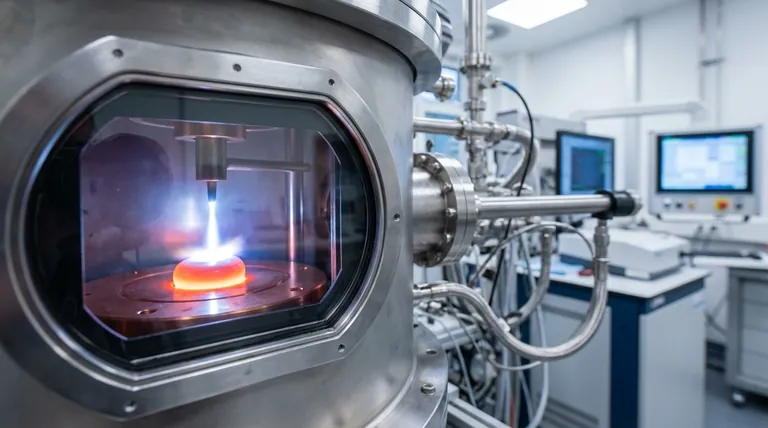
In materials science, arc melting is not a material itself, but a high-temperature fabrication process. It uses a powerful electric arc to melt metals and create alloys, particularly those with exceptionally high melting points. The entire process is conducted inside a sealed chamber with a controlled atmosphere to prevent the molten metal from reacting with air, ensuring a high-purity final product.
Arc melting is the essential laboratory technique for producing small, high-purity samples of metals and alloys that cannot be melted by conventional furnaces. Its core advantage is the ability to generate extreme, localized heat while minimizing contamination from the surrounding environment or crucible.

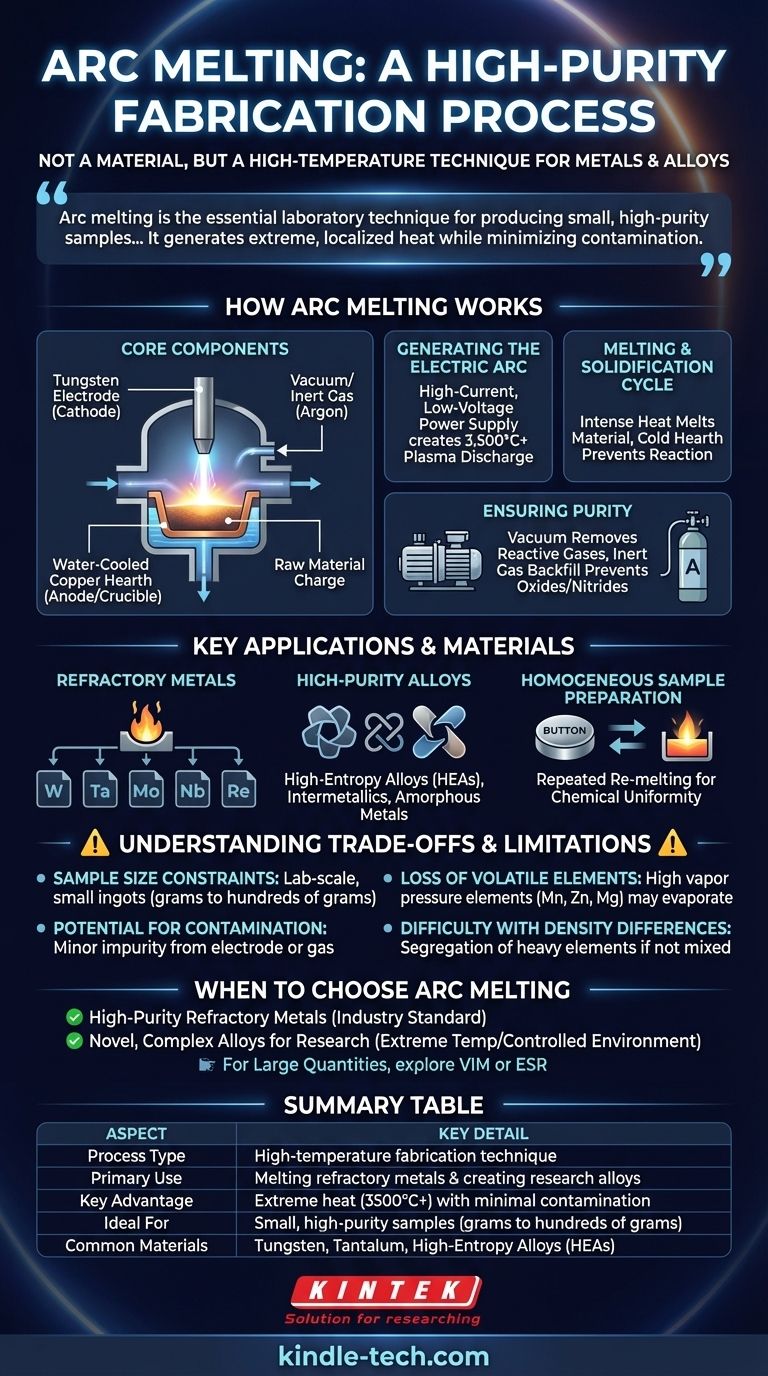
How Arc Melting Works
The elegance of arc melting lies in its direct and clean application of energy. The system is designed around a few critical components that work together to achieve extreme temperatures in a controlled way.
The Core Components
An arc melter consists of a non-consumable tungsten electrode (the negative cathode) and a water-cooled copper hearth (the positive anode). The raw materials are placed directly onto this copper hearth, which acts as a crucible. The entire assembly is housed within a chamber that can be evacuated to a vacuum or filled with an inert gas like argon.
Generating the Electric Arc
A high-current, low-voltage power supply creates an electrical potential between the tungsten electrode and the metallic charge on the hearth. This generates an incredibly hot and stable electric arc—a plasma discharge—that strikes the material, capable of reaching temperatures over 3,500°C (6,332°F).
The Melting and Solidification Cycle
This intense, localized heat rapidly melts the material. The water-cooled copper hearth is crucial; it draws heat away from the molten metal so effectively that the hearth itself does not melt or react with the sample. This "cold crucible" design is a key reason for the high purity of the final product.
Ensuring Purity with a Controlled Atmosphere
Before melting, the chamber is pumped down to a vacuum to remove oxygen, nitrogen, and other reactive gases. It is then backfilled with a high-purity inert gas, typically argon. This prevents the highly reactive molten metal from forming undesirable oxides or nitrides, which would compromise its properties.
Key Applications and Materials
Arc melting is not a bulk production method; it is a precision tool for research and development where purity and the ability to melt difficult materials are paramount.
Refractory Metals
The primary application of arc melting is for metals with extremely high melting points, known as refractory metals. These include tungsten (W), tantalum (Ta), molybdenum (Mo), niobium (Nb), and rhenium (Re). Conventional furnaces simply cannot reach the temperatures required to melt them.
High-Purity Alloys
Researchers use arc melting to synthesize novel and experimental alloys with precise compositions. This includes high-entropy alloys (HEAs), intermetallics, and amorphous metals (metallic glasses). The process allows for thorough mixing of constituent elements in the molten state.
Homogeneous Sample Preparation
A common practice is to flip the solidified "button" ingot and re-melt it multiple times. This process mechanically stirs the molten pool and ensures the final sample is chemically homogeneous, which is critical for accurate scientific characterization.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, arc melting is a specialized technique with clear limitations that make it unsuitable for certain applications.
Sample Size Constraints
Arc melting is fundamentally a lab-scale process. It is ideal for creating small ingots, often called "buttons," that typically weigh from a few grams up to a few hundred grams. It is not economical or practical for large-scale industrial production.
Loss of Volatile Elements
The combination of high temperature and low pressure can cause elements with high vapor pressure (e.g., manganese, zinc, magnesium) to boil out of the melt. This evaporation loss can alter the final composition of the alloy, making it difficult to create alloys containing these volatile elements accurately.
Potential for Contamination
Although designed for high purity, minor contamination can still occur. This might come from slight erosion of the tungsten electrode tip or from impurities present in the starting materials or the argon gas.
Difficulty with Density Differences
Creating a homogeneous alloy can be challenging if the constituent metals have vastly different densities. The heavier elements may sink to the bottom of the molten pool, leading to segregation upon cooling if not mixed sufficiently.
When to Choose Arc Melting
The decision to use arc melting depends entirely on your material requirements and production scale.
- If your primary focus is creating high-purity samples of refractory metals: Arc melting is the industry standard and the most effective method available for laboratory work.
- If your primary focus is developing novel, complex alloys for research: This technique provides the extreme temperatures and controlled environment essential for exploratory materials science.
- If your primary focus is producing large quantities of metal: You should investigate industrial-scale methods like vacuum induction melting (VIM) or electroslag remelting (ESR).
Ultimately, arc melting is an indispensable tool for materials research, enabling the synthesis and discovery of advanced materials that would otherwise be impossible to create.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Process Type | High-temperature fabrication technique |
| Primary Use | Melting refractory metals & creating research alloys |
| Key Advantage | Extreme heat (3500°C+) with minimal contamination |
| Ideal For | Small, high-purity samples (grams to hundreds of grams) |
| Common Materials | Tungsten, Tantalum, High-Entropy Alloys (HEAs) |
Ready to create high-purity metal samples for your research?
Arc melting is essential for developing next-generation materials, but selecting the right equipment is critical for success. KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment, including arc melting systems, designed to meet the rigorous demands of materials science.
We provide the tools you need to achieve extreme temperatures and unparalleled purity for your refractory metals and novel alloys. Let our expertise help you accelerate your R&D.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific lab requirements and find the perfect solution for your materials fabrication challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the disadvantages of induction heating? High Cost & Geometric Limits Explained
- Can an induction heater melt silver? Unlock Fast, Clean, and Precise Melting
- What are the structural advantages of a VIDP furnace? Achieve High-Purity Melting with Superior Efficiency
- What is the difference between core type furnace and coreless induction furnace? Choose the Right Tool for Your Foundry
- Is induction welding the same as brazing? Decoding the Key Differences in Metal Joining
- What is the function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Essential Guide for High-Purity FeCrAl Alloy Production
- Is induction heat instant? Discover the Secret to Lightning-Fast Cooking
- What are the main systems that comprise a vacuum induction melting furnace? A Guide to the 5 Core Components



















