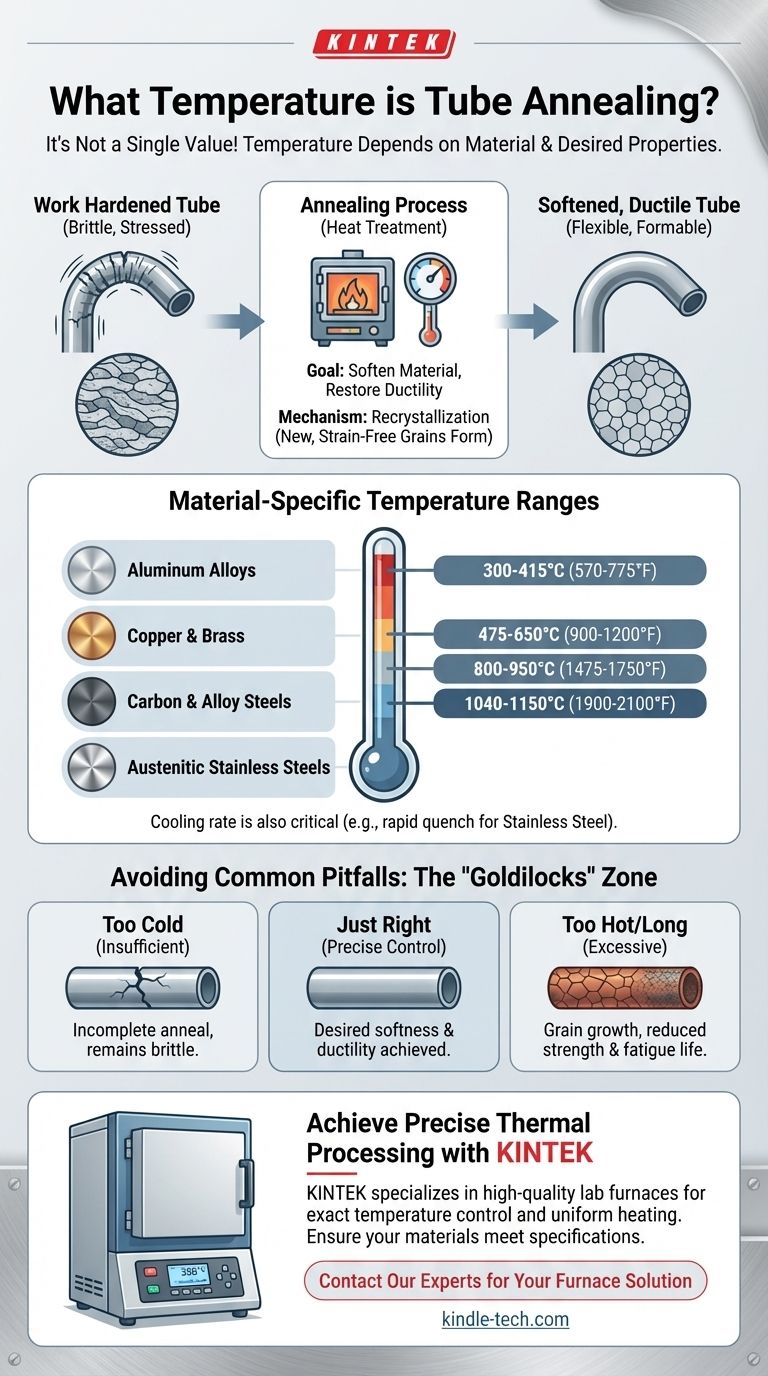
The annealing temperature for tubing is not a single value but a specific range that depends almost entirely on the material being treated. For example, aluminum alloys anneal at relatively low temperatures around 300-415°C (570-775°F), while austenitic stainless steels require much higher temperatures, typically 1040-1150°C (1900-2100°F). The correct temperature is critical for achieving the desired properties.
Annealing temperature is a critical process variable determined primarily by the tube's material composition and its degree of cold work. Choosing the correct temperature is essential for achieving the required mechanical properties—such as softness and ductility—without compromising the material's structural integrity.

Why Temperature Is the Defining Factor in Annealing
Annealing is a heat treatment process designed to alter a material's physical and sometimes chemical properties. For metal tubing that has been formed, drawn, or bent, the primary goal is to reverse the effects of work hardening.
The Goal: Softening the Material
Processes like tube drawing or bending introduce stress and dislocations into the metal's crystal structure. This is called work hardening (or strain hardening), and it makes the tube harder, stronger, and more brittle.
Annealing reverses this by allowing the internal structure to reform, restoring its ductility (ability to be drawn or deformed) and reducing its hardness.
The Mechanism: Recrystallization
The effectiveness of annealing hinges on reaching a temperature above the material's recrystallization temperature. At this point, new, strain-free grains begin to form within the metal, replacing the deformed grains created by cold working.
Temperature directly controls the rate and extent of this process. It is the most critical input to achieve a successful anneal.
Material Dictates the Temperature Range
Different metals and their alloys have vastly different melting points and crystal structures, resulting in unique annealing temperature requirements.
- Carbon and Alloy Steels: The temperature depends heavily on carbon content. For a full anneal, these are typically heated to around 800-950°C (1475-1750°F) and then cooled very slowly.
- Austenitic Stainless Steels (e.g., 304, 316): These require a high-temperature solution anneal, typically between 1040-1150°C (1900-2100°F). This is followed by a rapid cool (quench) to lock in the desired properties and prevent the loss of corrosion resistance.
- Copper and Brass: These non-ferrous metals anneal at much lower temperatures. Pure copper is annealed around 475-650°C (900-1200°F), while brasses anneal at slightly lower ranges.
- Aluminum Alloys: Aluminum has the lowest annealing temperature of these common materials, typically between 300-415°C (570-775°F).
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
Selecting the wrong temperature or holding time can lead to component failure. The process window can be narrow, and precision is key.
The Risk of Insufficient Temperature
If the tube is not heated to its required recrystallization temperature, the anneal will be incomplete. The material will remain partially hardened and brittle, which can lead to cracking during subsequent forming operations or premature failure in service.
The Danger of Excessive Temperature or Time
Overheating is equally problematic. Once recrystallization is complete, holding the tube at a high temperature can cause grain growth. Large grains can reduce the material's strength, toughness, and fatigue life.
In extreme cases, overheating can cause surface scaling (oxidation) or even incipient melting at the grain boundaries, which permanently damages the component.
The Critical Role of Cooling Rate
Temperature isn't the only variable; the cooling rate is also a defining part of the process.
Slowly cooling steel in a furnace promotes maximum softness. In contrast, rapidly quenching stainless steel is essential to prevent chromium carbides from forming, which would severely degrade its corrosion resistance.
How to Determine the Correct Annealing Process
To ensure a successful outcome, you must move beyond general temperature ranges and define a precise process for your specific application.
- If your primary focus is processing a known alloy: Always consult the material supplier's data sheet or established metallurgical standards (like those from ASM International or ASTM) for the exact annealing cycle.
- If your primary focus is relieving stress with minimal softening: Consider a lower-temperature stress-relief anneal, which heats the material below its recrystallization temperature to reduce internal stresses without significantly changing its hardness.
- If your primary focus is on austenitic stainless steel: Remember that a rapid quench after heating is just as important as the temperature itself to maintain corrosion resistance.
- If you are ever unsure of the material or process: Partner with a qualified metallurgist or a professional heat treatment service to specify and execute the process correctly.
Ultimately, precise control over the entire thermal cycle—heating, holding, and cooling—is the key to unlocking the desired performance of your material.
Summary Table:
| Material | Typical Annealing Temperature Range |
|---|---|
| Aluminum Alloys | 300-415°C (570-775°F) |
| Austenitic Stainless Steels | 1040-1150°C (1900-2100°F) |
| Carbon & Alloy Steels | 800-950°C (1475-1750°F) |
| Copper & Brass | 475-650°C (900-1200°F) |
Achieve precise thermal processing for your lab tubing with KINTEK.
Selecting and maintaining the correct annealing temperature is critical for material properties. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab furnaces and ovens that deliver the exact temperature control and uniform heating your annealing processes demand. Our equipment helps you avoid the pitfalls of incomplete annealing or grain growth, ensuring your materials achieve the desired softness, ductility, and performance.
Whether you are working with stainless steel, aluminum, or other alloys, KINTEK has the reliable lab equipment to support your research and production needs.
Contact our thermal processing experts today to find the perfect furnace for your annealing applications.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control
- What is quartz tube heating? Achieve Instant, Targeted Heat with Infrared Radiation
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing
- How do you clean a tubular furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan



















