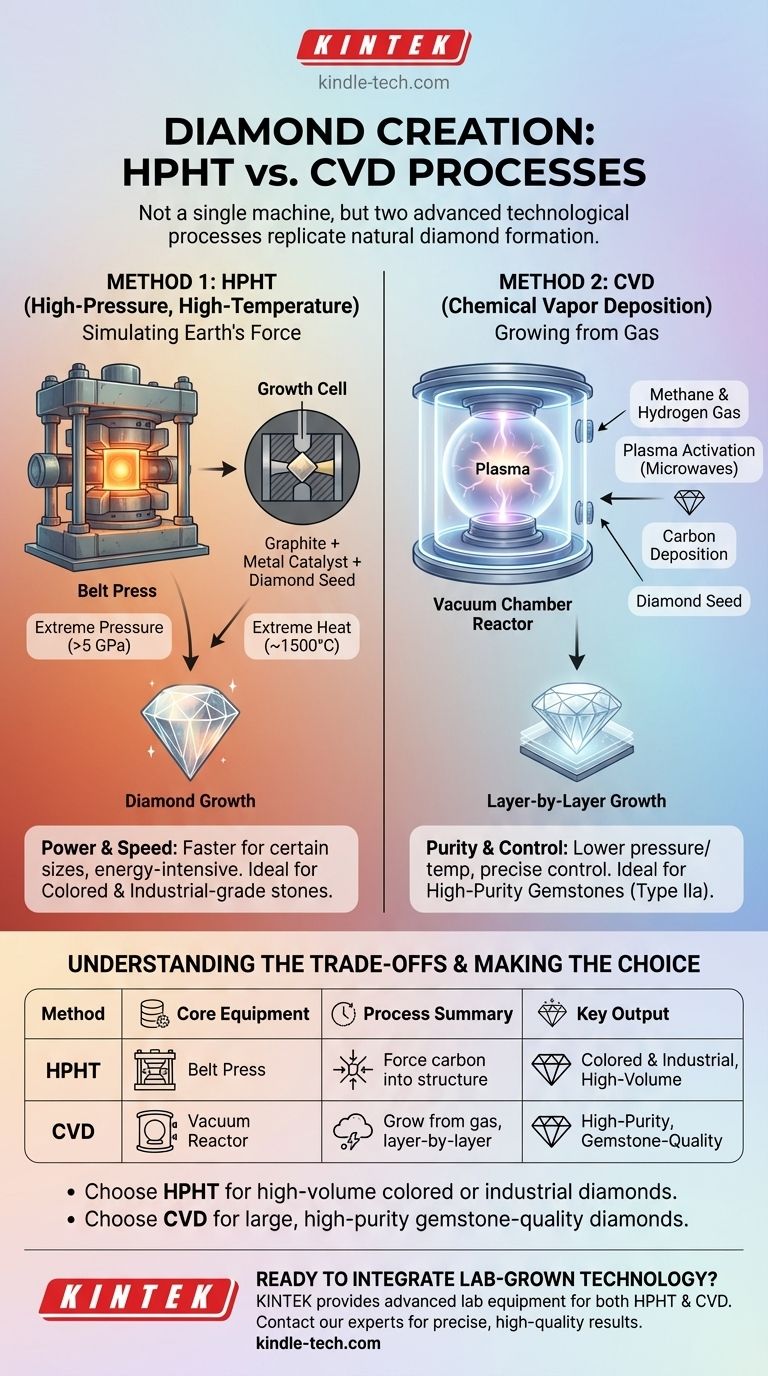
To make a lab-grown diamond, you don't use a single "machine," but rather one of two highly specialized technological processes. These are known as High-Pressure, High-Temperature (HPHT) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). Each method requires a complex system of equipment designed to replicate the extreme conditions of natural diamond formation or to build a diamond atom by atom.
The core choice is not about a single machine, but a fundamental approach: either you recreate the brute force of the Earth's mantle with immense pressure (HPHT), or you meticulously grow a crystal from a superheated gas in a vacuum (CVD).

Method 1: Simulating the Earth's Force (HPHT)
The High-Pressure, High-Temperature method is the original technique for creating diamonds and is a direct simulation of the natural process deep within the Earth.
The Core Principle
HPHT technology subjects a carbon source, like graphite, to the same extreme pressures and temperatures that form diamonds naturally. It essentially forces carbon atoms into the tightly bonded crystal structure of a diamond.
The "Machine": The Belt Press
The primary piece of equipment is a massive press, often a belt press, capable of generating immense, sustained force. These devices use multiple anvils to concentrate pressure on a small, central growth cell.
The Process
A tiny diamond seed is placed in the growth cell along with a carbon source (graphite) and a metal catalyst. The press then applies pressures exceeding 5 gigapascals (nearly 1 million PSI) and temperatures around 1,500°C (2,700°F). The metal catalyst melts, dissolving the carbon, which then crystallizes onto the diamond seed, growing a larger diamond.
Method 2: Growing a Diamond from Gas (CVD)
Chemical Vapor Deposition is a more recent innovation that builds a diamond in layers, offering a different kind of control over the growth process.
The Core Principle
CVD works by introducing a carbon-rich gas into a vacuum chamber and breaking it down, allowing carbon atoms to settle onto a diamond seed and build up a crystal layer by layer.
The "Machine": The Vacuum Chamber Reactor
The central piece of equipment is a vacuum chamber or reactor. This sealed environment is critical for preventing contamination and precisely controlling the atmospheric composition during growth.
The Process
A thin slice of a diamond seed is placed inside the chamber. All air is removed to create a vacuum, and the chamber is filled with a mixture of gases, typically methane and hydrogen. This gas is then heated, often with microwaves, to form a plasma. This breaks the gas molecules apart, and the freed carbon atoms rain down and bond to the diamond seed, slowly growing the crystal.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither method is universally superior; they are different tools for achieving the same result, each with distinct advantages and challenges.
HPHT: Power and Speed
The HPHT process is often faster than CVD for growing a diamond of a certain size. It is an established, powerful method that is very effective for certain applications, but it is extremely energy-intensive due to the massive pressures required.
CVD: Purity and Control
The CVD process operates at much lower pressures and more moderate temperatures. This allows for greater control over the growth environment, often resulting in diamonds with very high purity (Type IIa), a category that is rare in nature.
Resulting Diamond Characteristics
While both produce real diamonds, the different growth environments can leave behind subtle markers. HPHT diamonds may have growth patterns related to the press's geometry, while CVD diamonds often grow in distinct layers that can be identified by gemologists.
Making the Right Choice for the Goal
The decision between HPHT and CVD technology depends entirely on the desired outcome and operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is producing certain colored diamonds or industrial-grade stones: HPHT is a highly effective and mature technology capable of high-volume output.
- If your primary focus is creating large, high-purity gemstone-quality diamonds: CVD is often favored for its precise control over the growth conditions and final purity.
Ultimately, both methods create diamonds that are chemically, physically, and optically identical to their mined counterparts.
Summary Table:
| Method | Core Equipment | Process Summary | Key Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| HPHT | Belt Press | Extreme pressure & heat force carbon into diamond structure. | Colored & industrial diamonds, high-volume output. |
| CVD | Vacuum Chamber Reactor | Carbon-rich gas is broken down to grow diamond layer-by-layer. | High-purity, gemstone-quality diamonds (Type IIa). |
Ready to integrate lab-grown diamond technology into your research or production? KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables you need. Whether you're exploring HPHT or CVD methods, our expertise can help you achieve precise, high-quality results. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and find the perfect solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- High Precision Diamond Wire Cutting Machine Laboratory Saw Precision Wire EDM Cutting Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between MPCVD and HFCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application
- Which lab grown diamond process is best? Focus on Quality, Not the Method
- How do lab-grown diamonds compare to natural diamonds? Uncover the Truth About Origin, Price, and Value
- What is a microwave plasma reactor? Unlock Precision Synthesis of High-Performance Materials
- How does microwave plasma work? Unlock Precision Material Synthesis for Advanced Manufacturing



















