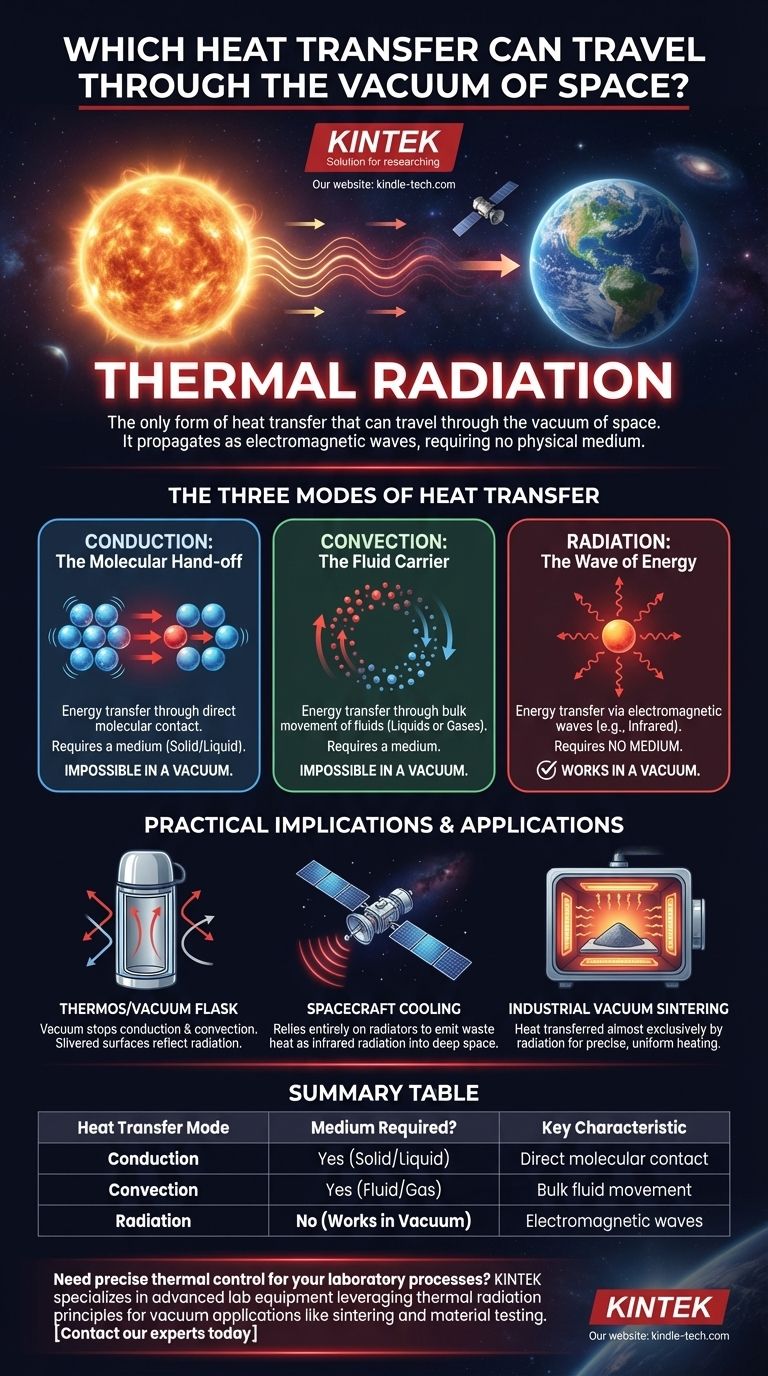
The only form of heat transfer that can travel through the vacuum of space is thermal radiation. Unlike conduction or convection, which require a physical medium of molecules to transfer energy, radiation propagates as electromagnetic waves. This is the exact same principle that allows sunlight to travel 93 million miles through the void of space to warm the Earth.
While conduction and convection rely on the interaction of matter, a vacuum is defined by its absence. Thermal radiation is fundamentally different—it is the transfer of energy via electromagnetic waves, which require no medium to travel.

The Three Modes of Heat Transfer Explained
To understand why only radiation works in a vacuum, we must first clearly define all three mechanisms of heat transfer. Each operates on a distinct physical principle.
Conduction: The Molecular Hand-off
Conduction is heat transfer through direct contact. Energetic, vibrating atoms and molecules transfer their energy to their less energetic neighbors.
Think of it as a line of people passing a hot potato. The potato (heat) moves down the line, but the people (molecules) stay in their fixed positions. This process is impossible in a vacuum, as there are no molecules to pass the energy along.
Convection: The Fluid Carrier
Convection is heat transfer through the bulk movement of fluids (liquids or gases). A heated fluid becomes less dense and rises, carrying thermal energy with it, while cooler, denser fluid sinks to take its place, creating a convection current.
This is the principle behind a boiling pot of water or a room heater warming the air. Since a vacuum contains no fluid to move, convection cannot occur.
Radiation: The Wave of Energy
Thermal radiation is unique. Every object with a temperature above absolute zero emits energy in the form of electromagnetic waves, primarily in the infrared spectrum.
These waves are pure energy and travel at the speed of light. They move in a straight line until they are absorbed by another object, transferring their energy and heating it. This requires no contact and no medium, only a line of sight between the source and the object.
Understanding the Practical Implications
The dominance of radiation in a vacuum is not just a theoretical concept; it has profound consequences for engineering and everyday life.
Why Your Thermos Has a Vacuum
A thermos, or vacuum flask, is a perfect example of engineering around all three heat transfer modes. The gap between the inner and outer walls is a vacuum, which effectively stops heat transfer by both conduction and convection.
However, radiation can still cross this gap. That is why the inner surfaces are silvered and highly reflective. This mirrored surface reflects thermal radiation back to its source, minimizing heat loss (for hot liquids) or heat gain (for cold liquids).
The Challenge of Cooling in Space
Getting rid of waste heat is a critical problem for spacecraft and satellites. On Earth, engineers can use fans to blow air (convection) over a hot component. In space, this is impossible.
Instead, spacecraft must rely entirely on radiation. They use large panels called radiators, which are designed to efficiently emit thermal energy as infrared radiation into the cold, empty backdrop of deep space.
Industrial Applications: Vacuum Sintering
In controlled industrial environments, this principle is used to our advantage. During vacuum induction sintering, materials are heated to extreme temperatures inside a vacuum chamber.
Because conduction and convection are negligible, heat is transferred almost exclusively by radiation from the heating element to the material. This allows for precise, uniform heating that would be impossible to achieve in the presence of a gas.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding how heat moves is fundamental to controlling it. Whether you are trying to keep something hot, keep it cold, or transfer energy efficiently, the principles remain the same.
- If your primary focus is to insulate an object: You must account for all three transfer modes. A vacuum is your most powerful tool against conduction and convection, but you must also use a reflective surface to block radiation.
- If your primary focus is to heat something in a vacuum: Your only option is radiation. This means ensuring your heat source is an effective emitter and your target object is an effective absorber of electromagnetic energy.
- If you are analyzing any system in a vacuum: Your analysis must center on radiation. Conduction and convection can be considered negligible, simplifying the problem to how well surfaces emit and absorb radiant energy.
Ultimately, grasping that radiation is energy in motion, not matter, is the key to understanding how heat can conquer the void.
Summary Table:
| Heat Transfer Mode | Medium Required? | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Conduction | Yes (Solid/Liquid) | Energy transfer via direct molecular contact |
| Convection | Yes (Fluid/Gas) | Energy transfer via bulk fluid movement |
| Radiation | No (Works in Vacuum) | Energy transfer via electromagnetic waves |
Need precise thermal control for your laboratory processes? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment that leverages thermal radiation principles for vacuum applications like sintering and material testing. Our solutions ensure accurate, uniform heating where other methods fail. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can optimize your thermal management systems!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- How hot does a furnace heat exchanger get? Understand Safe Operating Temperatures to Prevent Hazards
- What are the most commonly used metals in a vacuum furnace's hot zone? Discover the Key to High-Purity Processing
- What happens to heat generated in a vacuum? Mastering Thermal Control for Superior Materials
- Is heat Cannot travel in a vacuum True or false? Discover How Heat Crosses the Void of Space
- Why is high-temperature vacuum heat treatment critical for Cr-Ni steel? Optimize Strength & Surface Integrity



















