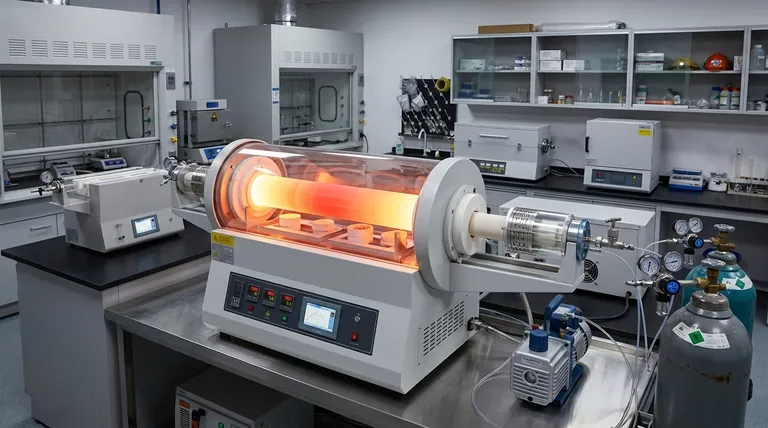
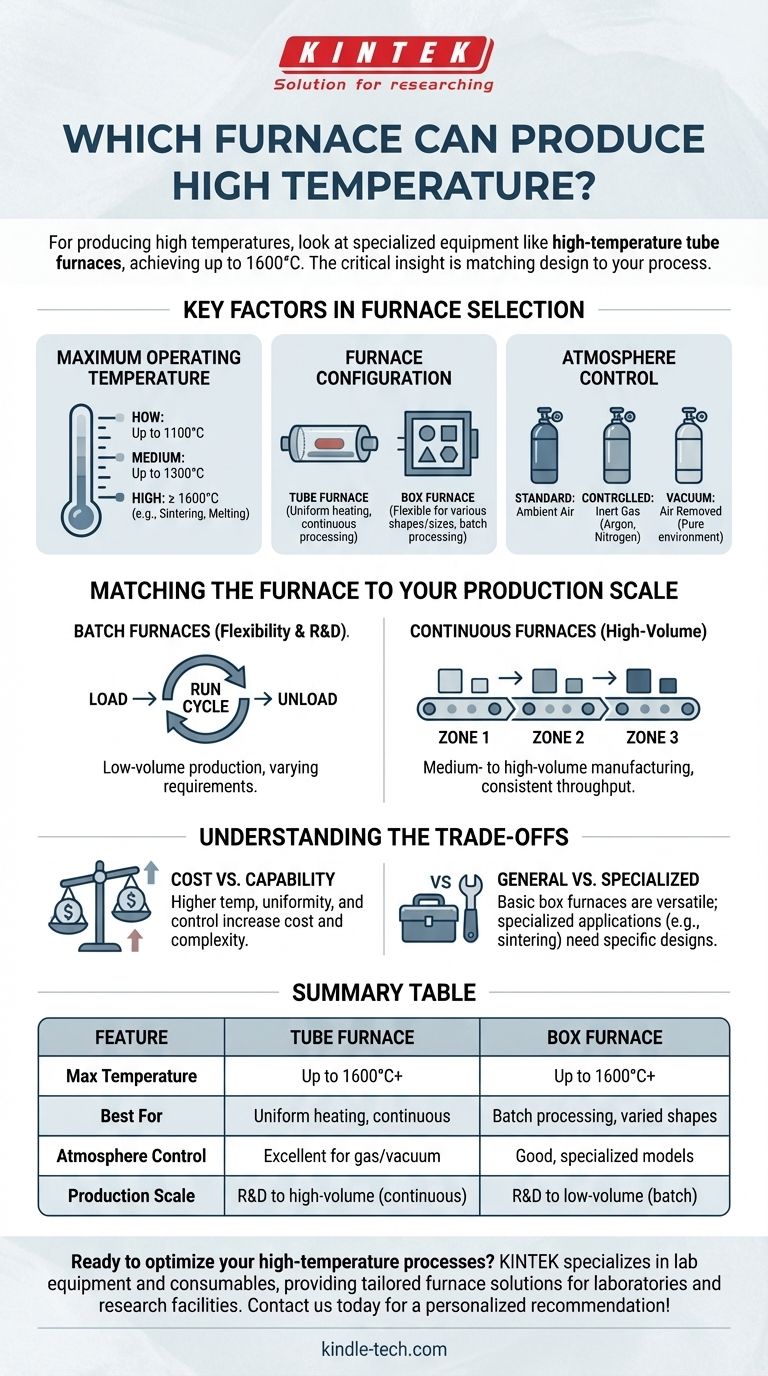
For producing high temperatures, you should look at specialized equipment like high-temperature tube furnaces, which can achieve temperatures up to 1600°C. Both tube and box furnaces are common configurations designed for high-temperature applications across various industries.
The critical insight is not simply finding the furnace with the highest temperature rating, but selecting one whose design—tube or box, batch or continuous, and with or without atmosphere control—precisely matches the requirements of your specific heat treatment process.

Key Factors in High-Temperature Furnace Selection
The term "high temperature" is relative. The right furnace is defined by its ability to meet the precise demands of a given application, from its maximum temperature to the environment it creates.
Maximum Operating Temperature
Furnaces are often categorized by their temperature capabilities. The references indicate a clear tiering, which is common in industrial and laboratory settings.
A low-temperature furnace typically operates up to 1100°C. A medium-temperature furnace can reach up to 1300°C.
For more demanding processes like sintering advanced ceramics or melting certain alloys, a high-temperature furnace capable of reaching 1600°C or more is required.
Furnace Configuration: Tube vs. Box
The physical shape of the furnace chamber is a fundamental design choice that dictates its use.
A tube furnace features a cylindrical chamber, ideal for processes requiring exceptional temperature uniformity or for continuous processing of materials that can pass through the tube.
A box furnace (also known as a muffle furnace) has a square or rectangular chamber, offering greater flexibility for heating objects of various shapes and sizes in a single batch.
Atmosphere Control
Many high-temperature processes are sensitive to the presence of oxygen or other reactive gases. This is where atmosphere control becomes essential.
A standard furnace operates with ambient air. This is sufficient for many basic heat treatments.
A controlled atmosphere furnace allows you to introduce specific inert gases, like argon or nitrogen, to prevent oxidation. A vacuum furnace removes the air entirely, creating a pure environment for the most sensitive materials.
Matching the Furnace to Your Production Scale
The choice between a batch or continuous system is driven entirely by your production volume and process flow. An incorrect choice here leads to significant inefficiency.
Batch Furnaces for Flexibility and R&D
For low-volume production, research and development, or processes with varying requirements, a batch furnace is the standard.
You load the material, run the heating cycle, and unload it. Both box furnaces and tube furnaces are commonly used in batch configurations.
Continuous Furnaces for High-Volume Production
For medium- to high-volume manufacturing, a continuous furnace is necessary to ensure consistent throughput.
In these systems, materials move through different temperature zones on a conveyor or by being pushed through a long tube, streamlining the heat treatment process into the main production line.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a furnace involves balancing capability with cost and complexity. Higher performance in one area often means a compromise in another.
Cost vs. Capability
As the maximum temperature, degree of temperature uniformity, and level of atmosphere control increase, so do the cost and complexity of the furnace. A high-vacuum furnace capable of 1600°C is a far greater investment than a simple air-atmosphere box furnace.
General Purpose vs. Specialized Application
A basic box furnace is a versatile workhorse for general-purpose heat treating. However, processes like binder burnout, sintering, or brazing often require highly specialized furnaces designed to manage contaminants and provide precise thermal and atmospheric conditions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
To select the correct furnace, start by defining the non-negotiable requirements of your process.
- If your primary focus is research and material testing: A versatile box or tube furnace with precise temperature and atmosphere controls provides the most flexibility.
- If your primary focus is consistent, low-volume production: A batch furnace designed specifically for your process (e.g., annealing, curing) offers the best balance of performance and cost.
- If your primary focus is high-volume manufacturing: A continuous furnace integrated into your production line is the only way to achieve the necessary scale and efficiency.
Ultimately, choosing the right furnace is about aligning its technical capabilities with the specific demands of your heat treatment goal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Tube Furnace | Box Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Max Temperature | Up to 1600°C+ | Up to 1600°C+ |
| Best For | Uniform heating, continuous processing | Batch processing, varied sample shapes |
| Atmosphere Control | Excellent for gas/vacuum environments | Good, with specialized models available |
| Production Scale | R&D to high-volume (continuous) | R&D to low-volume (batch) |
Ready to optimize your high-temperature processes? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing tailored furnace solutions for laboratories and research facilities. Whether you need precise temperature control, atmosphere management, or scalable production systems, our experts will help you select the ideal furnace for your specific application. Contact us today to discuss your requirements and get a personalized recommendation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why use a tube furnace? Achieve Superior Temperature Uniformity and Atmosphere Control
- How does an alumina tube furnace with a controlled atmosphere simulate conditions in CSP environments? Master Accuracy.
- What tube is used for tubular furnace? Choose the Right Material for Temperature & Atmosphere
- What are the advantages of using an alumina liner in a tube furnace for biomass combustion corrosion simulations?
- What is the ceramic tube high temperature? From 1100°C to 1800°C, Choose the Right Material



















