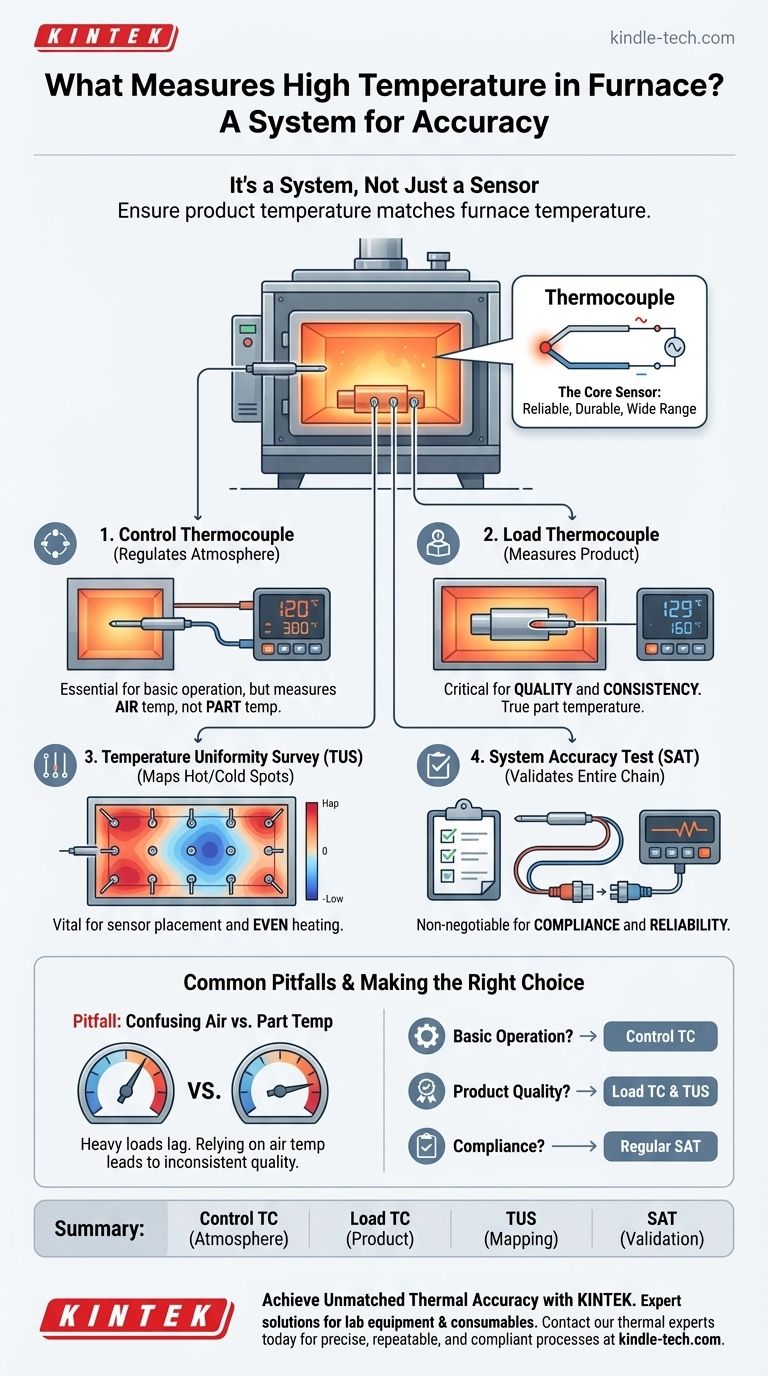
In a high-temperature furnace, the primary device used for measurement is a thermocouple. This robust sensor is chosen for its ability to withstand extreme heat and provide reliable readings essential for process control. However, accurate temperature monitoring is not about a single sensor, but a complete system that includes control thermocouples, load thermocouples, and periodic surveys to ensure the entire furnace operates as expected.
The critical insight is that measuring furnace temperature accurately depends less on a single device and more on a strategic system of measurement. This system ensures that the temperature you control is the same temperature your product actually experiences.
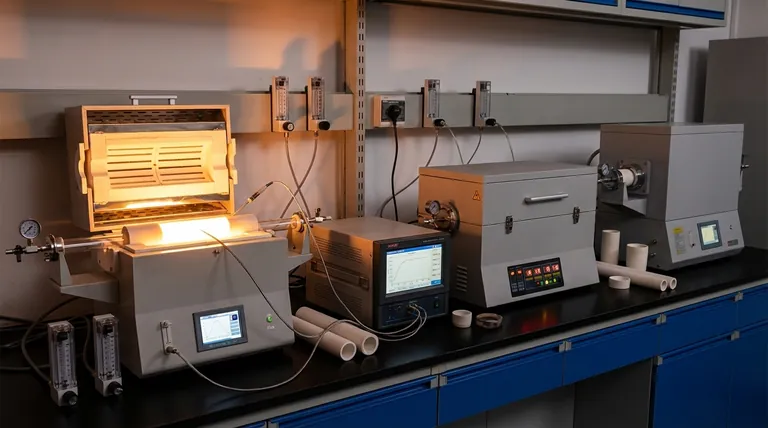

The Core Sensor: Understanding the Thermocouple
What is a Thermocouple?
A thermocouple is a sensor made from two different types of metal wires joined together at one end.
When this junction is heated, it creates a small, predictable voltage. This voltage changes in direct proportion to the temperature, allowing for precise measurement.
Why is it Ideal for Furnaces?
Thermocouples are the standard for industrial furnaces due to their wide temperature range, durability, and cost-effectiveness.
They can measure temperatures far beyond the capabilities of other common thermometers, making them perfect for applications like heat treating, metal casting, and ceramics firing.
Beyond a Single Sensor: A System for Accuracy
Effective furnace management requires more than just one temperature reading. A system of strategically placed thermocouples is used to get a complete picture of the thermal environment.
The Control Thermocouple
This is the primary sensor the furnace's control system uses to regulate its own temperature.
Its job is to tell the furnace when to turn the heat up or down to maintain the desired setpoint. It measures the furnace's internal atmosphere, but not necessarily the temperature of the parts inside.
The Load Thermocouple
A load thermocouple is placed in direct contact with, or embedded within, the actual parts being heated.
This is crucial because the temperature of the part can lag behind the furnace's air temperature. This sensor gives you the true temperature of your product, which is vital for quality control.
Mapping Hot and Cold Spots
No furnace heats perfectly evenly. A Temperature Uniformity Survey (TUS) uses multiple thermocouples placed throughout the chamber to map out the hottest and coldest spots.
This data is essential for understanding where to place parts for consistent results and for calibrating the overall system.
Common Pitfalls in Furnace Temperature Measurement
Achieving true thermal accuracy requires avoiding common oversimplifications. The difference between a reading on a screen and the actual temperature of your product can be significant.
Confusing Air Temperature with Part Temperature
The most common mistake is assuming the control thermocouple's reading reflects the actual temperature of the load.
Heavy or dense loads take longer to heat up. Relying only on the furnace's air temperature can lead to under-processed parts and inconsistent quality.
Neglecting System-Level Checks
A thermocouple might be accurate, but the wires, connectors, and reading instrument can all introduce errors.
A System Accuracy Test (SAT) verifies the entire measurement chain, from the thermocouple tip to the control display. This is often required for industry compliance and ensures the entire system is trustworthy.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your approach to temperature measurement should be dictated by your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is basic furnace operation: The built-in control thermocouple is your key instrument for maintaining a stable setpoint.
- If your primary focus is product quality and consistency: You must use load thermocouples and understand the results of Temperature Uniformity Surveys.
- If your primary focus is meeting compliance standards (e.g., Nadcap, AMS2750): Regular System Accuracy Tests are non-negotiable to validate your entire process.
Ultimately, mastering furnace temperature is about understanding it as a dynamic system, not just a single number on a display.
Summary Table:
| Measurement Component | Primary Function | Key Insight |
|---|---|---|
| Control Thermocouple | Regulates furnace atmosphere temperature. | Essential for basic operation, but may not reflect part temperature. |
| Load Thermocouple | Measures the actual temperature of the parts being heated. | Critical for ensuring product quality and consistency. |
| Temperature Uniformity Survey (TUS) | Maps hot and cold spots within the furnace chamber. | Vital for understanding where to place parts for even heating. |
| System Accuracy Test (SAT) | Validates the entire measurement chain from sensor to display. | Non-negotiable for industry compliance and process reliability. |
Achieve Unmatched Thermal Accuracy in Your Lab
Accurate temperature measurement is the foundation of reliable heat treatment, sintering, and other high-temperature processes. Don't let inconsistent results or compliance issues impact your work.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you select the right thermocouples and design a measurement system tailored to your specific furnace and application, ensuring you get the true temperature of your product—not just the furnace atmosphere.
Contact our thermal experts today to discuss your requirements and ensure your processes are precise, repeatable, and compliant.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between a tubular furnace and a muffle furnace? Choose the Right Tool for Your Application
- Why use a tube furnace? Achieve Superior Temperature Uniformity and Atmosphere Control
- How do you clean a tube furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Cleaning
- Why is an Alumina Ceramic Tube Support Necessary for 1100°C Experiments? Ensure Data Accuracy and Chemical Inertness
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis



















