating Blast Drying Oven
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Horizontal High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a laboratory drying oven in catalyst treatment? Ensure Structural Integrity & High Performance
- How does a controlled drying process ensure the quality of radiochromic films? Achieve Precise Dosimetric Results
- What is the role of a blast drying oven in COF synthesis? Driving High-Crystallinity Solvothermal Reactions
- What is the function of a laboratory drying oven in Zr2.5Nb alloy pretreatment? Ensure Precise Corrosion Test Results
- What is the function of a laboratory oven in W18Cr4V steel sample preparation? Expert Microstructural Drying Guide













