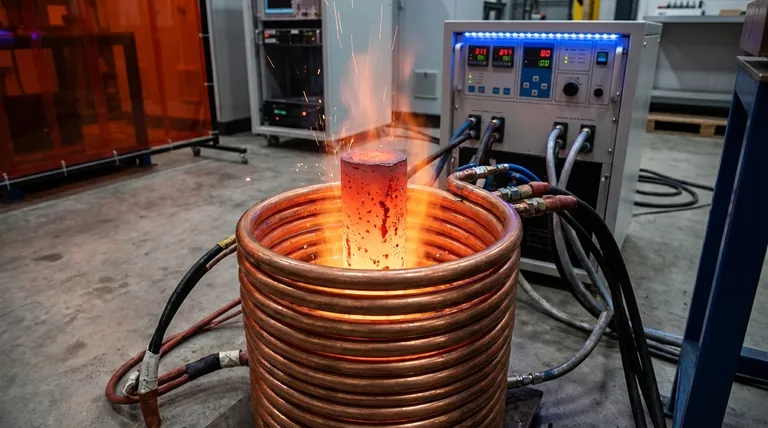
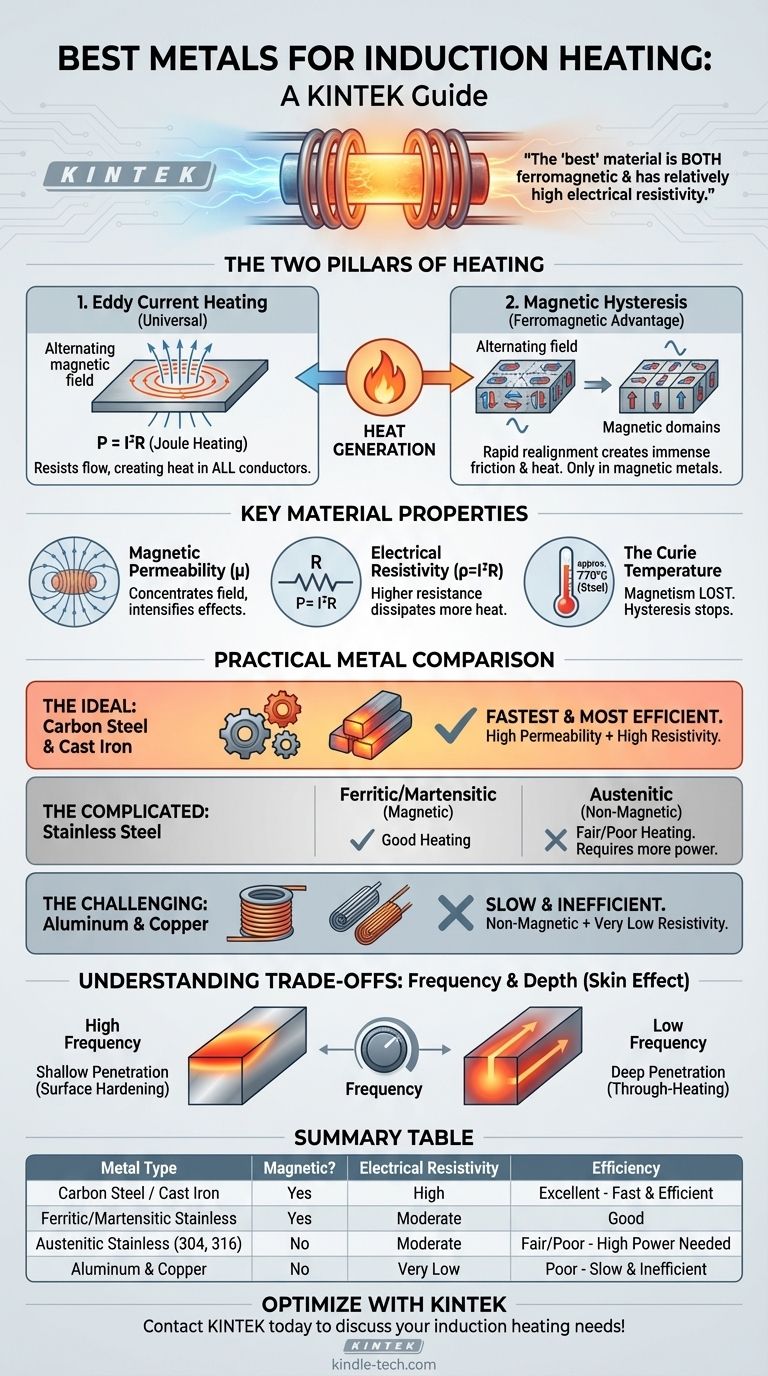
For rapid and efficient induction heating, ferromagnetic metals like carbon steel and cast iron are unquestionably the best choice. Their superiority comes from a unique combination of two powerful heating mechanisms: strong magnetic hysteresis losses and high electrical resistivity, which together generate heat far more effectively than in non-magnetic metals like aluminum or copper.
The "best" material for induction heating is not simply a good electrical conductor; it is one that is both ferromagnetic and has relatively high electrical resistivity. This combination allows the material to generate heat through internal magnetic friction (hysteresis) in addition to standard electrical resistance heating, dramatically increasing the process's speed and efficiency.

The Two Pillars of Induction Heating
To understand why some metals excel, you must first understand the two distinct physical phenomena that generate heat in this process. One is universal to all conductors, while the other is an exclusive advantage of a specific material class.
Eddy Current Heating: The Universal Principle
An induction coil generates a powerful, rapidly alternating magnetic field. When a conductive material is placed within this field, small, circular electrical currents—known as eddy currents—are induced within the metal.
These currents flow against the material's natural electrical resistivity, generating heat through a process called Joule heating (P = I²R). Every conductive metal, from copper to steel, heats up via this mechanism.
Magnetic Hysteresis: The Ferromagnetic Advantage
Ferromagnetic materials (like iron, nickel, cobalt, and their alloys) are composed of tiny magnetic regions called "domains." When the external magnetic field alternates, it forces these domains to rapidly flip their polarity to align with the field.
This rapid, constant realignment creates immense internal friction, which generates a significant amount of heat. This hysteresis heating is a secondary, powerful mechanism that only occurs in magnetic materials, giving them a massive advantage.
Key Material Properties That Determine Performance
Three core physical properties dictate how effectively a material will respond to an induction field. The ideal material possesses a winning combination of all three.
Magnetic Permeability (μ)
Magnetic permeability is a measure of how easily a material can be magnetized. Ferromagnetic materials have very high permeability, meaning they concentrate magnetic field lines within themselves.
This concentration dramatically intensifies the effects of both eddy currents and hysteresis, leading to much faster and more efficient heating. Non-magnetic materials like aluminum have low permeability and do not offer this advantage.
Electrical Resistivity (ρ)
While it may seem counterintuitive, higher electrical resistivity is actually beneficial for induction heating. According to the Joule heating formula (P = I²R), a higher resistance (R) results in more power (P), or heat, being dissipated for a given current (I).
This is why steel, with its relatively high resistivity, heats much more effectively from eddy currents than copper, which has very low resistivity. Copper's low resistance is why it's used for the induction coils themselves—to minimize self-heating.
The Curie Temperature
The magnetic properties of a material are not permanent. When a ferromagnetic material is heated to its Curie temperature (approximately 770°C or 1420°F for steel), it loses its magnetic properties and becomes paramagnetic.
At this point, all hysteresis heating ceases instantly. The material can still be heated by eddy currents alone, but the overall heating rate will drop significantly.
A Practical Comparison of Common Metals
Understanding the principles allows us to rank how different materials perform in a real-world setting.
The Ideal Candidates: Carbon Steel and Cast Iron
These materials are the gold standard for induction heating. They possess both high magnetic permeability for strong hysteresis heating and high electrical resistivity for efficient eddy current heating, resulting in the fastest and most energy-efficient outcomes.
The Complicated Case: Stainless Steel
Not all stainless steel is the same. Ferritic and martensitic stainless steels (like the 400 series) are magnetic and heat very well. However, austenitic stainless steels (like the common 304 or 316 grades) are non-magnetic and are therefore much more difficult to heat, relying only on their moderate resistivity.
The Challenging Candidates: Aluminum and Copper
These materials are both non-magnetic and have extremely low electrical resistivity. This is the worst combination for induction heating. While they can be heated, it requires significantly more power and much higher frequencies to induce sufficient eddy currents, making the process slow and inefficient.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Frequency and Depth
The "best" material choice is also linked to the specific goal of the heating process, which is controlled by the frequency of the induction system.
The Skin Effect
High-frequency alternating currents do not flow uniformly through a conductor. They tend to concentrate on the surface in a phenomenon known as the skin effect. This means the heat generated by induction is also concentrated on the surface.
Reference Depth: Controlling Heat Penetration
The depth to which the currents (and thus the heat) penetrate is known as the reference depth. This depth is determined by the material's properties and, critically, the frequency of the magnetic field.
A low frequency penetrates deeper, making it ideal for through-heating large parts for forging. A high frequency keeps the heat concentrated in a very shallow layer, which is perfect for surface-level applications like case hardening gears.
Selecting the Right Metal for Your Application
Ultimately, the best material is the one that allows you to achieve your specific heating goal with the most efficiency.
- If your primary focus is maximum heating speed and efficiency: Choose a ferromagnetic material with high resistivity, such as a high-carbon steel or cast iron.
- If you must heat a non-magnetic material like aluminum or 300-series stainless steel: You will need an induction system capable of delivering higher power at a higher frequency to compensate.
- If you are case hardening a surface: Select a ferromagnetic steel and use a high-frequency power source to precisely control the shallow heat zone.
- If you are through-heating a large billet for forging: Use a lower frequency to ensure the heat penetrates deep into the core of your chosen steel or iron workpiece.
By understanding these core principles, you can move from simply choosing a material to strategically engineering your desired heating outcome.
Summary Table:
| Metal Type | Magnetic? | Electrical Resistivity | Induction Heating Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel / Cast Iron | Yes (Ferromagnetic) | High | Excellent (Fast & Efficient) |
| Ferritic/Martensitic Stainless Steel | Yes (Ferromagnetic) | Moderate | Good |
| Austenitic Stainless Steel (304, 316) | No (Non-Magnetic) | Moderate | Fair/Poor (Requires High Power/Frequency) |
| Aluminum & Copper | No (Non-Magnetic) | Very Low | Poor (Slow & Inefficient) |
Ready to Optimize Your Induction Heating Process?
Understanding material properties is the first step. The next is having the right equipment to achieve precise, efficient results. At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment, including induction heating systems, tailored to meet the rigorous demands of modern laboratories.
Whether you are working with carbon steel, stainless steel, or challenging non-ferrous metals, our solutions are designed to deliver the control and efficiency you need. Let our experts help you select the perfect system for your specific application.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your induction heating needs and discover how we can enhance your lab's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How does the vacuum environment in a vacuum hot press furnace protect CoCrCuFeNi? Prevent oxidation for high-purity HEAs.
- How does the mechanical pressure from a vacuum hot-pressing furnace facilitate the densification of B4C/Al composites?
- Why is a vacuum hot pressing furnace essential for SiCf/Ti-43Al-9V? Achieving Full Densification and Purity
- Why is the vacuum system of a Vacuum Hot Pressing furnace critical for ODS ferritic stainless steel performance?
- What are the primary functions of a vacuum hot press furnace? Optimize Densification of CNT/Al Matrix Composites



















