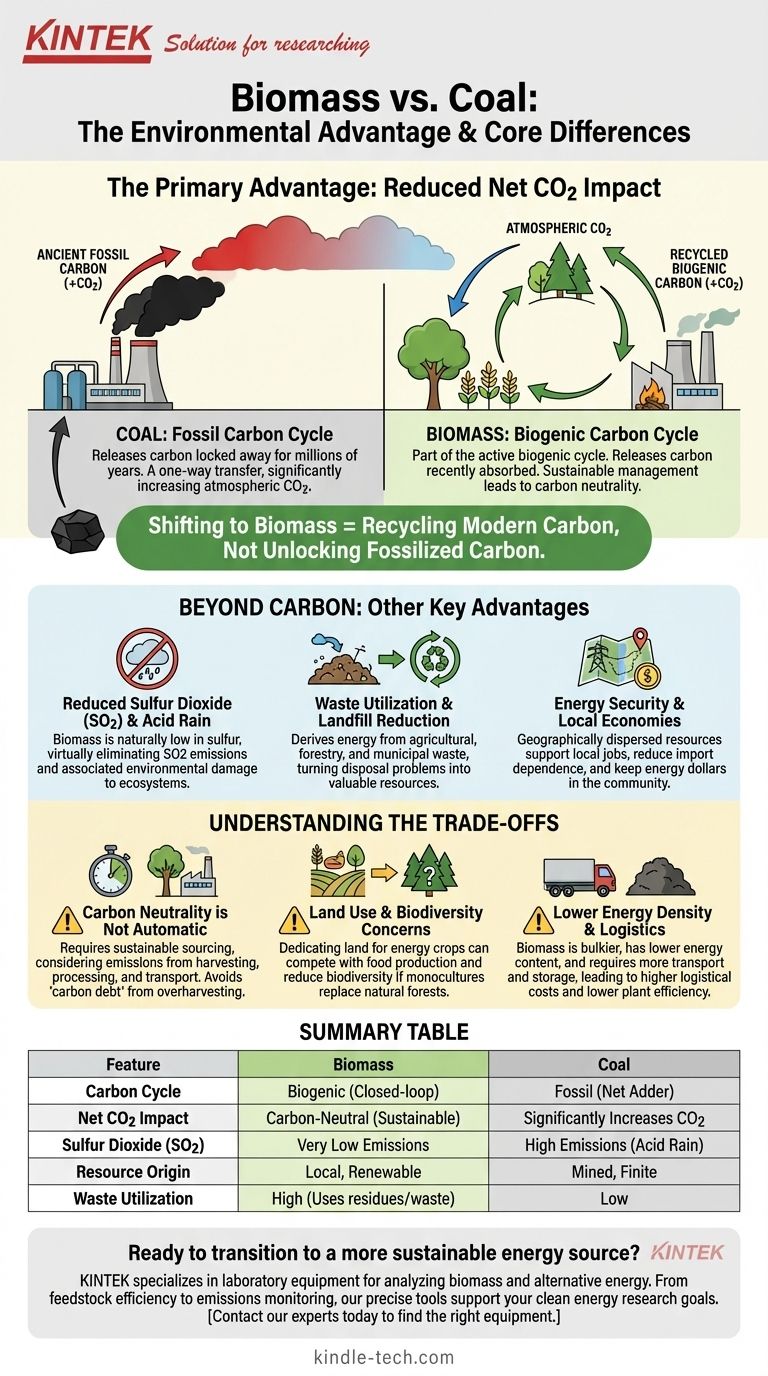
The primary advantage of biomass over coal is its significantly lower net impact on atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) levels. While both release CO2 when burned, biomass is part of the active biogenic carbon cycle, meaning the carbon it releases was recently absorbed from the atmosphere. In contrast, burning coal releases ancient, fossilized carbon, adding vast quantities of new CO2 to the atmosphere.
Shifting from coal to biomass is fundamentally about changing where the carbon comes from. Instead of unlocking carbon that has been sequestered for millions of years, you are largely recycling carbon that is already part of the modern ecosystem.

The Core Difference: Carbon Cycling
The most critical distinction between coal and biomass lies in their relationship with the global carbon cycle. Understanding this difference is key to evaluating their environmental impact.
Coal and "Fossil" Carbon
Coal is a fossil fuel formed from ancient organic matter subjected to intense heat and pressure over millions of years.
The carbon within coal has been locked away and removed from the active carbon cycle. Burning it represents a one-way transfer of this sequestered carbon into the atmosphere, directly increasing the concentration of greenhouse gases.
Biomass and the "Biogenic" Carbon Cycle
Biomass refers to organic material from plants or animals, such as wood, agricultural crops, and organic waste.
As plants grow, they absorb CO2 from the atmosphere through photosynthesis. When this biomass is burned for energy, it releases that same amount of carbon back into the air. This creates a relatively short, closed-loop system known as the biogenic carbon cycle.
Net Emissions Impact
Because of these different cycles, their net effect on the atmosphere is profoundly different.
Coal is a net adder of CO2 to the atmosphere. Biomass, when managed sustainably, is considered largely carbon-neutral because the carbon it emits is offset by the carbon absorbed during its growth.
Beyond Carbon: Other Key Advantages
While carbon is the main story, biomass offers other significant benefits over coal.
Reduced Sulfur Dioxide (SO2)
Coal often contains high levels of sulfur, and burning it releases sulfur dioxide (SO2), a primary cause of acid rain.
Biomass fuels are naturally very low in sulfur. Switching to biomass can dramatically reduce SO2 emissions and their associated environmental damage to forests, lakes, and infrastructure.
Waste Utilization
A significant portion of biomass fuel can be derived from waste streams.
This includes agricultural residue (corn stalks, straw), forestry waste (branches, sawdust), and the organic portion of municipal solid waste. Using these materials for energy reduces landfill burdens and turns a disposal problem into a valuable resource.
Energy Security and Local Economies
Unlike coal, which is often mined in concentrated locations and traded globally, biomass resources are typically more geographically dispersed.
Sourcing biomass locally can reduce dependence on imported fuels and support local agricultural and forestry economies, creating jobs and keeping energy dollars within the community.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Nuances
Biomass is a clear improvement over coal, but it is not a perfect solution. Acknowledging its challenges is crucial for effective implementation.
The "Carbon Neutrality" Debate
The idea of perfect carbon neutrality is an oversimplification. Emissions from harvesting, processing, and transportation must be factored in.
Furthermore, if forests are harvested faster than they can regrow, a "carbon debt" is created that can take decades to repay. Sustainable sourcing is therefore non-negotiable for biomass to be a climate solution.
Land Use and Biodiversity
Dedicating large areas of land to grow energy crops can create significant challenges.
This can compete with land needed for food production, potentially impacting food prices and security. It can also lead to monoculture farming, which reduces biodiversity compared to a natural forest ecosystem.
Lower Energy Density
Biomass is bulky and has a lower energy content per unit of weight compared to coal.
This means more material must be transported and stored to generate the same amount of power, leading to higher logistical costs and complexities. Power plant efficiency can also be lower than a comparable coal-fired plant.
Making the Right Choice for Your Energy Goals
Selecting an energy source requires weighing its benefits against its drawbacks in the context of your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is reducing net long-term CO2 emissions: Sustainably sourced biomass is a vastly superior alternative to coal, as it works within the existing biogenic carbon cycle.
- If your primary focus is improving local air and water quality: Biomass offers an immediate and clear advantage by virtually eliminating the sulfur dioxide emissions that cause acid rain.
- If your primary focus is developing local, resilient energy systems: Biomass leverages local resources, creating economic benefits and reducing reliance on a volatile global coal market.
Ultimately, biomass is a complex but valuable tool for transitioning away from the geological-scale damage caused by fossil fuels.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Biomass | Coal |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Cycle | Biogenic (Closed-loop) | Fossil (Net Adder) |
| Net CO2 Impact | Carbon-Neutral (Sustainable) | Significantly Increases CO2 |
| Sulfur Dioxide (SO2) | Very Low Emissions | High Emissions (Acid Rain) |
| Resource Origin | Local, Renewable | Mined, Finite |
| Waste Utilization | High (Uses residues/waste) | Low |
Ready to transition to a more sustainable energy source?
KINTEK specializes in laboratory equipment and consumables for analyzing and developing biomass and alternative energy solutions. Whether you are researching feedstock efficiency, optimizing conversion processes, or monitoring emissions, our precise and reliable tools can support your goals for a cleaner future.
Contact our experts today to find the right equipment for your biomass and energy research needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success








