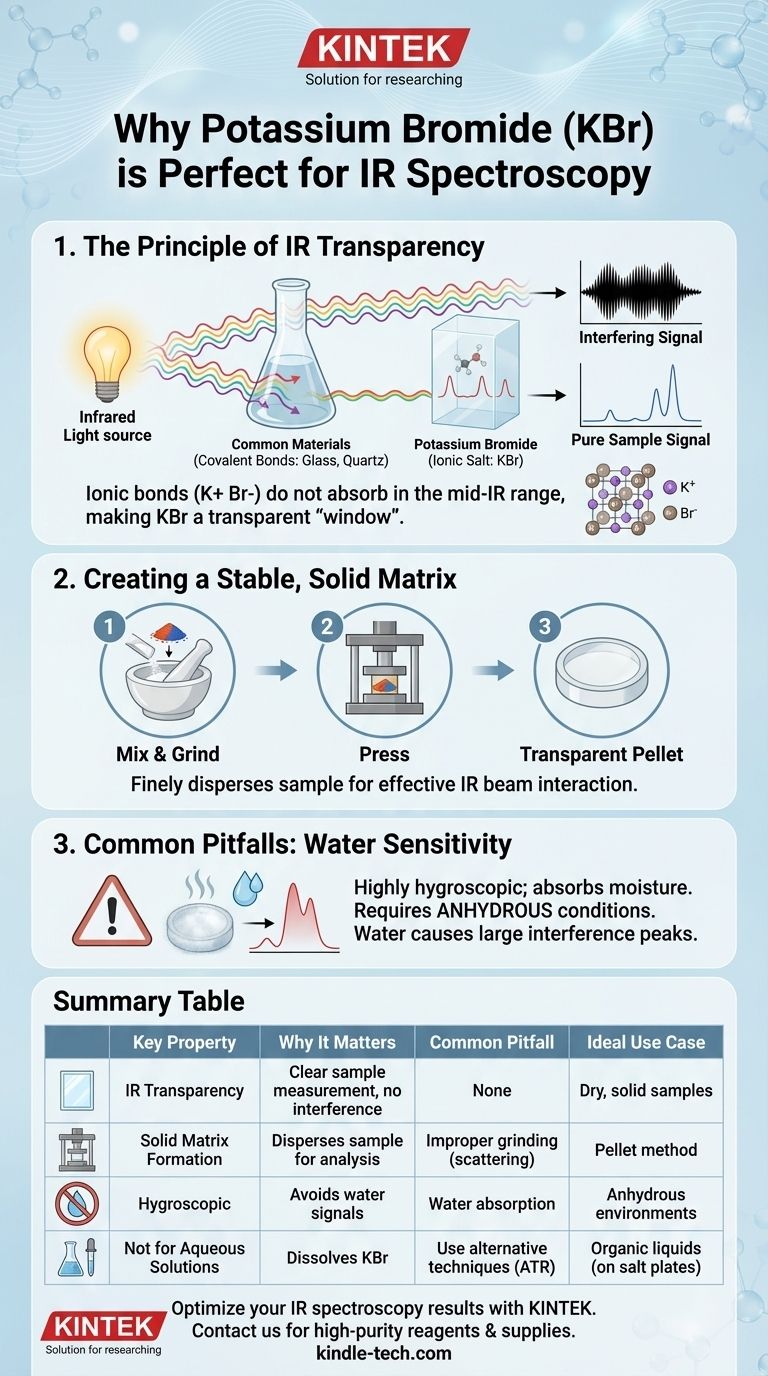
Potassium bromide (KBr) is a preferred reagent for infrared (IR) spectroscopy sample preparation because it is transparent to IR radiation. Its ionic structure does not absorb light in the typical mid-infrared range, meaning it can form a solid matrix for a sample without adding its own interfering spectral signals. This allows the spectrometer to measure only the absorbance of the sample itself.
The core challenge in IR sample preparation is finding a medium that can hold the sample without being "seen" by the spectrometer. KBr's lack of covalent bonds makes it effectively invisible to IR analysis, ensuring the resulting spectrum is a true representation of the sample, not the matrix.

The Principle of IR Transparency
Why Most Materials Are Unsuitable
IR spectroscopy works by measuring the vibrations of covalent bonds within a molecule. Nearly all common materials, such as glass, quartz, or plastic, are made of molecules with covalent bonds.
If you were to use a cuvette or matrix made of these materials, the IR beam would be heavily absorbed by the container itself. This would generate a massive, overwhelming signal that would completely obscure the much weaker signal from your sample.
The Advantage of Alkali Halides
Potassium bromide (KBr) is an alkali halide, a type of ionic salt. The bond between the potassium cation (K+) and the bromide anion (Br-) is ionic, not covalent.
This type of bond does not absorb energy in the mid-IR region (typically 4000-400 cm⁻¹) where most organic functional groups are analyzed. Therefore, KBr is transparent to the IR beam, acting as a perfect "window" through which to view the sample.
Other salts like Sodium Chloride (NaCl) and Silver Chloride (AgCl) share this property and are also used for the same reason.
Creating a Stable, Solid Matrix
For solid samples, KBr powder is intimately ground with the sample material. This mixture is then pressed under high pressure to form a thin, transparent pellet.
This process finely disperses the sample molecules throughout the non-absorbing KBr matrix, allowing the IR beam to pass through and interact with them effectively without scattering.
Common Pitfalls and Limitations
Extreme Sensitivity to Water
The primary drawback of KBr and other alkali halides is that they are highly soluble in water. KBr is also hygroscopic, meaning it will readily absorb moisture from the atmosphere.
Water has very strong, broad IR absorption bands. If present, it will introduce large, interfering peaks into your spectrum, potentially masking important signals from your sample.
The Need for Anhydrous Conditions
Because of this water sensitivity, it is critical that the sample, any solvents used, and the laboratory environment be as dry as possible (anhydrous).
Using wet samples or washing salt plates with aqueous solutions will dissolve them and ruin the analysis. Even moisture from your breath can begin to fog the surface of a KBr pellet.
The Impact of Improper Preparation
Proper sample preparation is crucial for obtaining a meaningful spectrum. Poor grinding of a solid sample can cause the IR light to scatter, leading to a sloping baseline and inaccurate peak intensities.
As the references note, improper technique can produce misleading results, such as cutoff peaks or signals from impurities (like water) that are not part of the actual sample.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To obtain a high-quality spectrum, your sample preparation method must align with the properties of both your sample and your matrix.
- If your primary focus is analyzing a dry, solid sample: Use the KBr pellet method, ensuring the KBr is spectroscopic grade and has been thoroughly dried in an oven before use.
- If your primary focus is analyzing an organic liquid: Use polished salt plates made of KBr or NaCl, but ensure your sample and any cleaning solvents are completely anhydrous.
- If your primary focus is analyzing a sample in an aqueous solution: Do not use KBr or any alkali halide. You must use an alternative technique like Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR) spectroscopy, which is designed for these types of samples.
Ultimately, understanding the properties of your sample matrix is the first step toward reliable and insightful spectroscopic analysis.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Why It Matters for IR Spectroscopy |
|---|---|
| IR Transparency | Ionic bonds don't absorb mid-IR radiation, allowing clear sample measurement. |
| Solid Matrix Formation | Can be pressed into a transparent pellet to finely disperse solid samples. |
| Common Pitfall | Highly hygroscopic; requires anhydrous conditions to avoid water interference. |
| Ideal Use Case | Best for dry, solid samples; not suitable for aqueous solutions. |
Optimize your IR spectroscopy results with the right equipment and consumables. KINTEK specializes in high-purity lab reagents and spectroscopy supplies, including spectroscopic grade KBr, to ensure your sample preparation is precise and contamination-free. Our experts can help you select the ideal materials for your specific application, whether you're working with solids, liquids, or challenging samples. Contact our team today to discuss your lab's needs and enhance the accuracy of your analyses!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- kbr pellet press 2t
- XRF & KBR steel ring lab Powder Pellet Pressing Mold for FTIR
- Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press for XRF KBR FTIR Lab Applications
- XRF & KBR plastic ring lab Powder Pellet Pressing Mold for FTIR
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press Machine for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- How do you prepare a KBr pellet for IR spectroscopy? Master the Key Steps for a Clear Spectrum
- What are the safety precautions for KBr? Achieve Flawless FTIR Pellet Preparation and Data Accuracy
- How much sample is needed for IR? Optimize Your Analysis with Minimal Material
- Why KBr is used for IR spectroscopy? The Ideal Medium for Solid Sample Analysis
- What are the different types of sampling techniques used in IR spectroscopy? A Guide to KBr, Mull, and ATR Methods














