Sintering is used to create a vast range of high-strength, precision components, from automotive gears and self-lubricating bearings to ceramic dental crowns and industrial cutting tools. This manufacturing process uniquely transforms powdered materials into a solid, dense part by applying heat below the material's melting point, making it ideal for creating complex shapes from materials with extremely high melting temperatures.
Sintering is not defined by the products it makes, but by the properties it imparts. It is the go-to method for mass-producing strong, dimensionally accurate components from materials that are otherwise difficult to shape, melt, or machine.

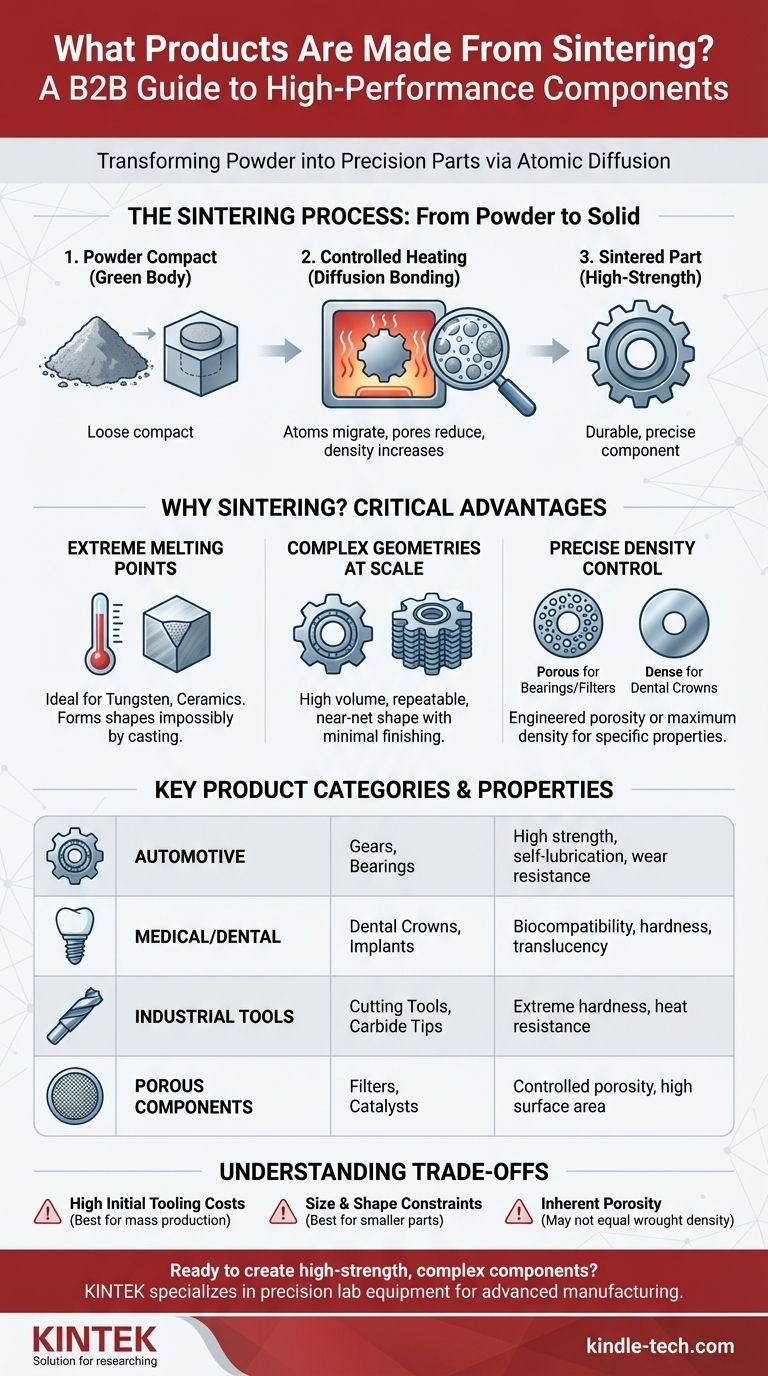
What is Sintering? A Focus on Transformation
Sintering is a thermal process that turns a compressed powder compact, often called a "green body," into a solid, coherent mass. It does so without melting the material, relying instead on atomic diffusion.
The Core Mechanism: From Powder to Solid
A part begins as a loose collection of powder particles, which are compressed into a desired shape. This green body is then heated in a controlled-atmosphere furnace to a temperature below its melting point.
At these high temperatures, the particles begin to fuse. Atoms migrate across the boundaries of the particles, a process known as diffusion bonding. This pulls the particle centers closer together.
The result is a significant reduction in the porous spaces between particles. This process dramatically increases the material's density, strength, and durability.
Controlling the Final Properties
The two most critical factors in the sintering process are sintering temperature and time. The temperature must be controlled with extreme precision, often within a range of ±3°C to 5°C.
By carefully managing these variables, manufacturers can achieve specific material properties, such as enhanced strength, electrical conductivity, transparency, or thermal conductivity.
Why Sintering is a Critical Manufacturing Process
Sintering is chosen when other manufacturing methods are impractical or cannot deliver the required properties. Its advantages are directly linked to the types of products it creates.
For Materials with Extreme Melting Points
Many high-performance materials, like tungsten and ceramics, have melting points so high that casting them is infeasible or impossible.
Since sintering operates below the melting point, it is the ideal method for forming these materials into usable, high-strength parts like cutting tool tips or filaments.
For Complex Geometries at Scale
Sintering excels at producing parts with non-machinable or intricate geometries in large volumes. The initial compacted powder takes the shape of a precise mold or die.
This makes the process highly repeatable and accurate, delivering great cosmetic results without needing secondary finishing processes. This is why it's used for small, complex gears and structural components.
For Precise Control Over Density
While the primary goal is often to eliminate pores, sintering also allows for intentional control over porosity.
This is critical for products like self-lubricating bearings, which are designed to hold oil in their porous structure, or for filters and catalysts that require high surface area and gas absorbency. Conversely, for a product like a zirconia dental crown, the goal is to achieve maximum density for extreme hardness and translucency.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, sintering is not the right solution for every application. Understanding its limitations is key to knowing when to use it.
High Initial Tooling Costs
Creating the precision dies used to form the initial powder compact can be expensive. This makes sintering most cost-effective for large production runs where the tooling cost can be amortized over many thousands of parts.
Size and Shape Constraints
Sintering is generally best suited for producing relatively small components. Large or very thick parts can be difficult to heat uniformly, leading to inconsistent density and internal stresses.
Inherent Porosity
Although sintering significantly reduces porosity, completely eliminating it can be challenging. For applications demanding absolute, flawless density found in forged or wrought materials, residual micro-porosity could be a limiting factor.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your decision to use sintering should be based on material properties, part complexity, and production volume.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective mass production: Sintering is an excellent choice for creating thousands of identical, complex parts with high dimensional accuracy.
- If your primary focus is high-performance materials: Choose sintering when working with ceramics, refractory metals, or carbides that cannot be processed by melting.
- If your primary focus is specialized functionality: Use sintering to engineer controlled porosity for applications like filtration, fluid storage, or acoustic damping.
Sintering empowers engineers to create high-performance components that would otherwise be impossible or prohibitively expensive to manufacture.
Summary Table:
| Product Category | Key Examples | Key Properties Achieved |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Gears, bearings | High strength, wear resistance, self-lubrication |
| Medical/Dental | Dental crowns, implants | Biocompatibility, high density, hardness, translucency |
| Industrial Tools | Cutting tools, carbide tips | Extreme hardness, heat resistance |
| Porous Components | Filters, catalysts | Controlled porosity, high surface area |
Ready to create high-strength, complex components for your project?
KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables for advanced manufacturing processes like sintering. Whether you are developing new materials or scaling production, our expertise and reliable equipment can help you achieve superior results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's sintering and material science needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
People Also Ask
- What are the main components of an industrial furnace? Explore Essential Elements for Precision Heating
- Why Use Ultra-High Vacuum Furnaces for LLZO? Ensure Chemical Stability & Interface Integrity in Solid Electrolytes
- Why is precise temperature control in a sintering furnace critical for NASICON electrolytes? Ensure Material Purity
- How does an atmosphere furnace ensure quality in BN nanotube synthesis? Precision Control for Cup-Stacked Structures
- Why is a high-precision atmosphere furnace essential for high-nickel cathode sintering? Unlock Battery Performance



















