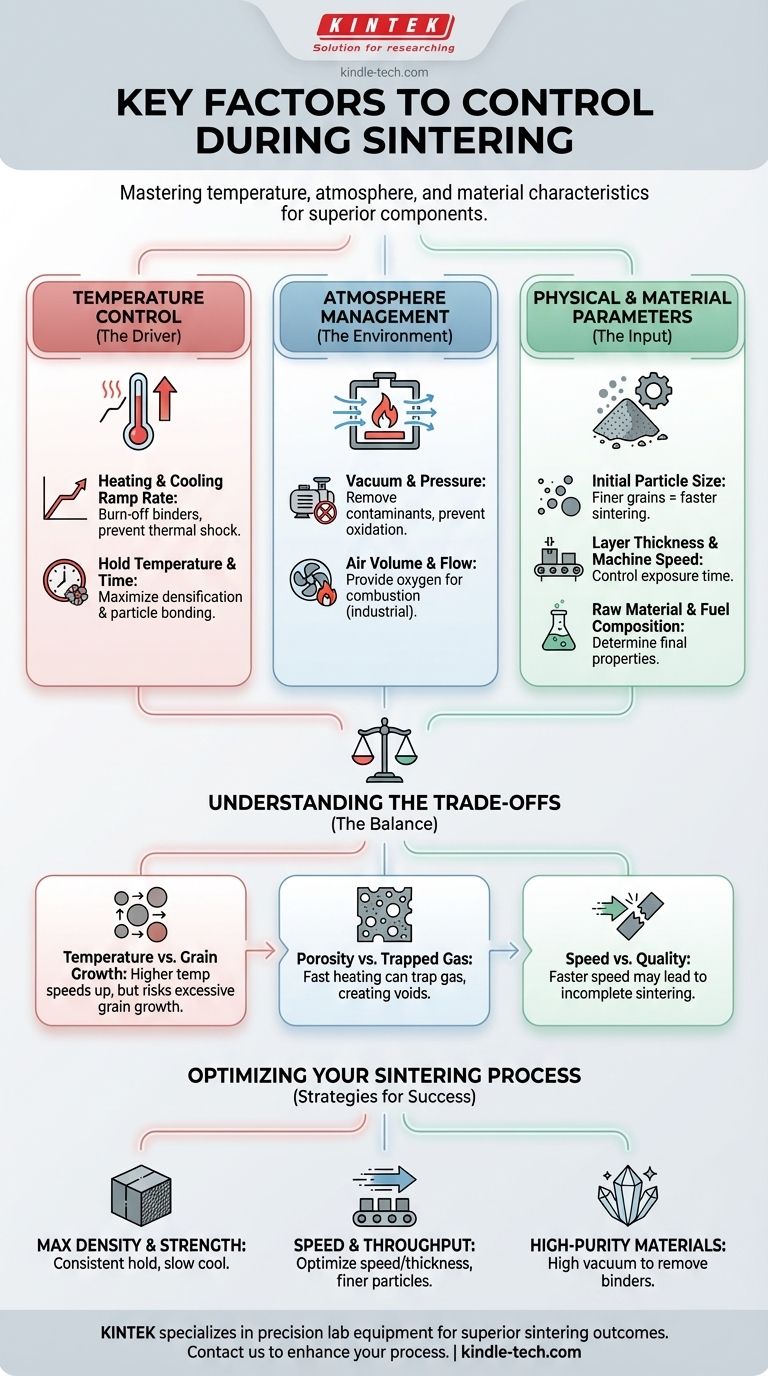
The key factors to control during sintering are temperature, atmosphere, and the physical characteristics of the material and equipment. Mastering these variables is the difference between producing a dense, strong final component and a defective one. This control dictates everything from the rate of particle bonding to the final porosity and strength of the material.
Sintering is not merely a heating process; it is a carefully orchestrated transformation at the particle level. While many factors are involved, the most critical element is precise temperature management—including the heating rate, hold time, and cooling rate—as this directly governs the atomic diffusion that bonds particles together and densifies the material.
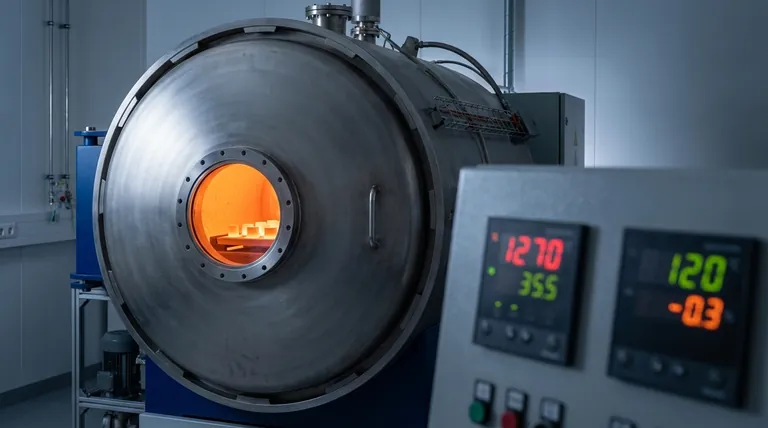

The Central Role of Temperature Control
Temperature is the primary driver of the sintering process. It provides the energy needed for atoms to move between particles, creating solid bonds and reducing the empty space, or porosity, within the material.
The Heating and Cooling Ramp Rate
The rate at which you heat the material to the target temperature is critical. During this initial phase, any residual organic binders from the "green body" are burned off. Heating too quickly can trap these gases, creating internal defects.
Similarly, the cooling rate after sintering is held is crucial. A controlled, gradual cool-down prevents thermal shock and cracking, which is especially important for brittle materials.
The Hold Temperature and Time
This is the phase where the most significant densification occurs. At a specific high temperature, powder particles begin to diffusion-bond at their points of contact.
Holding this temperature consistently allows the contact areas to grow, pulling the particle centers closer together. This systematically reduces porosity and increases the material's overall density and strength.
Managing the Sintering Atmosphere
The environment inside the furnace has a direct impact on the chemical and physical changes happening to the material. An uncontrolled atmosphere can introduce contaminants or interfere with the bonding process.
Vacuum and Pressure
Many high-performance sintering processes are conducted under a vacuum. This serves two purposes: it helps remove the burned-off binders during heating and prevents atmospheric gases like oxygen from reacting with the hot material, which could cause unwanted oxidation.
Achieving this requires a well-sealed furnace. Proper sealing ensures that contaminants are removed and the controlled atmosphere is maintained throughout the cycle. In some advanced processes, external pressure is also applied to aid in densification.
Air Volume and Flow
In large-scale industrial processes, such as sintering iron ore, controlling air volume is essential. The flow of air provides the necessary oxygen for solid fuel (like coke powder) to combust, generating the high temperatures required for sintering to occur.
Physical and Material Parameters
The variables you set before the process even begins have a profound influence on the outcome. These initial conditions determine how efficiently the material will sinter.
Initial Particle Size
The starting size of the powder particles is a key variable. Smaller, finer grains have a higher surface-area-to-volume ratio, which provides more points of contact for diffusion bonding to begin. This generally allows for sintering to occur more rapidly and at lower temperatures.
Layer Thickness and Machine Speed
For continuous sintering operations, the thickness of the material layer (e.g., 250-500mm for ore) and the speed of the machine (e.g., 1.5-4m/min) are tightly controlled. These two factors together determine the total time the material is exposed to the peak temperature, ensuring it is fully burned and sintered by the scheduled endpoint.
Raw Material and Fuel Composition
The precise mix of raw materials (iron ore, manganese ore, etc.) and fuel is fundamental. The type and quantity of fuel dictate the amount of heat generated, while the composition of the raw materials determines the final chemistry and properties of the sintered product.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Controlling the sintering process is an act of balancing competing factors. Optimizing for one property can often compromise another, making a clear understanding of the trade-offs essential.
Temperature vs. Grain Growth
While higher temperatures accelerate densification, they also promote grain growth, where smaller particles merge into larger ones. Excessive grain growth can be detrimental to the final mechanical properties, such as strength and hardness. The goal is to find the highest possible temperature that achieves density without causing unwanted microstructural changes.
Porosity vs. Trapped Gas
The primary objective of sintering is to reduce porosity. However, if the heating ramp is too fast or the material's surface sinters too quickly, gases from binder burnout can become trapped within the material, creating internal voids that are impossible to remove and weaken the final part.
Speed vs. Quality
In an industrial setting, throughput is always a concern. Increasing machine speed or reducing hold times can increase output, but it risks incomplete sintering. This can leave behind excessive porosity and result in a product that does not meet strength or density specifications.
Optimizing Your Sintering Process
The ideal control strategy depends entirely on the desired outcome for the final product. Your approach should be tailored to the most critical property you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is maximum density and strength: Prioritize a consistent hold at the highest feasible temperature without causing adverse grain growth, and ensure a controlled, slow cooling rate to prevent thermal shock.
- If your primary focus is process speed and throughput: Concentrate on optimizing the interplay between machine speed and layer thickness, potentially using finer initial grain sizes to accelerate the bonding process.
- If your primary focus is producing high-purity materials: Emphasize achieving and maintaining a high vacuum throughout the cycle to effectively remove all binders and prevent atmospheric contamination.
Ultimately, successful sintering comes from precisely balancing thermal energy, material science, and the process environment to achieve a predictable and repeatable transformation.
Summary Table:
| Key Control Factor | Why It Matters | Key Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Drives atomic diffusion for particle bonding | Heating/cooling rates, hold temperature, time |
| Atmosphere | Prevents contamination and aids densification | Vacuum levels, gas composition, pressure |
| Material Properties | Determines sintering efficiency and outcome | Particle size, layer thickness, raw material mix |
Ready to optimize your sintering process? At KINTEK, we specialize in precision lab equipment and consumables for sintering applications. Our expertise in temperature control systems, vacuum furnaces, and material science can help you achieve superior density, strength, and consistency in your sintered products. Whether you're focused on R&D or industrial-scale production, our solutions are tailored to meet your specific laboratory needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your sintering outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields
- What are the industrial applications of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Energy and Valuable Products
- What biomass is used in pyrolysis? Selecting the Optimal Feedstock for Your Goals
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing



















