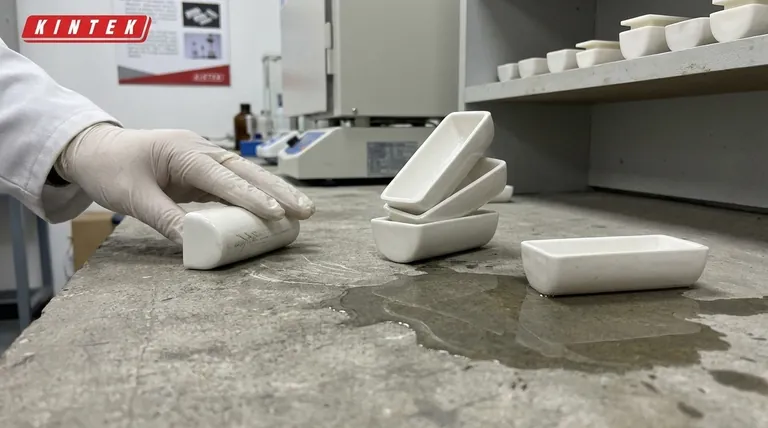
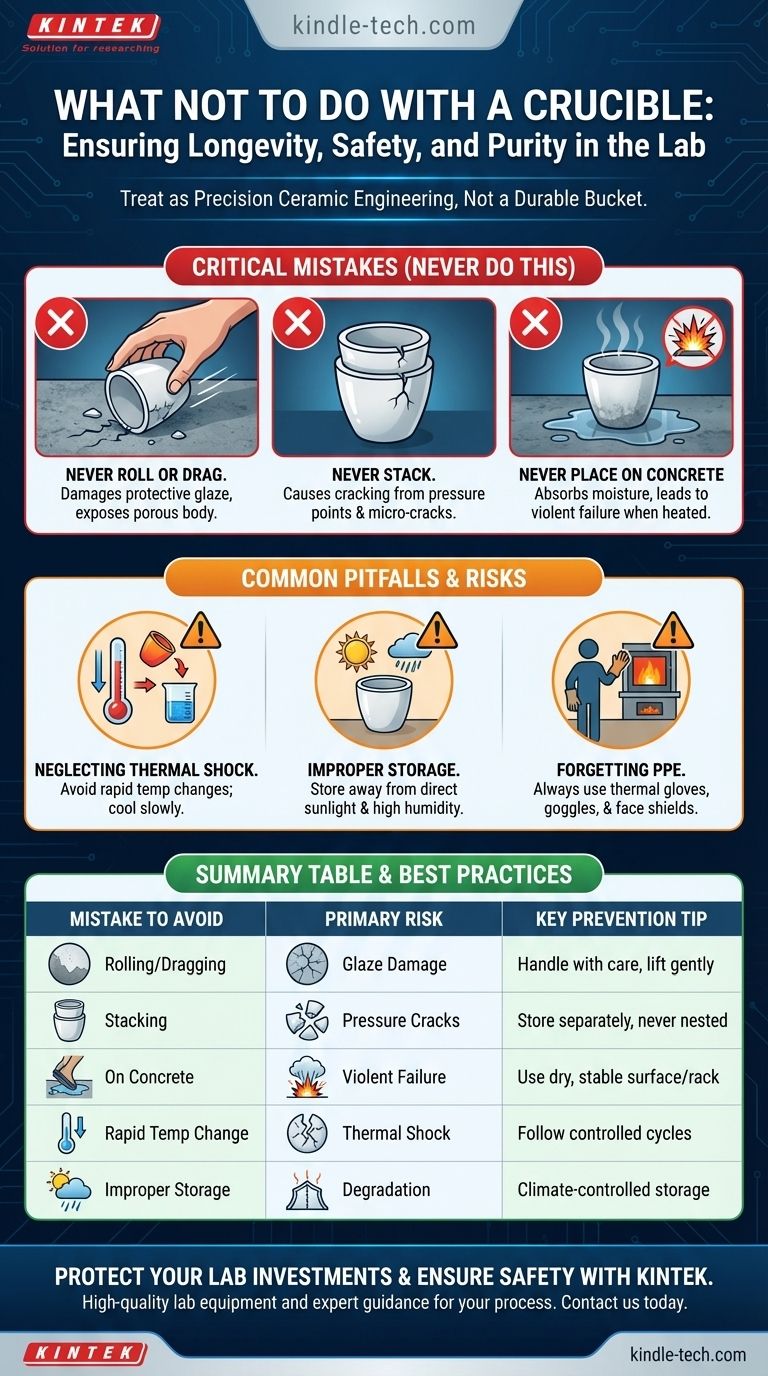
To ensure a crucible's longevity and your safety, there are several critical actions you must avoid. Never roll a crucible, as this damages its protective glaze. Do not stack them inside one another, which leads to cracking from pressure, and never place them directly on a concrete surface, where they can absorb moisture that will cause them to fail violently when heated.
The core principle is to treat a crucible not as a durable bucket, but as a piece of precision ceramic engineering. The rules for its handling are designed to protect its structural integrity from three primary threats: mechanical stress, thermal shock, and chemical contamination.

Understanding the Core Vulnerabilities
A crucible's strength is in its extreme heat and chemical resistance. However, it has specific weaknesses that improper handling can easily exploit, leading to equipment failure, contaminated results, and serious safety hazards.
The Fragility of the Protective Glaze
A crucible's glaze is not for aesthetics; it's a critical barrier. It protects the underlying ceramic from oxidation and chemical attack from the materials it will hold.
Never roll or drag a crucible. This type of handling creates abrasion that chips, scratches, and wears away the protective glaze, exposing the porous body to degradation.
The Danger of Mechanical Stress
Crucibles are designed to withstand immense heat, but they are often brittle and susceptible to cracking from focused physical pressure or impact.
Never stack crucibles inside one another. The pressure points created by stacking, especially during movement or thermal expansion, can easily form micro-cracks that will fail catastrophically once in the furnace.
The Catastrophic Effect of Moisture
Perhaps the most dangerous and commonly overlooked mistake is exposing a crucible to moisture. Porous ceramics act like a sponge.
Never set a crucible directly on concrete. Concrete floors often hold residual moisture, which the crucible will absorb through its base. When that hidden water is heated in a furnace, it turns to steam and expands violently, cracking or even shattering the crucible.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Beyond the most critical handling errors, several other common mistakes can shorten a crucible's life, compromise your work, and create unsafe conditions.
Neglecting Thermal Shock
Rapid temperature change is a primary enemy of ceramics. It creates immense internal stress as different parts of the crucible expand or contract at different rates.
Do not move a hot crucible into a cool environment too quickly. For example, after a burn-off, a crucible should cool to below 200℃ before being moved to a desiccator to prevent fractures and other process-related issues.
Improper Storage Conditions
A crucible's integrity can be compromised even when it's not in use. Long-term environmental exposure can slowly degrade its structure.
Avoid storing crucibles in direct sunlight or high humidity. These conditions can alter the material's properties over time, weakening it before it ever enters a furnace.
Forgetting Personal Safety
The crucible is a tool for containing extreme hazards. A failure to use proper personal protective equipment (PPE) is a critical error.
Never handle crucibles during high-temperature operations without proper protection. This includes thermal gloves, safety goggles, and face shields, especially when working with molten materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your specific goal determines which precautions are most critical. Following these guidelines will prevent costly failures and ensure safe, reliable results.
- If your primary focus is safety: Never introduce moisture by placing a crucible on concrete and always use full PPE when it is hot or contains molten material.
- If your primary focus is material purity: Never use a crucible for different alloys without meticulous cleaning to prevent cross-contamination, and protect the glaze from damage.
- If your primary focus is maximizing equipment lifespan: Always avoid mechanical stress (no rolling or stacking) and prevent thermal shock by managing your heating and cooling cycles.
Ultimately, treating your crucible as the precision instrument it is will ensure it performs its function safely and effectively every time.
Summary Table:
| Mistake to Avoid | Primary Risk | Key Prevention Tip |
|---|---|---|
| Rolling or Dragging | Damages protective glaze | Handle with care, lift and place gently |
| Stacking Crucibles | Causes cracking from pressure | Store separately, never nested |
| Placing on Concrete | Moisture absorption leads to violent failure | Always use a dry, stable surface or rack |
| Rapid Temperature Changes | Thermal shock and fractures | Follow controlled heating/cooling cycles |
| Improper Storage | Long-term degradation | Store in a dry, temperature-controlled environment |
Protect your lab investments and ensure operator safety with the right crucible handling practices.
Choosing the correct crucible and using it properly is fundamental to successful and safe laboratory operations. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including a wide range of crucibles designed for specific applications and materials. Our experts can help you select the perfect crucible for your process and provide guidance on best practices for handling and maintenance.
Don't risk equipment failure or safety hazards. Contact our team today to discuss your laboratory needs and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your efficiency, purity, and safety.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- How do graphite crucibles assist in the annealing process of glass melts? Enhance Structural Integrity Today
- What are the advantages of using a graphite crucible? Maximize Purity and Thermal Stability in Magnesium Reduction
- Why are high-alumina crucibles selected for Cs-zeolite heat treatment? Ensure Sample Purity at 1100 °C
- How to maintain a crucible? Prevent Thermal Shock and Ensure Longevity
- What crucible is best for melting steel? Find the Right Crucible for Your Steel Melting Needs
- What is the primary function of nickel crucibles in Li2OHCl synthesis? Ensure Purity & Chemical Inertness
- What can you do with a crucible? Unlock High-Temperature Melting for Metals, Glass, and More
- Why are alumina (corundum) crucibles used in static corrosion tests? Ensure Data Integrity and Thermal Stability



















