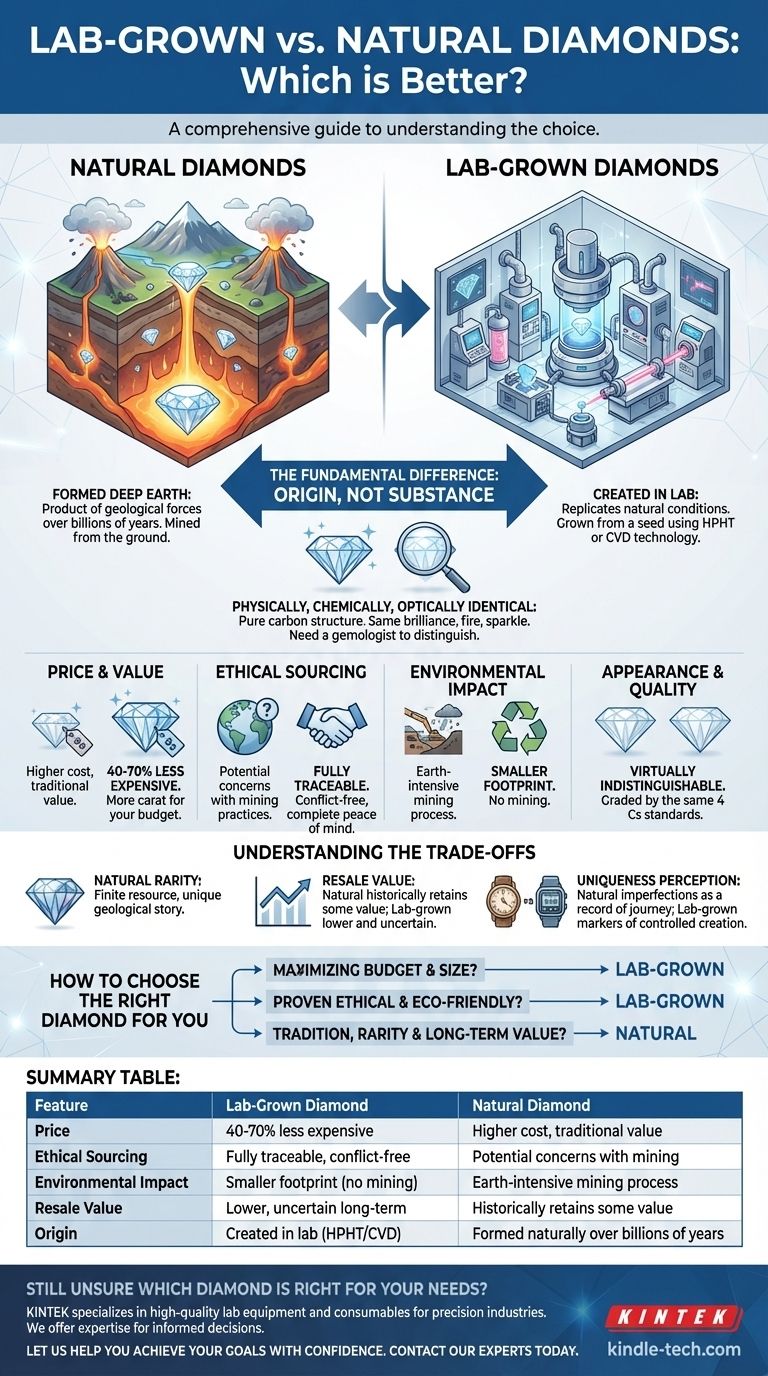
Choosing between a lab-grown and a natural diamond is less about determining which is "better" and more about understanding which is right for you. Physically, chemically, and optically, they are the same material. The choice hinges entirely on their origin story and what you value most: the rarity and tradition of a stone mined from the earth or the modern benefits of a stone created in a lab.
The core decision is not about the diamond's quality or appearance—they are identical to the naked eye. The choice is between the story of natural rarity versus the tangible benefits of price, size, and ethical peace of mind offered by lab-grown diamonds.

The Fundamental Difference: Origin, Not Substance
The only true distinction between these two diamonds is how they were formed. This single difference in origin is the source of all other considerations, from price to ethics.
How Natural Diamonds Are Formed
Natural diamonds are a product of immense geological forces. They formed deep within the Earth's mantle over billions of years under extreme heat and pressure before being brought to the surface by volcanic eruptions.
How Lab-Grown Diamonds Are Created
Lab-grown diamonds are created in highly controlled environments that replicate the conditions under which natural diamonds form. Using advanced technology, a small diamond "seed" is exposed to high pressure and high temperature (HPHT) or chemical vapor deposition (CVD) to grow into a complete diamond.
The Result: An Identical Gemstone
The end product of both processes is a stone with the same crystal structure and chemical composition. Both are pure carbon, and both can have inclusions or imperfections that affect their clarity grade. A trained gemologist is required to tell them apart.
Comparing the Key Deciding Factors
Because the stones are physically identical, the practical differences emerge in factors that surround the diamond itself.
Price and Value
This is the most significant differentiator for most buyers. Lab-grown diamonds typically cost 40-70% less than natural diamonds of the same size and quality. This allows you to purchase a significantly larger or higher-quality diamond within the same budget.
Ethical Sourcing
The origin of lab-grown diamonds is fully traceable, eliminating any concern about conflict diamonds or unethical labor practices associated with parts of the mining industry. This provides complete peace of mind.
Environmental Impact
Diamond mining is an earth-intensive process. Creating diamonds in a lab bypasses the need for mining, resulting in a substantially smaller environmental footprint.
Appearance and Quality
To the naked eye, a lab-grown diamond and a natural diamond of the same grade are virtually indistinguishable. They share the same brilliance, fire, and sparkle and are graded by gemological labs using the exact same standards (the 4 Cs).
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a lab-grown diamond is not without its considerations. Objectivity requires acknowledging what you may be giving up.
The Argument for Rarity
Natural diamonds are a finite resource, created by the Earth over an immense timescale. This inherent rarity gives them a unique story and a traditional romanticism that a manufactured product cannot replicate.
The Question of Resale Value
Historically, natural diamonds have held a portion of their value over time. The market for lab-grown diamonds is much newer, and as production technology improves and costs decrease, their long-term resale value is uncertain and generally expected to be significantly lower than that of natural diamonds.
The Perception of Uniqueness
While both types have imperfections, the inclusions in a natural diamond are a record of its unique geological journey. The subtle variations in a lab-grown diamond's crystal structure are markers of its controlled creation process. To some, the former holds more charm.
How to Choose the Right Diamond for You
The "better" diamond is the one that aligns with your personal priorities and budget.
- If your primary focus is maximizing your budget for a larger, higher-quality stone: Lab-grown is the definitive choice, offering more carat for your dollar.
- If your primary focus is on proven ethical and environmental sourcing: Lab-grown provides a clear and traceable path from creation to purchase.
- If your primary focus is on tradition, rarity, and potential long-term value retention: A natural diamond remains the traditional and established option.
Ultimately, the best choice is the one that allows you to acquire a beautiful stone that perfectly reflects your personal values.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Lab-Grown Diamond | Natural Diamond |
|---|---|---|
| Price | 40-70% less expensive | Higher cost, traditional value |
| Ethical Sourcing | Fully traceable, conflict-free | Potential concerns with mining practices |
| Environmental Impact | Smaller footprint (no mining) | Earth-intensive mining process |
| Resale Value | Lower, uncertain long-term | Historically retains some value |
| Origin | Created in lab (HPHT/CVD) | Formed naturally over billions of years |
Still unsure which diamond is right for your needs?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, supporting industries that rely on precision materials like diamonds. Whether you're a researcher, jeweler, or manufacturer, we offer the tools and expertise to help you make informed decisions.
Let us help you achieve your goals with confidence. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your work.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- How does microwave induced plasma work? A Complete Guide to MIP Technology
- What are the advantages of microwave plasma? Faster, Purer Processing for Demanding Applications
- Do lab grown diamonds pass a diamond tester? Yes, They're Chemically Identical.
- What industries use diamonds? Beyond Jewelry, They Power Modern Industry
- What advantages does a Multimode Cavity (MCC) reactor offer for large-area diamond films? Scale Beyond 4-Inch Wafers
- What is the future value of lab grown diamond? Understanding Its Depreciating Financial Worth
- What is the growth rate of CVD diamond? Discover the Secret to High-Purity Lab-Grown Gems
- How are lab-grown diamonds created? Discover the HPHT and CVD Manufacturing Process



















