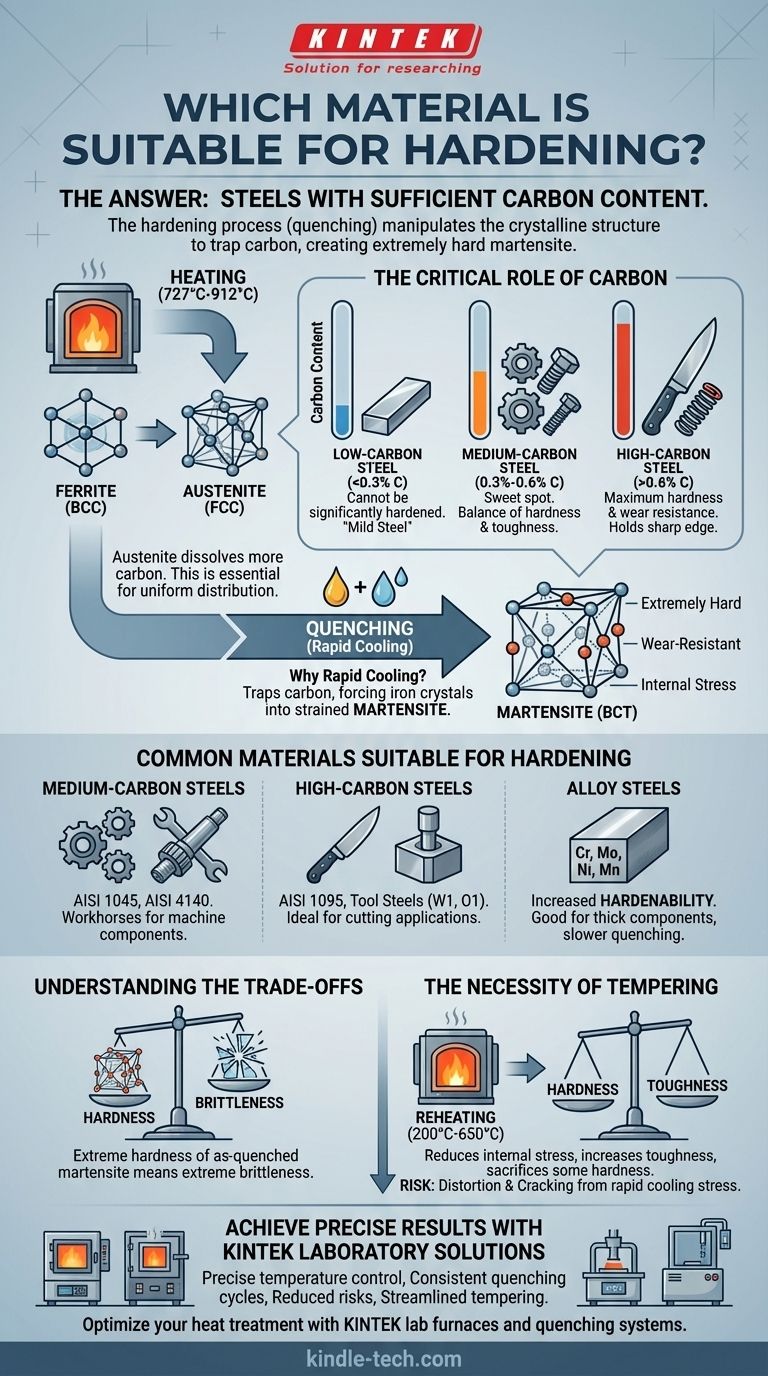
The most common and suitable materials for hardening are steels with sufficient carbon content. The process of heating, holding, and rapidly cooling—known as quenching—is specifically designed to manipulate the crystalline structure of steel. This thermal cycle traps carbon within the iron matrix, creating an extremely hard and wear-resistant structure called martensite, which is the entire goal of the hardening process.
A material's suitability for hardening is not arbitrary; it is a direct function of its chemical composition. For steel, hardenability is almost entirely dependent on having enough carbon (typically above 0.3%) to enable the formation of the hard martensitic structure upon rapid cooling.

The Fundamental Principle: Carbon and Transformation
The hardening process is a controlled phase transformation. Understanding the role of carbon is critical to selecting the right material and achieving the desired outcome.
What Happens During Heating?
When you heat steel past a critical point (typically between 727°C and 912°C), its crystal structure changes. The room-temperature structure, ferrite, transforms into a high-temperature structure called austenite.
The key difference is that austenite can dissolve significantly more carbon within its crystal lattice than ferrite can. This step is essential for distributing the carbon uniformly throughout the material before cooling.
The Critical Role of Carbon Content
The amount of carbon available for this process dictates the potential hardness.
- Low-Carbon Steel (< 0.3% C): These steels, often called "mild steel," lack sufficient carbon to form a fully martensitic structure. They cannot be significantly hardened through quenching alone.
- Medium-Carbon Steel (0.3% - 0.6% C): This is the sweet spot for many structural applications. These steels have enough carbon to achieve substantial hardness while retaining reasonable toughness after further heat treatment.
- High-Carbon Steel (> 0.6% C): These steels can achieve very high levels of hardness and are prized for their ability to hold a sharp edge and resist wear.
Why Rapid Cooling is Essential
When austenitic steel is cooled rapidly (quenched), the carbon atoms do not have time to move out of the crystal lattice as it tries to transform back to ferrite.
This "traps" the carbon, forcing the iron crystals into a highly strained, body-centered tetragonal structure known as martensite. Martensite's internal stress and distorted structure are what make it exceptionally hard and brittle.
Common Materials Suitable for Hardening
Based on the principle of carbon content, several classes of steel are routinely used for hardening.
Medium-Carbon Steels
These offer a versatile balance of strength, hardness, and toughness. They are the workhorses for machine components.
Examples include AISI 1045 and alloy steels like AISI 4140 (chromo-moly steel). They are commonly used for bolts, gears, axles, and shafts.
High-Carbon Steels
Valued for extreme hardness and wear resistance, these materials are ideal for cutting applications.
Examples include AISI 1095 (used in knives and springs) and tool steels like W1 or O1, which are designed specifically for dies, punches, and cutting tools.
Alloy Steels
Elements like chromium (Cr), molybdenum (Mo), nickel (Ni), and manganese (Mn) are added to steel for specific purposes. While they don't necessarily increase the maximum achievable hardness (which is still set by carbon), they dramatically increase hardenability.
Hardenability is the ability of the steel to form martensite deeper into the material and at slower cooling rates. This is crucial for hardening thick components or for reducing the risk of cracking from an aggressive quench.
Understanding the Trade-offs of Hardening
Hardening is not a "free" upgrade; it involves critical compromises that must be managed.
Hardness vs. Brittleness
The primary trade-off is that the extreme hardness of as-quenched martensite comes at the cost of extreme brittleness. A fully hardened, untempered steel part is often too fragile for any practical use and can shatter like glass under impact.
The Necessity of Tempering
Because of this brittleness, nearly all hardened steel parts undergo a second heat treatment called tempering. The part is reheated to a much lower temperature (e.g., 200°C - 650°C) and held for a period.
Tempering reduces internal stresses and allows the martensite to transform into a more stable structure, sacrificing a small amount of hardness for a significant gain in toughness. The final properties are controlled by the tempering temperature.
Risk of Distortion and Cracking
The rapid cooling and massive volume change during the transformation to martensite create immense internal stress. This stress can cause parts to warp, distort, or even crack during the quenching process, especially with complex geometries or very fast quench rates (like with water).
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your material selection must be guided by the final properties your component requires.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose strength and moderate hardness: A medium-carbon steel like 1045 or an alloy steel like 4140 is your ideal starting point.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness and wear resistance for cutting edges: A high-carbon steel like 1095 or a dedicated tool steel (e.g., W-series or O-series) is necessary.
- If your primary focus is hardening thick sections or reducing distortion risk: An alloy steel with high hardenability (like 4140 or 4340) is required to allow for a less severe oil or air quench.
Understanding that hardenability is driven by carbon content empowers you to select the precise steel that balances hardness, toughness, and processability for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Carbon Content | Key Characteristics | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low-Carbon Steel | < 0.3% C | Cannot be significantly hardened | General fabrication, structural components |
| Medium-Carbon Steel | 0.3% - 0.6% C | Good balance of hardness and toughness | Gears, axles, bolts, shafts (e.g., AISI 1045, 4140) |
| High-Carbon Steel | > 0.6% C | Maximum hardness and wear resistance | Knives, cutting tools, springs (e.g., AISI 1095, O1 tool steel) |
| Alloy Steels | Varies | Increased hardenability for thicker sections | Critical components requiring deep hardening (e.g., 4340) |
Achieve Precise Hardening Results with KINTEK Laboratory Solutions
Selecting the right material is only the first step—achieving consistent, controlled hardening requires precise thermal processing equipment. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and quenching systems designed for metallurgical applications like heat treatment and hardening.
Our equipment helps you:
- Maintain exact temperature control for proper austenitizing
- Execute consistent quenching cycles to achieve optimal martensite formation
- Reduce distortion and cracking risks with programmable cooling rates
- Streamline your tempering process for the perfect balance of hardness and toughness
Whether you're working with medium-carbon steels for structural components or high-carbon tool steels for cutting applications, KINTEK has the laboratory equipment to support your hardening processes.
Ready to optimize your heat treatment results? Contact our thermal processing experts today to discuss how our laboratory furnaces and quenching systems can enhance your hardening operations.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- High Purity Zinc Foil for Battery Lab Applications
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer Corrosion Resistant Cleaning Rack Flower Basket
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Containers
People Also Ask
- What is the strongest ceramics? Silicon Carbide Leads in Hardness & Thermal Strength
- What is the temperature resistance of silicon carbide? Withstands Extreme Heat Up to 1500°C
- Is silicon carbide better than ceramic? Discover the Superior Technical Ceramic for Your Application
- What is the thermal expansion of SiC? Master Its Low CTE for Superior High-Temp Performance
- Which is harder silicon carbide or tungsten carbide? Discover the Key to Material Selection



















