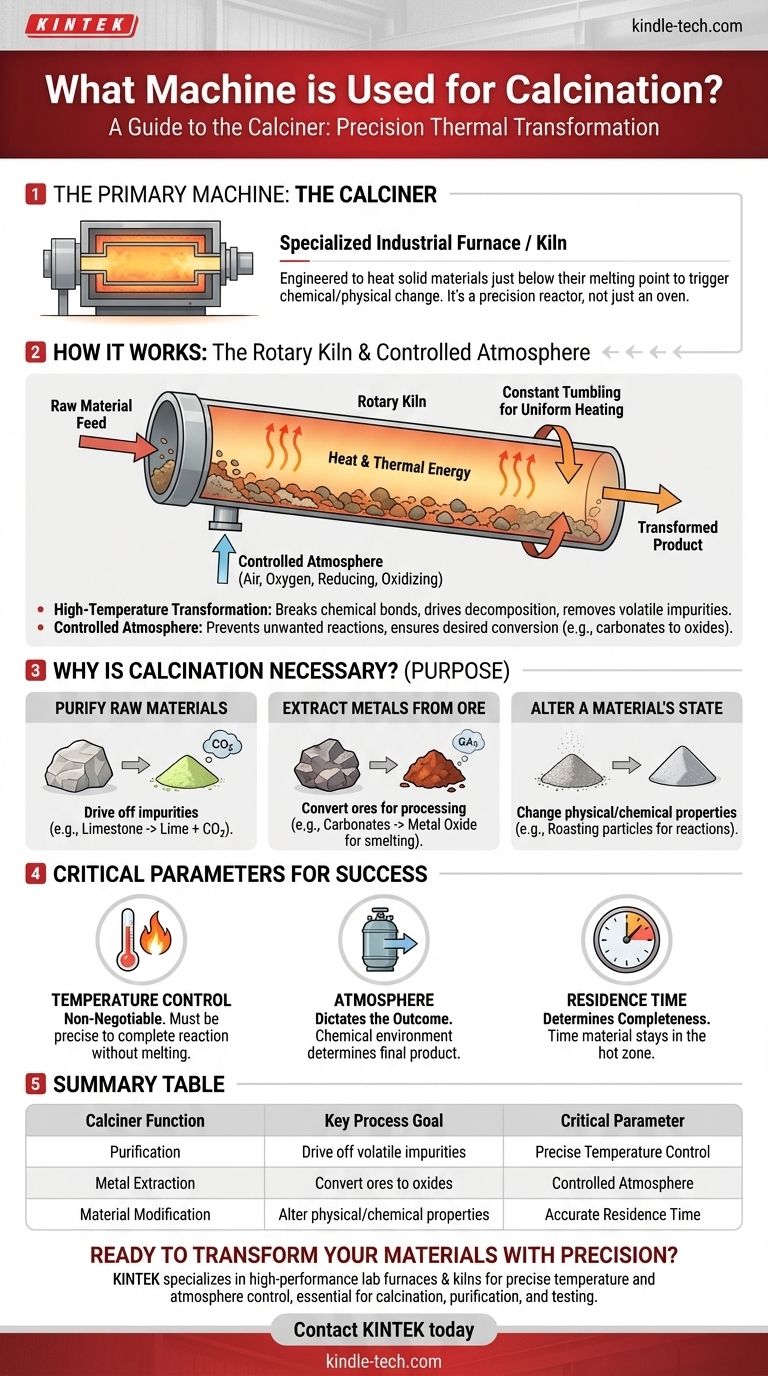
The primary machine used for calcination is a calciner, which is a specialized industrial furnace or kiln. This equipment is engineered to heat solid materials to very high temperatures, just below their melting point, within a precisely controlled atmosphere to trigger a chemical or physical change.
A calciner is not merely a high-temperature oven; it is a precision reactor. Its purpose is to fundamentally alter a material's chemical composition by removing volatile substances or causing thermal decomposition, all without melting the substance itself.

How a Calciner Works
A calciner's design is dictated by its core function: applying precise thermal energy under specific atmospheric conditions. While designs vary, the underlying principles remain consistent.
The Core Principle: High-Temperature Transformation
The fundamental job of a calciner is to heat materials to a specific temperature and hold them there. This temperature is high enough to break chemical bonds but strategically kept below the material's melting point.
This process drives thermal decomposition, where compounds break down into simpler substances. It is also used to remove volatile impurities, such as water, carbon dioxide, or sulfur compounds.
Common Design: The Rotary Kiln
Many calciners are designed as a rotary kiln, a large, rotating cylindrical vessel. The raw material is fed into one end, and as the cylinder slowly rotates, the material tumbles and moves toward the other end.
This constant tumbling ensures every particle is heated uniformly. This design allows for a continuous process, making it highly efficient for industrial-scale production.
The Importance of a Controlled Atmosphere
Calcination is not just about heat; the atmosphere inside the calciner is critical. The process is often conducted with a limited supply of air or oxygen, or even in a specific reducing or oxidizing atmosphere.
This control prevents unwanted reactions and ensures the desired chemical transformation occurs, such as converting metal carbonates or sulfates into their respective oxides during ore processing.
The Purpose: Why Calcination is Necessary
Industries use calcination to prepare or purify materials for subsequent steps. The goal is to create a more refined, concentrated, or chemically stable product.
To Purify Raw Materials
The most common use of calcination is to drive off impurities. For example, heating limestone (calcium carbonate) in a calciner drives off carbon dioxide, leaving behind lime (calcium oxide), a critical ingredient in cement and steel manufacturing.
To Extract Metals from Ore
In metallurgy, calcination is a vital step. It's used to convert metal ores into a form that is easier to process. Heating a metal carbonate ore removes the carbon dioxide, leaving a metal oxide that can then be smelted into pure metal.
To Alter a Material's State
The process can also be used to change the physical or chemical properties of a material. This includes processes like roasting fine metal particles to prepare them for further chemical reactions under specific atmospheric conditions.
Understanding the Critical Parameters
Successful calcination depends on precise control over several variables. Failure to manage these parameters results in an incomplete reaction or a ruined product.
Temperature Control is Non-Negotiable
The entire process hinges on maintaining the correct temperature. If the temperature is too low, the reaction won't complete. If it's too high and the material melts, the process fails and can damage the equipment.
Atmosphere Dictates the Outcome
The chemical environment inside the calciner determines the final product. Using a reducing atmosphere (low oxygen) will produce a different chemical result than an oxidizing atmosphere (high oxygen). This must be tailored to the specific material and desired outcome.
Residence Time Determines Completeness
Residence time refers to how long the material stays inside the hot zone of the calciner. This is controlled by the rotation speed and tilt of a rotary kiln. Insufficient residence time leads to an incomplete reaction, while excessive time can be inefficient and waste energy.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific setup of the calcination process is always tailored to the end goal.
- If your primary focus is purification (e.g., making lime from limestone): Your main concern is achieving the temperature needed to drive off the volatile compound (CO2) completely.
- If your primary focus is metal extraction (e.g., from an ore): You must tightly control both temperature and atmosphere to ensure the ore decomposes into the desired metal oxide without unwanted side reactions.
- If your primary focus is material modification (e.g., roasting powders): Your success depends almost entirely on maintaining the precise atmospheric composition to induce the specific chemical change required.
Ultimately, the calciner is an essential industrial tool used to precisely transform raw materials into more valuable, purified, or reactive forms through the controlled application of heat.
Summary Table:
| Calciner Function | Key Process Goal | Critical Parameter |
|---|---|---|
| Purification | Drive off volatile impurities (e.g., CO2 from limestone) | Precise Temperature Control |
| Metal Extraction | Convert ores to oxides for easier processing | Controlled Atmosphere |
| Material Modification | Alter physical/chemical properties of a substance | Accurate Residence Time |
Ready to transform your materials with precision?
Calcination is a delicate process where the right equipment makes all the difference. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and kilns designed for precise temperature and atmosphere control, essential for successful calcination, purification, and material testing.
Whether you are developing new materials, processing ores, or ensuring product purity, our equipment delivers the reliability and accuracy your laboratory demands.
Contact KINTEK today to find the perfect calcination solution for your specific application and goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- How does a rotary extractor work? Master Continuous High-Volume Solid Processing
- How does precision temperature control impact TiAl alloy sintering? Master Microstructure Development
- How is the operational mode of bed motion selected for a rotary kiln? Optimize Heat Transfer and Material Homogeneity
- What is a rotary kiln reactor? A Guide to Industrial Thermal Processing



















