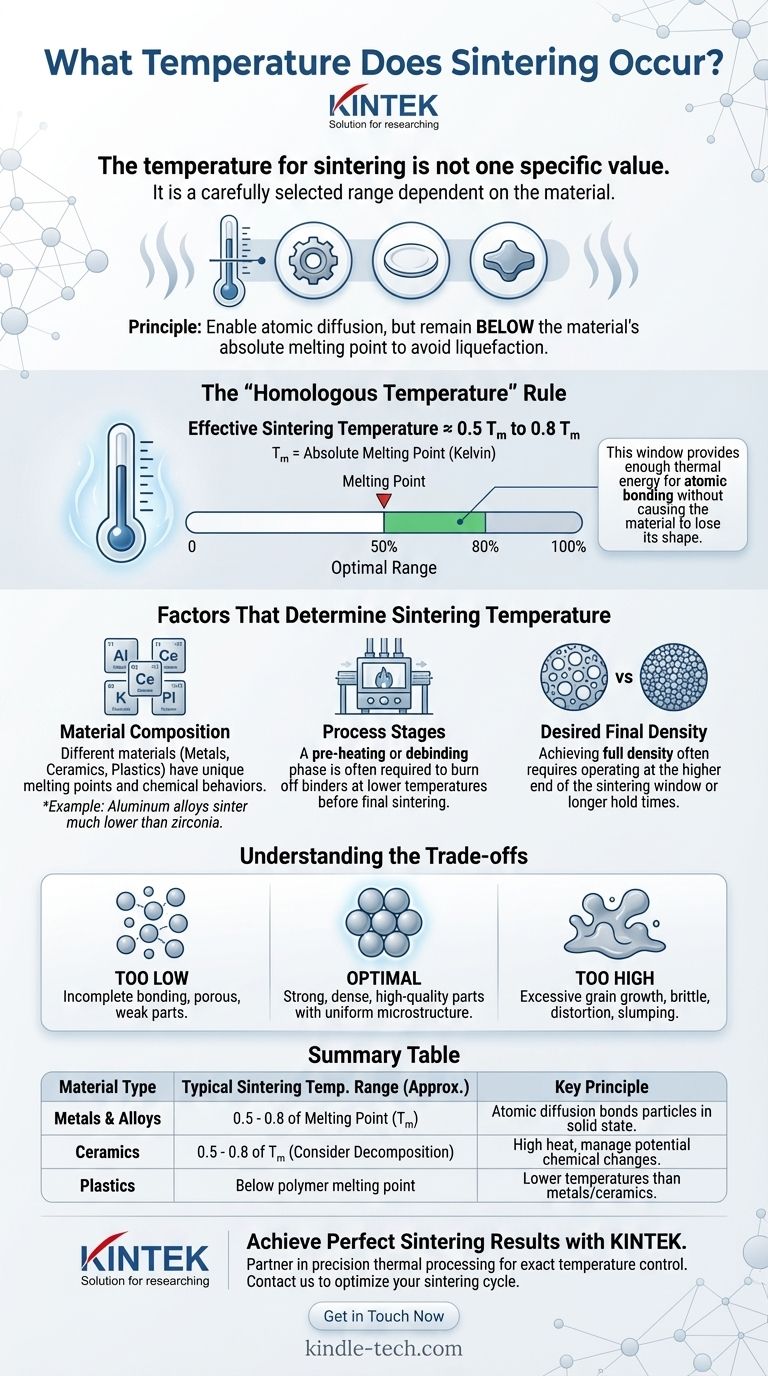
The temperature for sintering is not one specific value but is a carefully selected range that is entirely dependent on the material being processed. The core principle is that the temperature must be high enough to enable atoms to diffuse across particle boundaries, fusing them together, but must remain below the material's absolute melting point to prevent it from turning into a liquid. For example, some processes are completed at 630°C, while others involve reactions that begin around 720°C.
The ideal sintering temperature is a function of the material's melting point, typically falling within the range of 50% to 80% of its absolute melting temperature. This provides enough thermal energy for atomic bonding without causing the material to lose its shape.

The Principle: Diffusion Without Melting
Sintering is a thermal process that transforms a powder compact into a dense, solid mass. The temperature is the most critical variable in this transformation, and its control is a delicate balance.
Activating Atomic Diffusion
Heat gives the atoms within the powder particles the energy they need to move. At the right sintering temperature, atoms migrate across the boundaries where particles touch, forming strong metallic or chemical bonds.
This process, known as atomic diffusion, is what closes the pores between particles and causes the material to densify and strengthen.
Staying Below the Melting Point
If the temperature reaches or exceeds the material's melting point, the part will simply liquefy. This would destroy the component's intended shape and internal microstructure.
The goal of sintering is to create a solid-state bond, fusing particles together while they remain substantially solid.
The "Homologous Temperature" Rule
As a guiding principle in materials science, the effective sintering temperature is often expressed as a fraction of the material's absolute melting point (T_m), measured in Kelvin.
Most materials sinter effectively in a range of 0.5 T_m to 0.8 T_m. This "homologous temperature" provides a reliable starting point for identifying the correct processing window for any given material.
Factors That Determine Sintering Temperature
There is no universal sintering temperature because the ideal range is influenced by several factors unique to the material and the desired outcome.
Material Composition
Metals, plastics, and ceramics all have vastly different melting points and chemical behaviors. A sintering process for an aluminum alloy will occur at a much lower temperature than one for a technical ceramic like zirconia.
Furthermore, some materials undergo chemical changes. For example, calcium carbonate (CaCO₃) begins to decompose at around 720°C, a factor that must be managed during its sintering cycle.
Process Stages
A complete thermal cycle involves more than just the peak sintering temperature. A pre-heating or debinding phase is often required to burn off binders used to shape the part.
This debinding stage typically occurs at a lower temperature, often finishing around 600°C, before the furnace ramps up to the final sintering temperature.
Desired Final Density
The target density of the final part also influences the temperature. Achieving full density, where almost all porosity is eliminated, often requires temperatures at the higher end of the sintering window or longer hold times.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a temperature is about balancing competing effects. The ideal temperature is often a narrow window, and deviations can compromise the final product.
Temperature Too Low
If the temperature is insufficient, atomic diffusion will be too slow. This results in an incomplete bond between particles, leaving the final part porous, weak, and with poor mechanical properties.
Temperature Too High
Exceeding the optimal temperature, even while staying below the melting point, is also detrimental. It can cause excessive grain growth, which can make the material brittle. In a worst-case scenario, it can lead to distortion, slumping, or partial melting.
Time as a Critical Variable
Sintering is a function of both temperature and time. A slightly lower temperature can sometimes achieve the same densification as a higher temperature if the part is held at that temperature for a longer duration. This interplay is critical for process optimization.
Finding the Right Temperature for Your Goal
To determine the correct sintering temperature, you must first understand your material and your objective. Use established principles as your guide.
- If your primary focus is processing a specific metal or alloy: Start by finding its absolute melting point (T_m) and use the 0.5 - 0.8 T_m range as your initial guide for process development.
- If your primary focus is working with ceramics or compounds: Research not only the melting point but also any potential decomposition temperatures that could affect the material during the cycle.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum part density and strength: Plan to operate at the higher end of the material's sintering window, which demands precise temperature control to avoid overheating.
Ultimately, mastering sintering is about controlling a precise thermal profile, not just reaching a single number.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Typical Sintering Temperature Range (Approx.) | Key Principle |
|---|---|---|
| Metals & Alloys | 0.5 - 0.8 of Melting Point (T_m) | Atomic diffusion bonds particles in solid state. |
| Ceramics | 0.5 - 0.8 of T_m, but must consider decomposition. | High heat required, but chemical changes must be managed. |
| Plastics | Below polymer melting point. | Lower temperatures than metals/ceramics. |
Achieve Perfect Sintering Results with KINTEK
Mastering the precise thermal profile for your specific material is the key to achieving strong, dense, and high-quality sintered parts. The wrong temperature can lead to weak, porous components or distorted, melted products.
KINTEK is your partner in precision thermal processing. We specialize in supplying advanced laboratory furnaces and consumables designed for exact temperature control and uniform heating, ensuring your sintering processes are repeatable and successful.
Let us help you optimize your sintering cycle. Our experts understand the nuances of material science and can provide the equipment and support you need to push the boundaries of what's possible.
Contact us today to discuss your application and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your lab's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of rotary furnace? Maximize Uniformity & Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What is the process of zirconium production? From Ore to High-Performance Metal & Ceramic
- What reaction conditions do high-temperature tube furnaces provide for biochar reduction? Optimize Ore Processing
- What is the primary function of an industrial rotary tube furnace? Master Tungsten Powder Hydrogen Reduction
- What are the advantages of a rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Homogeneity & Efficiency for Powders & Granules



















