While many people associate annealing exclusively with steel, the process is fundamental to a wide range of metals. Any metal that becomes harder and more brittle through physical manipulation (a process called work hardening) can have its original softness and ductility restored through annealing. The most common examples include steel, alloy steels, copper, brass, and aluminum.
The essential question isn't just which metals can be annealed, but why they require it. Annealing is a foundational heat treatment that reverses the effects of work hardening, relieving internal stresses and restoring a metal's ductility to make it easier to form or machine.
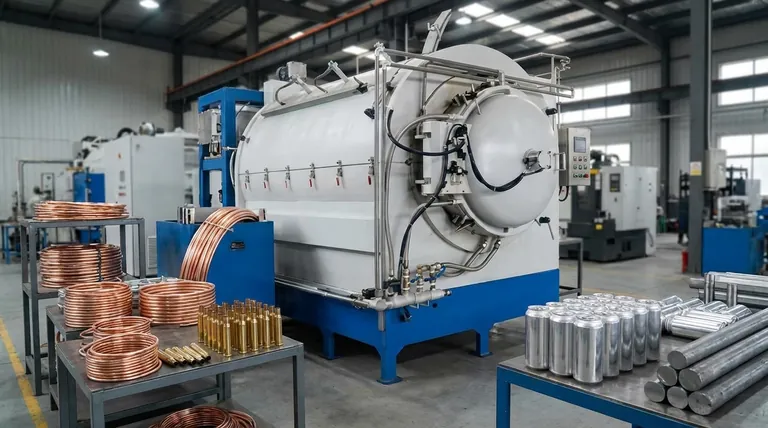

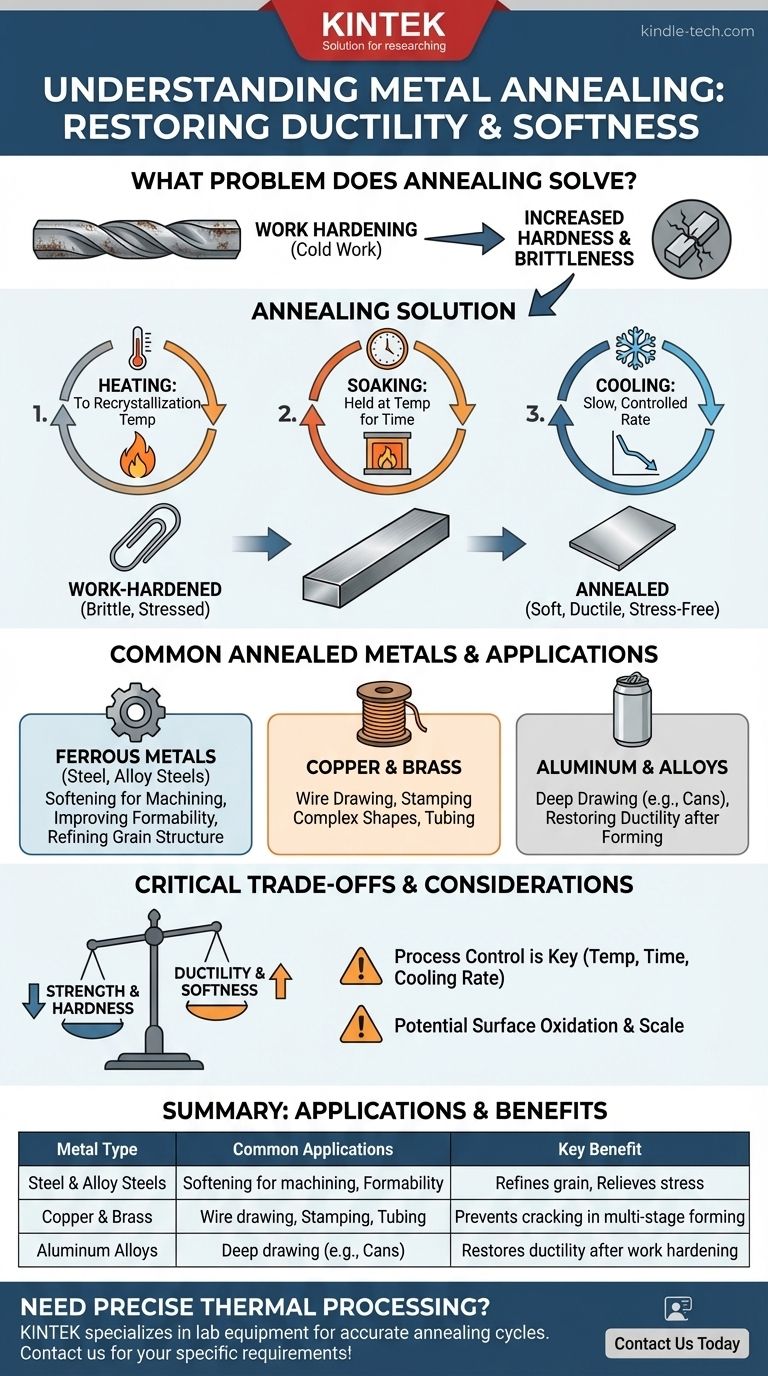
What Problem Does Annealing Solve?
Annealing is not a random process; it is a precise solution to a common problem in metalworking known as work hardening. Understanding this concept is key to understanding the purpose of annealing.
The Concept of Work Hardening
When you bend, roll, hammer, or draw a metal at room temperature, you are performing "cold work." This process distorts the metal's internal crystalline structure, making it harder and stronger.
Think of bending a paperclip back and forth. The first bend is easy, but each subsequent bend in the same spot becomes more difficult. The metal in that spot has been work-hardened.
Brittleness: The Unwanted Side Effect
While increased hardness can be desirable, work hardening also significantly reduces the metal's ductility, or its ability to deform without fracturing.
As a metal becomes more work-hardened, it also becomes more brittle. If you continue to work it, it will eventually crack and fail. This limits how much you can shape a part in one go.
How Annealing Reverses the Process
Annealing is a three-stage heat treatment that effectively resets the metal's internal structure.
- Heating: The metal is heated to a specific recrystallization temperature, which varies for each alloy.
- Soaking: It is held at this temperature for a set amount of time to allow a new, stress-free grain structure to form throughout the material.
- Cooling: It is then cooled at a very slow, controlled rate. This slow cooling is critical to ensure the grains are uniform and the internal stresses are fully relieved.
The result is a metal that is soft, ductile, and ready for further forming operations.
A Closer Look at Common Annealed Metals
While the principle is the same, the specific reasons for annealing vary by metal type.
Ferrous Metals (Steel and Alloy Steels)
This is the most common application. Steels are annealed to soften them for easier machining, to improve formability for stamping, or to refine their grain structure before a final hardening and tempering process. Different types of annealing (e.g., full anneal, process anneal) achieve different levels of softness and ductility.
Copper and Brass
Copper is extremely ductile and is often drawn into wire or tubing. Brass (a copper-zinc alloy) is frequently stamped into complex shapes like ammunition casings. Both metals work-harden quickly, so in-process annealing is essential to allow for multiple, successive forming operations without the material cracking.
Aluminum and its Alloys
Though naturally soft, aluminum also work-hardens when formed. Annealing is critical in manufacturing processes like deep drawing, which is used to create seamless products like aluminum beverage cans from a flat sheet of metal.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Annealing is a powerful tool, but it is not without critical considerations and potential downsides. An objective assessment requires acknowledging these trade-offs.
The Primary Trade-off: Strength for Ductility
The entire purpose of annealing is to make a metal softer and more ductile. This means you are inherently sacrificing hardness and tensile strength. The annealed state is often the weakest state of a metal, a factor that must be accounted for in the engineering design.
Process Control is Non-Negotiable
Annealing is a science. If the temperature is too low, the internal structure won't fully recrystallize. If it's too high or held for too long, the grains can grow too large, making the metal weak and brittle. The cooling rate is equally critical; cooling too quickly can partially re-harden the metal, defeating the purpose.
Surface Oxidation and Scale
Heating metals in the presence of oxygen causes a layer of oxide, or mill scale, to form on the surface. This layer often needs to be removed through chemical pickling or mechanical cleaning, which adds time, cost, and complexity to the overall manufacturing process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Annealing is a specific tool for a specific set of problems. Use it when your material's properties stand in the way of your manufacturing goal.
- If your primary focus is preparing a metal for extensive forming (like deep drawing or stamping): Annealing is essential to restore ductility and prevent cracking between forming stages.
- If your primary focus is improving machinability: A specific type of anneal can soften the material and create a more favorable grain structure, reducing tool wear and improving surface finish.
- If your primary focus is relieving internal stress from welding or machining: A lower-temperature stress relief anneal is often sufficient to prevent distortion and cracking without a significant loss of overall strength.
Ultimately, annealing provides control over a metal's internal structure, allowing you to tailor its properties for the task at hand.
Summary Table:
| Metal Type | Common Annealing Applications | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Steel & Alloy Steels | Softening for machining, improving formability | Refines grain structure, relieves stress |
| Copper & Brass | Wire drawing, stamping, tubing | Prevents cracking during multi-stage forming |
| Aluminum Alloys | Deep drawing (e.g., beverage cans) | Restores ductility after work hardening |
Need precise thermal processing for your lab materials? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables that ensure accurate annealing cycles for metals like steel, copper, and aluminum. Our solutions help you achieve optimal ductility and stress relief for reliable research and production. Contact us today to discuss your laboratory's specific annealing requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the most important factor influencing the strength of the brazed joint? Master Joint Clearance for Maximum Strength
- How is the greatest joint strength obtained in brazing? Master the 3 Keys to Superior Metallurgical Bonds
- What metals can be joined by brazing? Discover the Versatility of Modern Brazing Techniques
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing



















