At its core, a hydraulic press is primarily constructed from high-strength steel. Key structural components like the frame, hydraulic cylinder, and bed are all made from specific steel alloys chosen for their ability to withstand immense operational forces without failing or deforming.
A hydraulic press operates by converting fluid pressure into massive compressive force. The choice of material is not arbitrary; it is a direct response to this fundamental principle, requiring a material with exceptional strength and rigidity, making steel the universal standard.

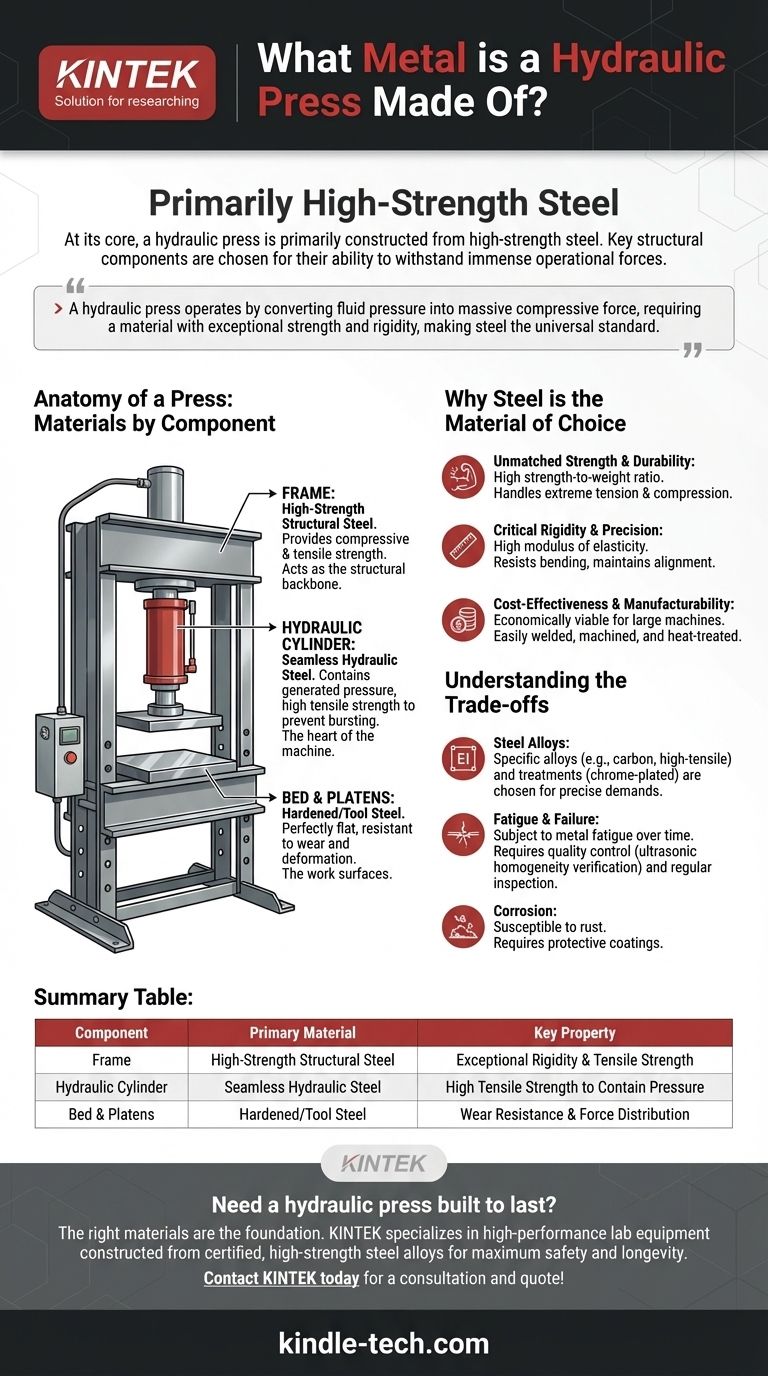
The Anatomy of a Press: Materials by Component
A hydraulic press is not monolithic; it is an assembly of parts, each with a specific function and a material tailored to that role. The selection of high-strength steel is the common thread that ties them together.
The Frame: The Structural Backbone
The frame is the main structure that holds all other components in place and resists the immense forces generated during a press cycle. It must be incredibly rigid to ensure accuracy and prevent catastrophic failure.
For this reason, the frame is almost always fabricated from high-strength structural steel. This material provides the necessary compressive and tensile strength to contain the opposing forces exerted by the hydraulic cylinder and the workpiece.
The Hydraulic Cylinder: The Heart of the Machine
The hydraulic cylinder is where the fluid pressure is generated and contained. It consists of a cylinder barrel and a moving piston or ram that extends to apply force.
This component is typically made from specialized hydraulic steel, often seamless and honed to a smooth internal finish. The steel must have a high tensile strength to prevent the cylinder from bursting under the extreme internal pressure, which can reach thousands of PSI.
The Bed and Platens: The Work Surfaces
The bed, or bolster, is the stationary table that supports the material being pressed. The moving plate attached to the ram is often called the platen. These surfaces must be perfectly flat, parallel, and resistant to wear and deformation.
These components are frequently made from high-quality, hardened sheet steel or tool steel. As noted in quality control procedures, this steel is often verified for internal consistency to ensure it can distribute force evenly without developing weak spots.
Why Steel is the Material of Choice
While other materials exist, steel provides an unparalleled combination of properties that make it uniquely suited for the demands of a hydraulic press. The decision is based on non-negotiable physical requirements.
Unmatched Strength and Durability
Steel's primary advantage is its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio. It can handle extreme tension and compression, which are the defining forces within a press. This ensures the machine can operate safely and reliably for millions of cycles.
Critical Rigidity and Precision
A press's effectiveness depends on its ability to apply force evenly and without deflection. Steel has a high modulus of elasticity, meaning it is extremely stiff and resists bending under load. This rigidity is essential for maintaining the precise alignment between the ram and the bed.
Cost-Effectiveness and Manufacturability
For a machine that is both large and heavy, material cost is a significant factor. Steel provides the required performance at a cost that makes the final product economically viable. It is also easily welded, machined, and heat-treated, simplifying the manufacturing process.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right material is a game of balancing performance with practical limitations. While steel is the ideal choice, not all steel is created equal, and it is not without its own considerations.
The Importance of Steel Alloys
The term "steel" is a broad category. The frame might use a cost-effective carbon steel, while the cylinder requires a high-tensile alloy. Pistons and rams are often chrome-plated to reduce friction and resist corrosion and wear. The specific alloy is chosen to match the precise demands of the component.
The Risk of Fatigue and Failure
Despite its strength, steel is subject to metal fatigue over time, especially under high-cycle applications. This is why quality control, such as ultrasonic homogeneity verification, is performed to detect internal flaws before manufacturing. Regular inspection and maintenance are critical to ensuring the long-term structural integrity of the press.
The Challenge of Corrosion
Unless it is a stainless alloy, steel is susceptible to rust and corrosion. The hydraulic fluid (usually oil) provides internal protection for the cylinder, but the external frame and other components must be painted or otherwise coated to protect them from environmental factors.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Understanding the material composition of a hydraulic press helps you evaluate its quality, safety, and suitability for a specific task.
- If your primary focus is safety and longevity: Confirm that the manufacturer uses certified, high-strength steel for the frame and a seamless hydraulic steel for the cylinder.
- If your primary focus is precision and performance: Look for a press with a highly rigid, heavy-gauge steel frame and platens made from hardened, ground steel to minimize deflection under load.
Ultimately, the construction of a hydraulic press from steel is a direct reflection of its purpose: to safely master and apply immense physical force.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Material | Key Property |
|---|---|---|
| Frame | High-Strength Structural Steel | Exceptional Rigidity & Tensile Strength |
| Hydraulic Cylinder | Seamless Hydraulic Steel | High Tensile Strength to Contain Pressure |
| Bed & Platens | Hardened/Tool Steel | Wear Resistance & Force Distribution |
Need a hydraulic press built to last? The right materials are the foundation of a safe, precise, and durable machine. At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment, including hydraulic presses constructed from certified, high-strength steel alloys for maximum safety and longevity. Let our experts help you select the perfect press for your laboratory's specific needs.
Contact KINTEK today for a consultation and quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
People Also Ask
- What is the pressed powder pellet method? A Guide to Accurate FTIR Sample Preparation
- Are hydraulic presses powered by water? Discover the critical role of hydraulic oil.
- What is the pellet technique in IR? Master Solid Sample Preparation for Clear Spectroscopy
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in the preparation of solid electrolyte pellets? Ensure Data Accuracy
- Why are KBr pellets used in FTIR? Achieve Clear, Accurate Solid Sample Analysis



















