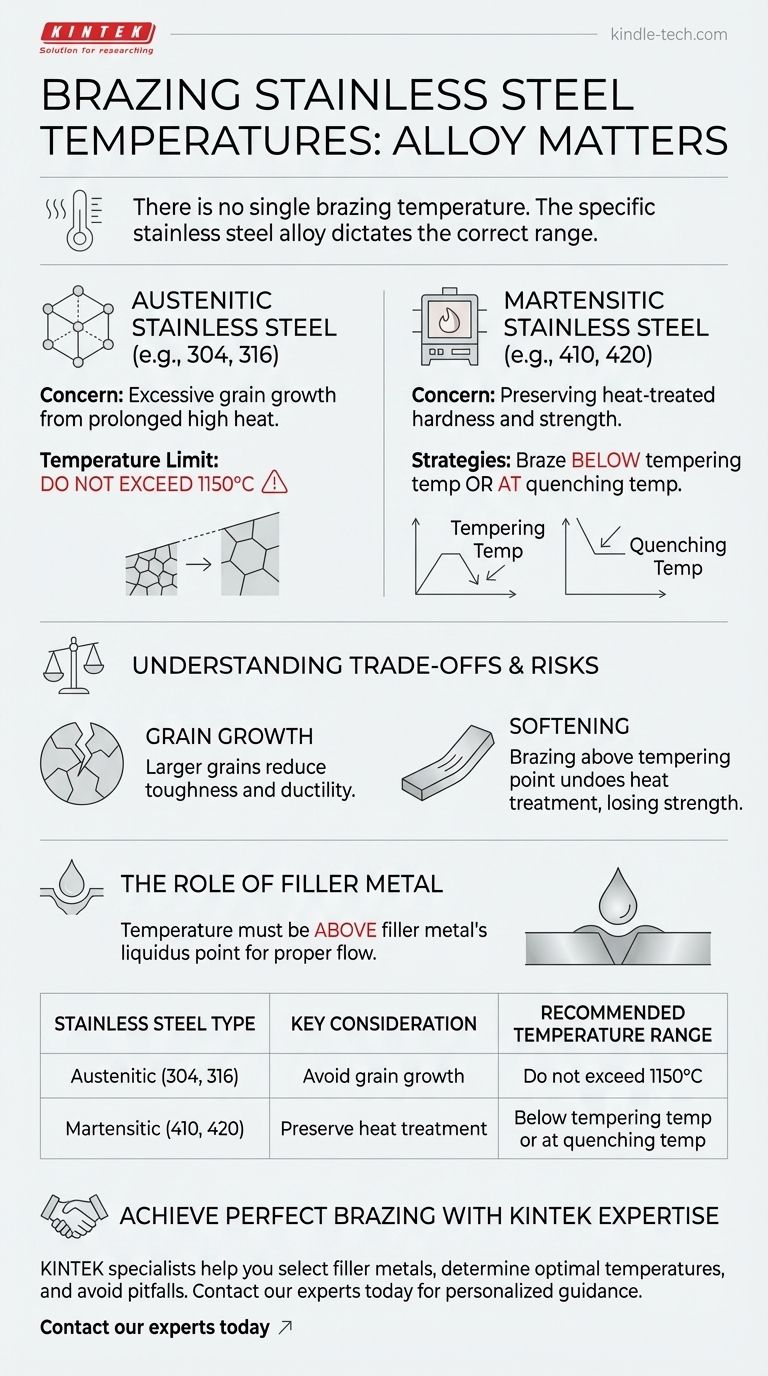
There is no single brazing temperature for stainless steel. The correct temperature is determined by the specific type of stainless steel alloy you are working with, as different families have unique metallurgical properties that must be preserved. For austenitic grades, the temperature should not exceed 1150°C to prevent weakening, while for martensitic grades, the temperature must align with its specific heat treatment requirements.
The core principle is that the brazing temperature must be high enough to melt the filler metal but low enough to avoid damaging the base metal's inherent strength and structure. This means the specific alloy, not the process, dictates the temperature.

Why the Stainless Steel Type is Critical
"Stainless steel" is a broad category of alloys, each with a different internal structure and response to heat. Understanding which family your material belongs to is the first and most important step in determining the correct brazing temperature.
For Austenitic Stainless Steel (e.g., 304, 316)
Austenitic stainless steels are the most common type. They are not hardenable by heat treatment.
The primary concern when brazing these alloys is excessive grain growth. Heating them too high for too long can cause the internal crystalline grains to enlarge, which can reduce the material's toughness and ductility.
Because of this, the heating temperature for austenitic stainless steel brazing should not exceed 1150°C.
For Martensitic Stainless Steel (e.g., 410, 420)
Martensitic stainless steels are hardenable, meaning their strength is achieved through specific heat treatment cycles of quenching and tempering. Applying the wrong brazing temperature can easily ruin these properties.
You have two primary strategies for selecting a brazing temperature:
-
Brazing Below the Tempering Temperature: This is the safest approach to preserve the material's existing hardness. You must use a brazing filler alloy whose working temperature is lower than the final tempering temperature of the part. This prevents any softening of the base material.
-
Brazing at the Quenching Temperature: This advanced technique combines brazing with the hardening process. The part is heated to its quenching (austenitizing) temperature, the braze is performed, and then the assembly is quenched as a single unit. This requires careful selection of a high-temperature filler metal.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
Choosing a brazing temperature is a balancing act. The ideal temperature must be hot enough for the filler metal to flow properly but cool enough to protect the stainless steel.
The Risk of High Temperatures: Grain Growth
As mentioned with austenitic steels, excessive heat leads to larger grain structures. This can make the material more susceptible to cracking under stress, even if the brazed joint itself is strong.
The Risk of Incorrect Temperatures: Softening
For hardenable martensitic alloys, this is the most critical risk. If you braze at a temperature above the material's tempering point, you will effectively undo the heat treatment, causing a significant loss of strength and hardness in the final part.
The Role of the Filler Metal
The choice of brazing filler metal is inseparable from the temperature. The brazing process must be conducted at a temperature above the filler metal's liquidus point (the temperature at which it is fully molten) to ensure proper flow and wetting into the joint.
This means you must first identify the temperature constraints of your stainless steel and then select a filler alloy that functions properly within that safe temperature window.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your goal determines your strategy. The temperature you choose must align with the intended properties and processing steps of the final assembly.
- If your primary focus is preserving the existing strength of a heat-treated part: Choose a low-temperature filler alloy and ensure your brazing cycle stays well below the martensitic steel's tempering temperature.
- If your primary focus is brazing a common, non-hardenable part (austenitic): Select a filler that flows freely below 1150°C to get a strong joint without risking grain growth in the base metal.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency: Consider combining the brazing and hardening steps by using a high-temperature filler that aligns with the martensitic alloy's quenching temperature.
By treating the brazing temperature as a function of your specific alloy, you ensure both a strong joint and an uncompromised base material.
Summary Table:
| Stainless Steel Type | Key Consideration | Recommended Temperature Range |
|---|---|---|
| Austenitic (304, 316) | Avoid grain growth | Do not exceed 1150°C |
| Martensitic (410, 420) | Preserve heat treatment | Below tempering temp or at quenching temp |
Achieve perfect stainless steel brazing results with KINTEK's expertise.
Brazing stainless steel requires precise temperature control to avoid damaging the base metal while ensuring strong, reliable joints. As specialists in lab equipment and consumables, KINTEK provides the solutions and support you need to master this critical process.
Our team can help you:
- Select the right filler metals for your specific stainless steel alloy
- Determine the optimal brazing temperature to preserve material properties
- Avoid common pitfalls like grain growth and softening
Don't compromise your stainless steel components—contact our experts today for personalized guidance on brazing temperatures and techniques tailored to your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is oxidation in brazing? How to prevent it for strong, durable joints
- What are some applications of brazing? Join Dissimilar Metals with Strong, Leak-Proof Bonds
- How is the greatest joint strength obtained in brazing? Master the 3 Keys to Superior Metallurgical Bonds
- Does brazing require heat? Yes, it's the catalyst for creating strong, permanent bonds.
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing



















