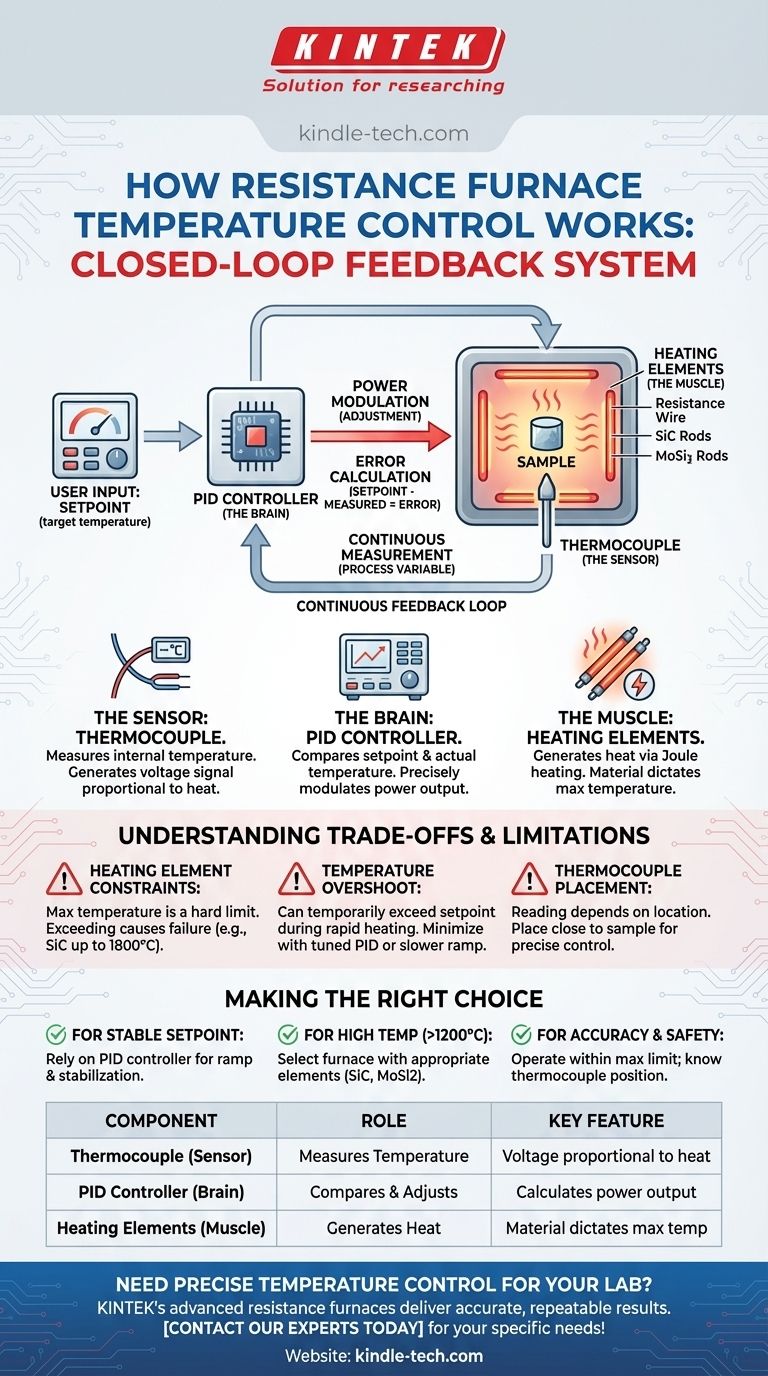
At its core, temperature control in a resistance furnace operates on a closed-loop feedback system. A sensor measures the internal temperature, and a controller adjusts the electrical power supplied to the heating elements to match the user-defined setpoint.
The essential principle is continuous measurement and adjustment. A thermocouple acts as the system's "eyes," constantly reporting the temperature to a controller—the "brain"—which then precisely modulates the power to the heating elements to maintain the desired thermal environment.

The Core Components of Temperature Control
To understand how a resistance furnace maintains a precise temperature, you must first understand its three critical components: the sensor, the controller, and the heating element. These parts work in concert to create a stable system.
The Sensor: The Thermocouple
A thermocouple is the primary sensor used for temperature measurement. It consists of two different types of metal wires joined at one end.
This junction generates a small voltage that changes predictably with temperature. The control system reads this voltage to determine the exact temperature inside the furnace chamber.
The Brain: The Temperature Controller
The thermocouple sends its signal to a temperature controller, which is the brain of the operation. This is often part of a control panel where the user sets the target temperature, or "setpoint."
Modern furnaces typically use a PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controller. This sophisticated algorithm calculates the difference between the setpoint and the actual measured temperature and then determines the precise amount of power to send to the heating elements.
The Muscle: The Heating Elements
The heating elements are the components that actually generate the heat. They are conductors that heat up when an electric current passes through them, a principle known as Joule heating.
The material of the heating element dictates the furnace's maximum operating temperature. Common materials include resistance wire for lower temperatures, silicon carbide (SiC) rods for mid-range, and silicon molybdenum (MoSi2) rods for very high temperatures.
How the Control Loop Works in Practice
The process of temperature regulation is a continuous cycle of measurement, comparison, and correction. This feedback loop ensures the furnace doesn't just get hot, but reaches and holds a specific, stable temperature.
1. Setting the Target (Setpoint)
The process begins when an operator enters the desired temperature into the control panel.
2. Measuring the Reality (Process Variable)
The thermocouple, placed strategically within the furnace, continuously measures the actual internal temperature and reports it back to the controller.
3. Calculating the Difference (Error)
The controller constantly compares the setpoint temperature with the measured temperature from the thermocouple. The difference between these two values is known as the "error."
4. Making the Adjustment (Power Modulation)
Based on the error, the PID controller calculates the necessary change in power output. If the furnace is too cool, it increases power to the heating elements. If it's too hot, it reduces or cuts the power. This cycle repeats many times per second, resulting in highly stable temperature control.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While effective, this control method has inherent constraints and factors that users must consider for safe and accurate operation.
Heating Element Constraints
A furnace's maximum temperature is not a suggestion; it is a hard limit defined by its heating elements. For example, a furnace with standard resistance wire may be limited to 1200°C, while one with silicon molybdenum rods can reach 1800°C.
Exceeding this limit will cause rapid degradation and failure of the heating elements, potentially damaging the furnace itself.
The Risk of Temperature Overshoot
When heating rapidly, a furnace can temporarily exceed the setpoint temperature before stabilizing. This is known as overshoot.
A well-tuned PID controller minimizes overshoot, but it is a factor to consider for highly sensitive materials. Slowing the heating ramp rate can also mitigate this effect.
Thermocouple Placement and Accuracy
The location of the thermocouple matters. A reading taken near the heating element will be different from one taken near the sample being heated. For precise control of the sample's temperature, the thermocouple should be placed as close to it as is safely possible.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Achieving your desired outcome depends on understanding and correctly utilizing the furnace's control system.
- If your primary focus is reaching a stable setpoint: Rely on the furnace's PID controller to manage the ramp rate and stabilization, avoiding manual overrides that can introduce instability.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature work (above 1200°C): Ensure you select a furnace equipped with the appropriate heating elements, such as silicon carbide or silicon molybdenum rods.
- If your primary focus is process accuracy and safety: Always operate within the furnace's maximum rated temperature and understand where the control thermocouple is located relative to your sample.
Mastering temperature control is the key to achieving repeatable and successful results in your thermal processing work.
Summary Table:
| Component | Role | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Thermocouple (Sensor) | Measures internal temperature | Generates voltage proportional to heat |
| PID Controller (Brain) | Compares setpoint to actual temperature | Calculates and adjusts power output |
| Heating Elements (Muscle) | Generates heat through electrical current | Material determines max temperature (e.g., SiC, MoSi2) |
Need precise temperature control for your lab processes? KINTEK's advanced resistance furnaces feature sophisticated PID controllers and durable heating elements to deliver accurate, repeatable results for your thermal applications. Contact our experts today to find the perfect furnace solution for your laboratory's specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- What is the primary advantage of using a tube furnace? Achieve Superior Temperature and Atmosphere Control
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation



















