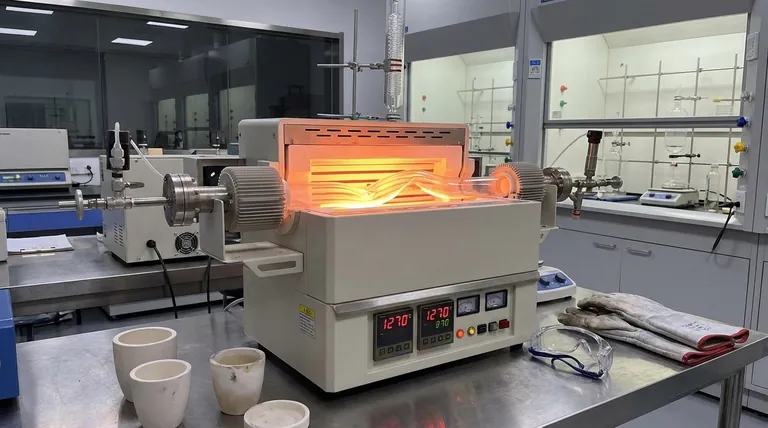
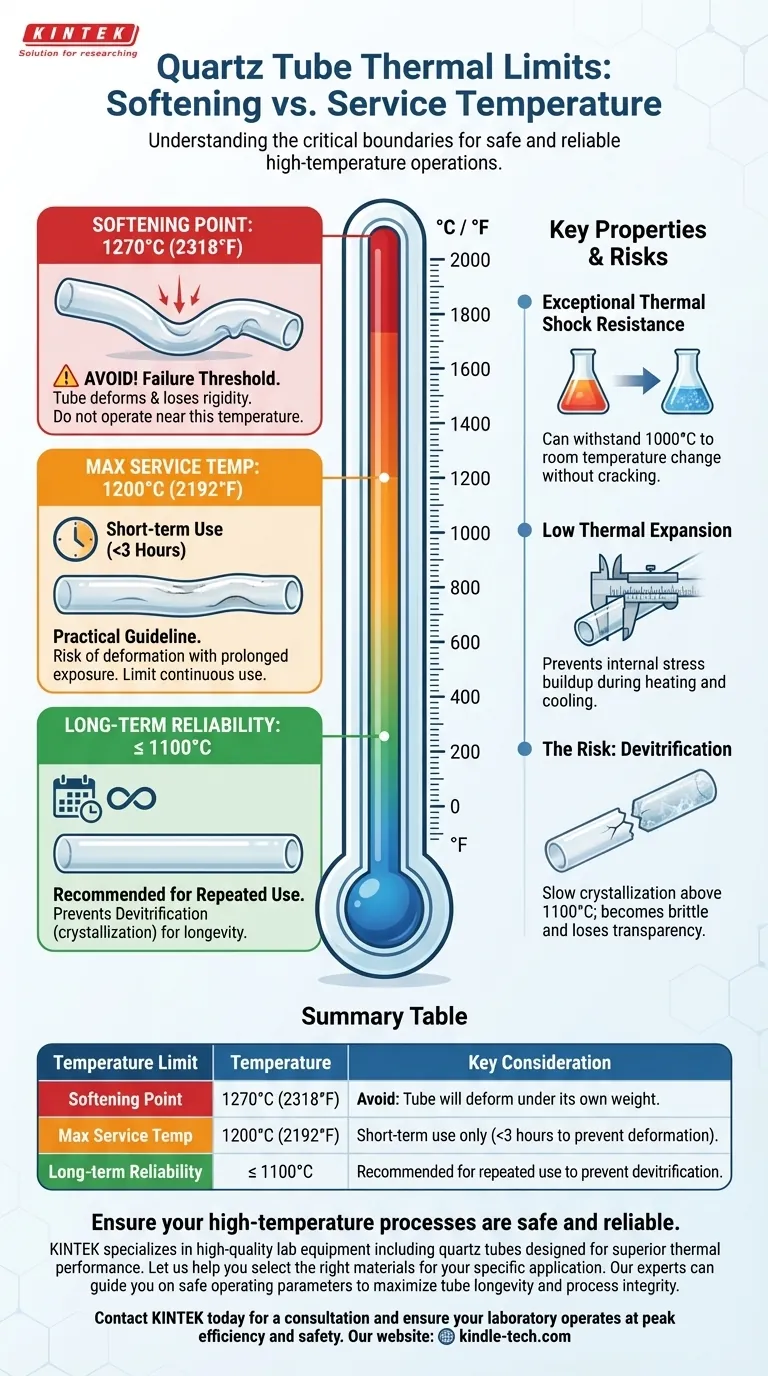
The softening point of a standard quartz tube is 1270°C (2318°F). However, this number represents a failure threshold, not a safe operating temperature. For practical applications, you must operate at a lower temperature to prevent permanent damage and ensure the tube's structural integrity.
Understanding the difference between a material's absolute softening point and its practical service temperature is critical. While a quartz tube begins to soften at 1270°C, its reliable, short-term service limit is closer to 1200°C, and even that has strict time constraints.

Understanding Thermal Limits: Softening vs. Service
When working with high-temperature materials like quartz, the datasheet numbers represent distinct physical boundaries. Confusing them can lead to equipment failure.
The Softening Point: A Limit to Avoid
The official softening point of 1270°C is the temperature at which the quartz (fused silica) begins to lose its rigidity and will deform under its own weight. Operating at or near this temperature will cause the tube to sag, bend, or warp.
The Maximum Service Temperature: A Practical Guideline
For reliable use, the maximum recommended service temperature is significantly lower. For quartz tubing, this is generally considered to be 1200°C (2192°F).
The Critical Factor of Time
Even at the service temperature, time is a crucial variable. Prolonged exposure to high heat can cause damage. As a rule, continuous use at 1200°C should not exceed three hours to prevent the risk of deformation.
Key Properties and Risks
A material's performance is defined by more than just its melting point. For quartz, its exceptional thermal stability is a balance of several factors.
Exceptional Thermal Shock Resistance
Quartz tubes can withstand extreme and rapid temperature changes. They can be taken from a temperature of 1000°C and exposed to room temperature air without cracking.
The Reason: Low Thermal Expansion
This resistance to thermal shock is due to quartz's extremely low coefficient of thermal expansion. It does not significantly expand or contract when heated or cooled, which prevents internal stresses from building up and causing fractures.
The Risk: Devitrification
When held at high temperatures for extended periods (especially above 1100°C), quartz can undergo a process called devitrification. The amorphous glass structure slowly crystallizes, becoming brittle and losing its transparency. This is another reason long-duration exposure near the service limit is ill-advised.
Guidelines for Safe Operation
To select the right parameters for your work, consider your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is a short, high-heat process: You can operate near 1200°C, but you must strictly limit the exposure time to less than three hours to avoid deformation.
- If your primary focus is long-term reliability and repeated use: Operate at a more conservative temperature (e.g., 1100°C or lower) to ensure the tube's longevity and prevent devitrification.
- If your primary focus is rapid heating and cooling cycles: Quartz is an ideal material due to its superb thermal shock resistance, but always respect the peak service temperature of 1200°C.
Knowing the operational limits, not just the material's failure point, is the key to successful and safe high-temperature work.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Limit | Temperature | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Softening Point | 1270°C (2318°F) | Avoid: Tube will deform under its own weight. |
| Max Service Temp | 1200°C (2192°F) | Short-term use only (<3 hours to prevent deformation). |
| Long-term Reliability | ≤ 1100°C | Recommended for repeated use to prevent devitrification. |
Ensure your high-temperature processes are safe and reliable.
Understanding the precise thermal limits of your quartz tubes is critical for protecting your experiments and equipment. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including quartz tubes designed for superior thermal performance.
Let us help you select the right materials for your specific application. Our experts can guide you on safe operating parameters to maximize tube longevity and process integrity.
Contact KINTEK today for a consultation and ensure your laboratory operates at peak efficiency and safety.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How does the vacuum environment impact sintering of diamond-copper composites? Protect Against Thermal Damage
- What is the primary purpose of using vacuum-sealed quartz tubes? Ensure High-Purity Battery Material Synthesis
- What is the role of high-purity quartz tubes in vacuum chromization? Secure High-Performance Superalloy Coating
- What environmental conditions does a vacuum tube furnace provide for copper sintering? Ensure High-Purity Results
- What is the role of a HPHT tube furnace in HTGR simulation? Achieve Precise Nuclear Environment Replications



















