The short answer is that Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) can use a vast range of source materials, primarily metals, alloys, and ceramics. The specific material chosen is determined entirely by the desired properties of the final coating, such as hardness, color, temperature resistance, or electrical conductivity.
The versatility of PVD lies in its ability to transform solid source materials—from pure titanium to complex ceramic compounds—into a high-performance thin film. The material you start with directly dictates the function of the final coated part.

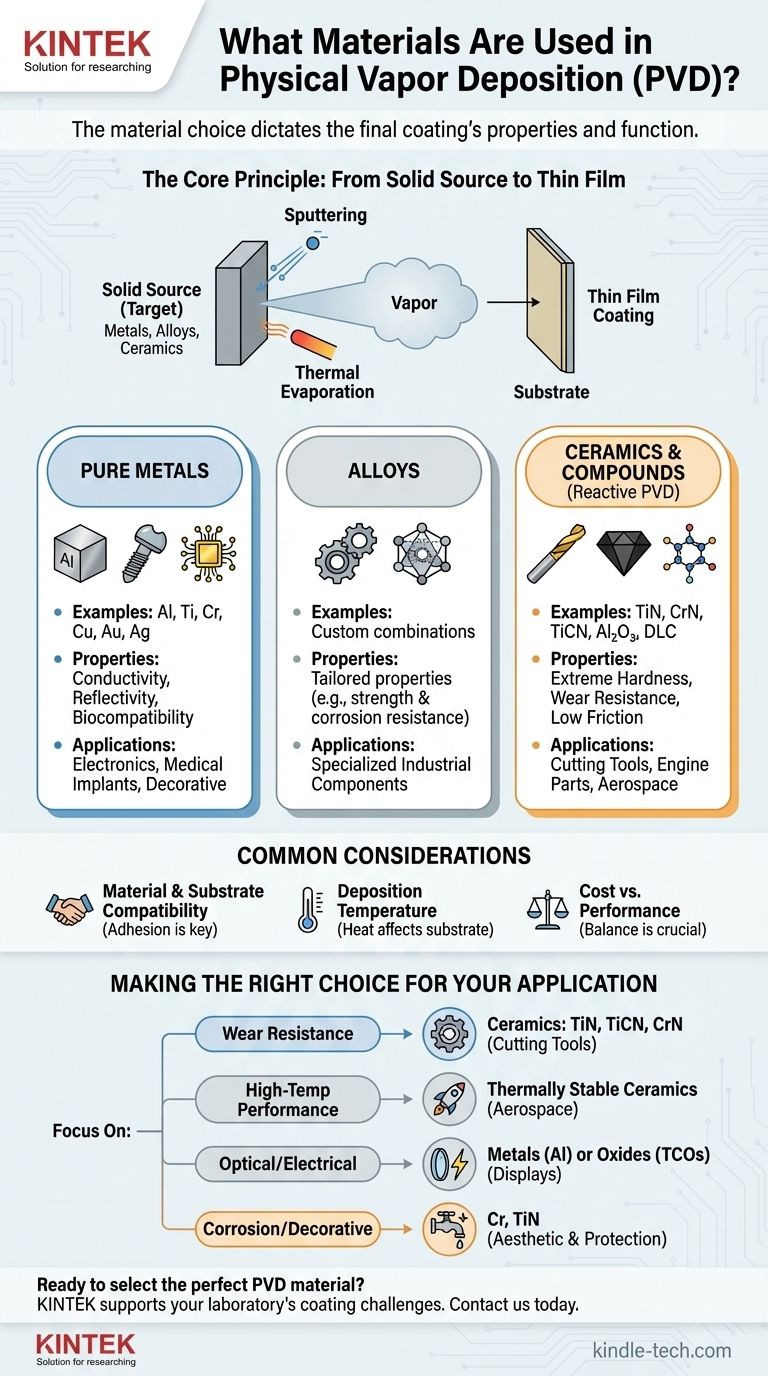
The Core Principle: From Solid Source to Thin Film
To understand what materials can be used, you first need to understand the PVD process. It's a "line-of-sight" technique where a solid material is vaporized in a vacuum, transported atom-by-atom, and condensed onto a substrate as a thin film.
The Source Material (or "Target")
The process begins with a solid source material, often called a target. This material must be in a highly pure, solid form, such as a block, ingot, or powder.
The Vaporization Process
The two most common methods for vaporizing this source material are sputtering and thermal evaporation. Sputtering uses energetic ions to physically knock atoms off the target, while evaporation uses heat to boil the material into a vapor. The suitability of a material for PVD depends on its ability to undergo one of these processes efficiently.
A Taxonomy of PVD Materials
The materials used in PVD are selected to impart specific properties to a surface. They generally fall into three categories.
Pure Metals
Pure metals are widely used for their unique properties. They are typically deposited through sputtering or evaporation.
Common examples include:
- Aluminum (Al): For reflective coatings and conductive layers in electronics.
- Titanium (Ti): As a base for hard coatings and for its biocompatibility in medical implants.
- Chromium (Cr): For decorative finishes and as a hard, corrosion-resistant layer.
- Copper (Cu): For conductive tracks in integrated circuits.
- Gold (Au) & Silver (Ag): For electrical contacts and decorative purposes.
Alloys
Alloys are used when a combination of properties is needed that a single metal cannot provide. The alloy is fabricated into a single source target and deposited together.
Ceramics and Compounds
This is where PVD becomes exceptionally powerful. Extremely hard, durable, and temperature-resistant ceramic coatings are a primary application. These are often formed using a technique called reactive PVD.
In this process, a pure metal target (like titanium) is vaporized, but a reactive gas (like nitrogen) is also introduced into the vacuum chamber. The metal and gas react and combine on the substrate's surface to form a new compound.
Common examples include:
- Titanium Nitride (TiN): A very hard, gold-colored ceramic used on cutting tools and drills.
- Chromium Nitride (CrN): Provides superior corrosion resistance and hardness for tools and components.
- Titanium Carbonitride (TiCN): An even harder coating than TiN, used for high-wear applications.
- Aluminum Oxide (Al₂O₃): An electrical insulator used in semiconductor applications.
- Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC): An extremely hard and low-friction coating used on engine parts and blades.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
Choosing a material is not just about the final properties. The process itself introduces practical limitations.
Material and Substrate Compatibility
Not all coating materials adhere well to all substrates. Surface preparation is critical, and sometimes an intermediate "bond layer" of a different material (like titanium) is required to ensure the primary coating sticks properly.
Deposition Temperature
The PVD process generates heat, and the substrate's temperature can impact the final film properties. Some substrates, like plastics, cannot withstand high temperatures, which limits the types of coatings or process parameters that can be used.
Cost vs. Performance
Complex ceramic coatings formed by reactive sputtering are more difficult and expensive to produce than simple evaporated aluminum films. The required performance must justify the cost and complexity of the process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final material choice is always driven by the problem you need to solve.
- If your primary focus is wear resistance: Your best options are hard ceramic coatings like Titanium Nitride (TiN), Titanium Carbonitride (TiCN), or Chromium Nitride (CrN), which are ideal for cutting tools and industrial components.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature performance: You should look at dense, thermally stable ceramic coatings used in aerospace to protect components from extreme heat.
- If your primary focus is optical or electrical properties: The choice will be highly specific, ranging from metals like aluminum for reflectivity to transparent conductive oxides for solar panels and displays.
- If your primary focus is corrosion resistance or a decorative finish: Materials like Chromium (Cr) or Titanium Nitride (TiN) offer both protection and a high-quality aesthetic finish.
Ultimately, the material selection in PVD is a precise engineering decision that defines the capability of the finished product.
Summary Table:
| Material Category | Common Examples | Key Properties | Primary Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pure Metals | Aluminum (Al), Titanium (Ti), Chromium (Cr), Gold (Au) | Conductivity, Reflectivity, Biocompatibility | Electronics, Medical Implants, Decorative Finishes |
| Alloys | Custom metal combinations | Combined properties (e.g., strength & corrosion resistance) | Specialized industrial components |
| Ceramics/Compounds | Titanium Nitride (TiN), Chromium Nitride (CrN), Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) | Extreme Hardness, Wear Resistance, Low Friction | Cutting Tools, Engine Parts, Aerospace Components |
Ready to select the perfect PVD coating material for your application? The right material choice is critical for achieving the desired hardness, corrosion resistance, or electrical performance in your components. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for all your PVD coating development and production needs. Our experts can help you navigate material selection and process parameters to ensure optimal results. Contact our team today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's PVD coating challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Centrifuge Tube Racks
People Also Ask
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What is plasma enhanced? A Guide to Low-Temperature, High-Precision Manufacturing
- What are the advantages of plasma enhanced CVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications



















