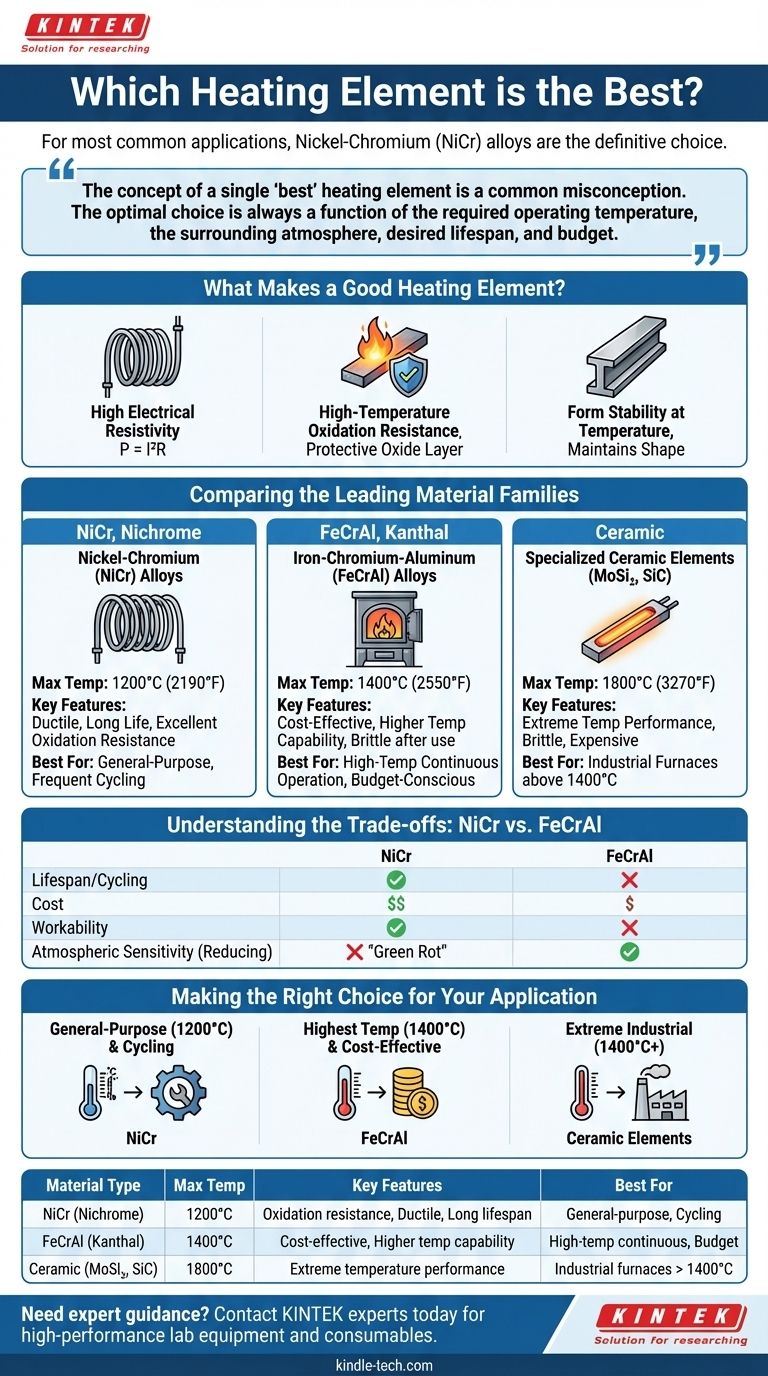
For most common applications, Nickel-Chromium (NiCr) alloys are the definitive choice for heating elements. Their high electrical resistance allows for efficient heat generation, and more importantly, they form a stable, protective layer of chromium oxide when heated. This layer prevents the underlying metal from oxidizing and failing, granting it a long and reliable service life.
The concept of a single "best" heating element is a common misconception. The optimal choice is always a function of the required operating temperature, the surrounding atmosphere, desired lifespan, and budget. Understanding these trade-offs is the key to a successful design.

What Makes a Good Heating Element?
To select the right material, you must first understand the fundamental properties that govern its performance. A heating element's job is to convert electrical energy into heat reliably and for a long time, often under extreme conditions.
High Electrical Resistivity
A material with high resistance generates significant heat with less current, as described by the formula for power: P = I²R (Power = Current² x Resistance). This allows for elements of a practical size and shape; a low-resistance material would need to be impractically long or thin to generate the same amount of heat.
High-Temperature Oxidation Resistance
This is arguably the most critical property. When heated in the presence of air, metals react with oxygen (oxidize). A good heating element material forms a thin, adherent, and protective oxide layer on its surface. This layer acts as a barrier, preventing oxygen from reaching the fresh metal underneath, which dramatically slows down degradation and burnout.
Form Stability at Temperature
The material must not melt, sag, or become excessively brittle at its intended operating temperature. It needs to maintain its physical shape and structural integrity through thousands of heating and cooling cycles.
Comparing the Leading Material Families
While NiCr is the famous workhorse, it is not the only option. Different material families are optimized for different performance windows.
Nickel-Chromium (NiCr) Alloys
Often known by the trade name Nichrome, this family is the industry standard for a reason. NiCr alloys (typically 80% nickel, 20% chromium) are highly ductile and maintain their strength well when hot. Their protective chromium-oxide layer gives them excellent service life in applications up to 1200°C (2190°F).
Iron-Chromium-Aluminum (FeCrAl) Alloys
Commonly known by the trade name Kanthal, these alloys offer a compelling alternative. By replacing expensive nickel with an iron base, FeCrAl alloys are more cost-effective. They also form an aluminum-oxide layer, which has a higher melting point, allowing them to be used at temperatures up to 1400°C (2550°F).
Specialized Ceramic Elements (MoSi₂, SiC)
For extreme industrial furnaces operating above 1400°C, metallic alloys are no longer suitable. Materials like Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) and Silicon Carbide (SiC) are used. These are ceramic-based elements that can operate reliably at temperatures approaching 1800°C (3270°F), but they are significantly more brittle and expensive.
Understanding the Trade-offs: NiCr vs. FeCrAl
For most projects, the decision comes down to NiCr and FeCrAl. Choosing between them requires a clear understanding of their respective strengths and weaknesses.
Lifespan and Cycling
While FeCrAl can reach higher temperatures, NiCr often has a longer service life in applications with frequent on-off cycling. FeCrAl alloys can become brittle after repeated heating, whereas NiCr retains more of its ductility.
Cost
FeCrAl is consistently less expensive than NiCr. The primary driver for this is the cost difference between its iron base and the nickel base used in NiCr alloys.
Workability
NiCr alloys are more ductile and easier to work with. They are less prone to cracking or breaking when being formed into coils. FeCrAl's tendency to become brittle after use can also complicate maintenance or repair.
Atmospheric Sensitivity
In certain reducing atmospheres (low oxygen), NiCr alloys can suffer from "green rot," a type of corrosion that can lead to premature failure. FeCrAl alloys are generally more resistant to these specific conditions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the optimal element, align the material's strengths with your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heating up to 1200°C and long-term reliability in cycling applications: Nickel-Chromium (NiCr) is the most proven and balanced choice.
- If your primary focus is reaching the highest possible temperature (up to 1400°C) at a lower cost, especially in continuous operation: Iron-Chromium-Aluminum (FeCrAl) is the superior economic and performance option.
- If your primary focus is extreme industrial furnace applications above 1400°C: You must invest in specialized ceramic elements like Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) or Silicon Carbide (SiC).
Ultimately, matching the material to the specific demands of the temperature, atmosphere, and duty cycle is the defining characteristic of a successful design.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Max Temp | Key Features | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| NiCr (Nichrome) | 1200°C (2190°F) | Excellent oxidation resistance, ductile, long lifespan | General-purpose heating, frequent cycling |
| FeCrAl (Kanthal) | 1400°C (2550°F) | Cost-effective, higher temp capability | High-temp continuous operation, budget-conscious projects |
| Ceramic (MoSi₂, SiC) | 1800°C (3270°F) | Extreme temperature performance | Industrial furnaces above 1400°C |
Need expert guidance to select the perfect heating element for your lab equipment?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific research and industrial needs. Whether you're working with standard NiCr alloys or require advanced ceramic elements for extreme temperatures, our team can help you optimize your heating system for reliability, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
Contact our experts today to discuss your application requirements and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your laboratory's performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
People Also Ask
- What material is used for furnace heating? Select the Right Element for Your Process
- Which high temperature furnace elements to be used in oxidizing atmosphere? MoSi2 or SiC for Superior Performance
- What is the thermal expansion coefficient of molybdenum disilicide? Understanding its role in high-temperature design
- What is the temperature range of molybdenum disilicide heating elements? Choose the Right Grade for Your High-Temp Needs
- What are the heating elements for high temperature furnaces? Select the Right Element for Your Atmosphere











