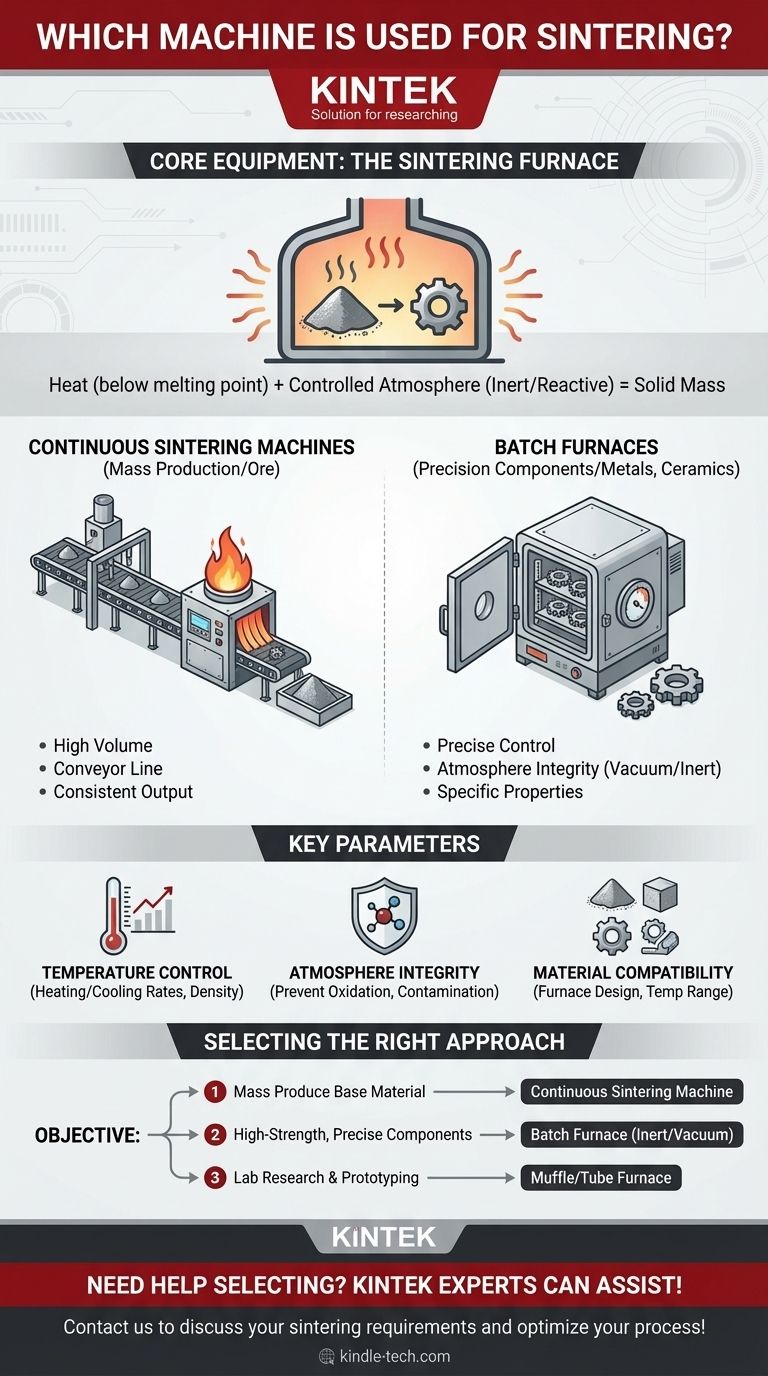
At its core, sintering is performed in a high-temperature furnace. The specific type of machine used, however, varies significantly based on the material and the scale of production. For large-scale industrial processes like ore treatment, a specialized "sintering machine" is used, while for creating precise components, various types of batch furnaces are employed.
The term "sintering machine" doesn't refer to a single device. Instead, it describes a category of equipment whose primary function is to provide precise control over temperature and atmosphere to fuse powdered materials into a solid mass without melting them.
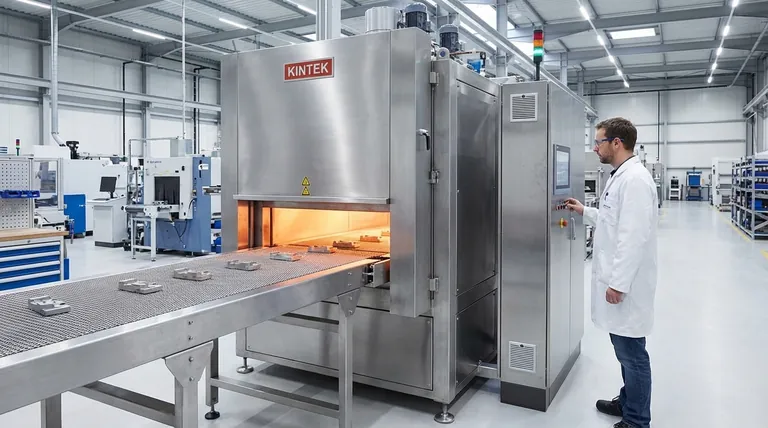

The Core Equipment: The Sintering Furnace
Sintering fundamentally relies on thermal energy to bond particles. The furnace is the equipment that delivers this energy in a highly controlled environment.
The Function of Heat
The primary role of any sintering machine is to heat a material to a temperature below its melting point. This thermal energy allows atoms to diffuse across the boundaries of the particles, fusing them together and creating a solid, coherent piece.
The Critical Role of Atmosphere
Most sintering processes cannot happen in open air. The high temperatures would cause the material, especially metals, to oxidize and degrade.
To prevent this, sintering furnaces are designed to maintain a specific atmosphere. This is often an inert or protective atmosphere (like argon or nitrogen) or a reactive one (like hydrogen) that helps remove surface oxides, as noted in the references.
Types of Sintering Machines for Different Applications
The right equipment is dictated by the end goal, whether it's processing tons of raw material or creating a small, intricate gear.
Continuous Sintering Machines
For mass production of raw materials like iron ore, a continuous sintering machine is used. This is a large piece of industrial equipment that operates like a moving production line.
A mixture of materials moves along a conveyor and passes under an igniter, which provides the initial intense heat to start the sintering process. This setup is designed for high volume and consistent output.
Batch Furnaces
For creating finished or near-finished parts from powdered metals or ceramics, batch furnaces are the standard. Materials are loaded into the furnace, the sintering cycle is run, and the finished parts are removed.
These furnaces offer extremely precise control over temperature and atmosphere, which is essential for achieving the desired mechanical properties in components like gears, bearings, and structural parts.
Common Furnace Examples
Several types of furnaces are used for batch sintering. A muffle furnace, while also used for processes like ashing, can be used for basic sintering. More advanced applications use specialized vacuum furnaces or controlled-atmosphere belt furnaces to ensure the highest purity and part quality.
Understanding the Key Parameters
Success in sintering depends on the machine's ability to precisely manage several variables. The choice of machine is often based on how well it can control these factors for a specific material.
Temperature Control
Achieving the exact temperature profile—heating rate, holding time, and cooling rate—is the most critical function. This determines the final density and strength of the sintered part.
Atmosphere Integrity
The furnace must prevent leaks that could introduce oxygen or other contaminants. For materials like stainless steel or bronze, even a small amount of oxygen can ruin the final product.
Material Compatibility
The materials being processed dictate the type of machine needed. Sintering ceramics requires extremely high temperatures, while some polymers can be sintered at much lower temperatures, influencing furnace design and construction.
Selecting the Right Sintering Approach
To choose the correct equipment, you must first define your objective.
- If your primary focus is mass-producing a base material like iron ore: A continuous sintering machine with an ignition system is the necessary industrial tool.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing high-strength, precise metal or ceramic components: A batch furnace with excellent atmosphere control is the correct choice.
- If your primary focus is lab-scale research or rapid prototyping: A versatile and smaller muffle furnace or tube furnace is often the most practical option.
Ultimately, selecting the right machine is about matching the equipment's control capabilities to the specific demands of your material and production goals.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Machine Type | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Large-Scale Ore Processing | Continuous Sintering Machine | High volume, conveyor belt, ignition system |
| Precision Components (Metals/Ceramics) | Batch Furnace | Precise temperature & atmosphere control (inert/vacuum) |
| Lab Research & Prototyping | Muffle/Tube Furnace | Versatile, smaller scale, good for testing |
Need help selecting the perfect sintering furnace for your application?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you choose a furnace that provides the precise temperature and atmosphere control your materials require, whether for R&D or production.
Contact us today to discuss your sintering requirements and optimize your process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the byproducts of pyrolysis oil? Unlocking the Value of Biochar and Syngas
- What safety precautions would you have to consider during quench? Ensure Safe Vacuum Oil Quenching with Nitrogen Control
- What is the principle of vacuum system? Creating a Controlled Low-Pressure Environment
- Why is a molecular pump vacuum system necessary for titanium matrix composites? Achieve $1 \times 10^{-3}$ Pa High Purity
- What role does a high-temperature experimental furnace play in the carbonization process of Magnetic Composite Carbon?
- Why is my brazing rod not sticking to copper? Master the 3 pillars for perfect brazing joints
- Which material is also used as a high temperature resistance material? Explore Advanced Ceramics & Alloys
- Why is a heating system with dynamic vacuum required for FJI-H14 activation? Ensure Peak Adsorption Performance



















