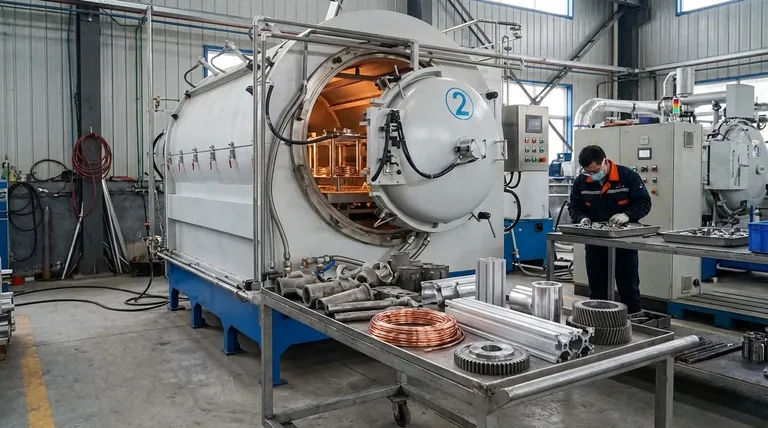
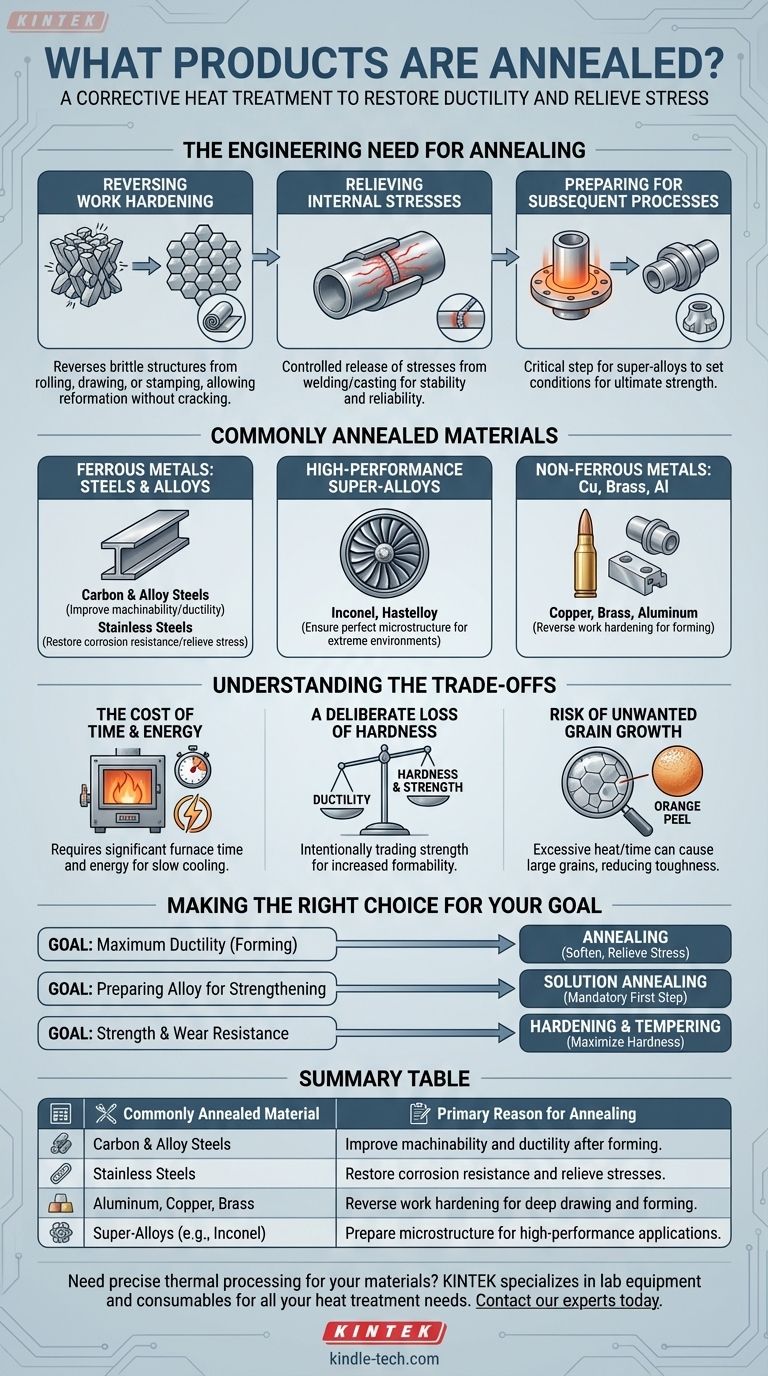
At its core, annealing is a corrective heat treatment applied to a wide range of metals that have been hardened or stressed during manufacturing. The most commonly annealed materials include various steels (carbon, alloy, and stainless), super-alloys like Inconel, and non-ferrous metals such as aluminum, brass, and copper. The process is used to restore ductility and relieve internal stresses, making the material easier to work with.
The key takeaway is that annealing isn't defined by the final product, but by the material's condition. It's a fundamental process used whenever a metal becomes too brittle from manufacturing, requiring a "reset" to a softer, more workable state.

The Engineering Need for Annealing
Annealing is not an arbitrary step; it is a precise solution to problems created during metal fabrication. When metals are bent, stretched, or machined, their internal crystalline structure changes, leading to increased hardness and brittleness.
Reversing Work Hardening
Many manufacturing processes, such as rolling, drawing, or stamping, cause work hardening. This makes the metal stronger but also significantly less ductile.
Annealing reverses this by heating the metal, allowing the crystal structure to reform into a more uniform and less stressed state. This makes subsequent forming operations possible without the risk of cracking.
Relieving Internal Stresses
Processes like welding or casting can introduce significant internal stresses within a material. These hidden stresses can lead to premature failure or dimensional instability over time.
By heating the material uniformly and allowing it to cool slowly, annealing provides a controlled way to release these stresses, resulting in a more stable and reliable component.
Preparing for Subsequent Processes
For certain high-performance alloys, annealing is a critical preparatory step.
For example, precipitation hardening steels (like 17-4 or 15-5 stainless) and super-alloys are often "solution annealed" to put them in the correct condition for a final age hardening process, which gives them their ultimate strength.
A Look at Commonly Annealed Materials
While the principle is universal, the application of annealing varies based on the material's properties and intended use.
Ferrous Metals: Steels and Alloys
Steel and its alloys are the most frequently annealed materials. The process is essential for improving the machinability of high-carbon steels or making alloy steel ductile enough for complex forming operations.
For stainless steels, annealing also plays a crucial role in restoring maximum corrosion resistance, which can be compromised during fabrication.
High-Performance Super-Alloys
Materials like Inconel and Hastelloy are used in extreme environments where material integrity is non-negotiable.
These alloys undergo precise annealing cycles, often in a vacuum furnace, to ensure a perfect microstructure free from defects before they are put into service in aerospace or chemical processing applications.
Non-Ferrous Metals: Copper, Brass, and Aluminum
Copper and brass are known for work-hardening very quickly. In processes like deep drawing a brass cartridge case, the material must be annealed between each drawing stage to prevent it from becoming too brittle and fracturing.
Aluminum is also frequently annealed to soften it for forming operations, especially for producing parts with complex shapes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Annealing is a powerful tool, but it involves clear and intentional compromises that engineers must consider.
The Cost of Time and Energy
The annealing process is defined by its slow cooling rate. This requires significant furnace time and energy consumption, adding both time and cost to the manufacturing cycle.
A Deliberate Loss of Hardness
The primary goal of annealing is to increase ductility, which comes at the direct expense of hardness and tensile strength. You are intentionally trading strength for formability.
This is a critical distinction from other heat treatments like hardening and tempering, where the goal is to maximize strength.
Risk of Unwanted Grain Growth
The final stage of annealing involves grain growth, where the reformed crystals in the metal expand. If the temperature is too high or the holding time is too long, these grains can become excessively large.
Large grains can reduce the material's toughness and lead to a poor surface finish after forming, a condition known as "orange peel." Proper control is essential to avoid this.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a heat treatment is about matching the process to the desired outcome. Annealing is just one tool among many.
- If your primary focus is maximum ductility for forming: Annealing is the ideal choice to soften the material, relieve stress, and prevent cracking during fabrication.
- If your primary focus is preparing an alloy for final strengthening: Solution annealing is the mandatory first step for precipitation hardening materials to ensure a successful final heat treatment.
- If your primary focus is strength and wear resistance: Hardening and tempering, not annealing, are the processes designed to maximize a material's hardness.
Ultimately, annealing is the strategic decision to prioritize a material’s workability and structural integrity over its raw strength.
Summary Table:
| Commonly Annealed Material | Primary Reason for Annealing |
|---|---|
| Carbon & Alloy Steels | Improve machinability and ductility after forming. |
| Stainless Steels | Restore corrosion resistance and relieve stresses. |
| Aluminum, Copper, Brass | Reverse work hardening for deep drawing and forming. |
| Super-Alloys (e.g., Inconel) | Prepare microstructure for high-performance applications. |
Need precise thermal processing for your materials? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for all your heat treatment needs. Whether you're working with hardened steel or high-performance alloys, our solutions ensure optimal material properties. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's efficiency and success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the factors that affect the strength of a brazed joint? Master the 4 Keys to a Perfect Bond
- What is oxidation in brazing? How to prevent it for strong, durable joints
- What are the advantages of brazing over braze welding? Achieve Stronger, Cleaner, and Repeatable Joints
- What are vacuum furnaces used for? Unlock Ultimate Material Purity and Performance
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing



















