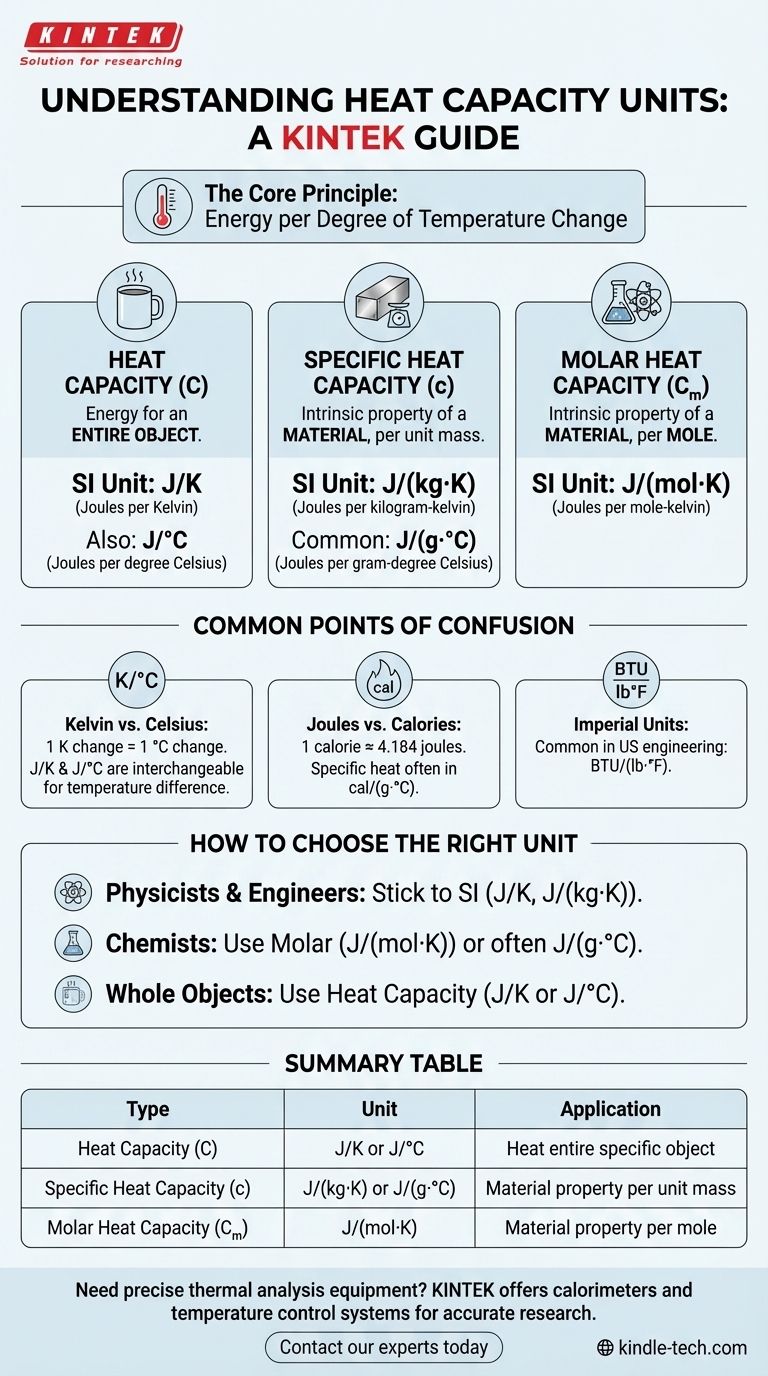
The primary SI unit for heat capacity is joules per kelvin (J/K). This unit describes the amount of energy (in joules) required to raise the temperature of an entire object or system by one degree Kelvin. However, the specific units you encounter will change depending on whether you are measuring a whole object, a specific mass of a substance, or a molar amount.
The units for heat capacity always represent energy per degree of temperature change. Understanding the difference between heat capacity, specific heat capacity, and molar heat capacity is the key to identifying and using the correct unit for your calculation.

What the Units Actually Mean
Heat Capacity (C)
Heat capacity refers to the energy needed to raise the temperature of an entire object by one degree. Because it's for a whole, specific object (like a coffee mug or an engine block), its mass is already factored in.
The unit is simply energy divided by temperature: joules per kelvin (J/K). You may also see it expressed as joules per degree Celsius (J/°C).
Specific Heat Capacity (c)
This is the most common measurement you will encounter. Specific heat is an intrinsic property of a material, not an object. It is the energy required to raise the temperature of one unit of mass of a substance by one degree.
The standard SI unit is joules per kilogram-kelvin (J/(kg·K)).
In chemistry and other lab contexts, it is very common to see units based on grams and Celsius, such as joules per gram-degree Celsius (J/(g·°C)).
Molar Heat Capacity (Cₘ)
Molar heat capacity is also an intrinsic property of a material, but it is defined per mole instead of per mass. This is particularly useful in chemistry, where reactions are described in terms of moles.
The standard SI unit is joules per mole-kelvin (J/(mol·K)).
Common Points of Confusion
Kelvin vs. Celsius
For heat capacity calculations, a change of one degree Kelvin (1 K) is exactly the same as a change of one degree Celsius (1 °C).
Therefore, the units J/K and J/°C are functionally interchangeable when you are calculating a temperature difference. The same is true for J/(kg·K) and J/(kg·°C).
Joules vs. Calories
The calorie (cal) is an older, non-SI unit for energy. It is still used in some contexts, particularly chemistry and nutrition.
The conversion is approximately 1 calorie = 4.184 joules. You may see specific heat expressed as cal/(g·°C). For example, the specific heat of water is very close to 1.0 cal/(g·°C).
Imperial and US Customary Units
In some engineering fields, particularly in the United States, you may encounter Imperial units.
The most common unit for specific heat in this system is the British Thermal Unit per pound per degree Fahrenheit (BTU/(lb·°F)).
How to Choose the Right Unit for Your Application
-
If you are a physicist or engineer: Stick to the standard SI units. Use J/K for whole systems and J/(kg·K) for material properties.
-
If you are a chemist: Molar heat capacity (J/(mol·K)) is often the most useful for reaction calculations, though you will frequently use J/(g·°C) for lab work.
-
If you are working with an entire, specific object: Use the general heat capacity unit, J/K or J/°C, as the object's mass is already accounted for.
Understanding which quantity is being measured—a whole object, a unit of mass, or a mole—is the definitive guide to choosing the correct unit.
Summary Table:
| Type of Heat Capacity | Unit | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Capacity (C) | J/K or J/°C | Energy to heat a specific, entire object |
| Specific Heat Capacity (c) | J/(kg·K) or J/(g·°C) | Intrinsic property of a material (per unit mass) |
| Molar Heat Capacity (Cₘ) | J/(mol·K) | Intrinsic property of a material (per mole) |
Need precise thermal analysis equipment for your lab? Understanding heat capacity is crucial for experiments in chemistry, materials science, and engineering. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including calorimeters and temperature control systems, to ensure your measurements are accurate and reliable. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory's thermal analysis needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Customizable XRD Sample Holders for Diverse Research Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between PPF and coating? Armor vs. Slick Shell for Your Car
- Why is a laboratory vacuum drying oven or a high-vacuum manifold essential for recovered monomers and catalysts?
- What is the difference between pyrolysis and decomposition? Unlock the Power of Controlled Thermal Processing
- How do laboratory shakers or stirrers ensure coating quality? Achieve Uniform Sol-Gel Nanocoatings with Precision
- What is the FDM extrusion process? A Complete Guide to Layer-by-Layer 3D Printing
- Why must a forced air drying oven be used for fluorosilicone rubber post-curing? Ensure Peak Material Performance
- What is the physics of pyrolysis? Mastering Thermal Decomposition for Targeted Resource Recovery
- How does a constant temperature magnetic stirrer contribute to electroless plating quality? Enhancing Surface Integrity



















