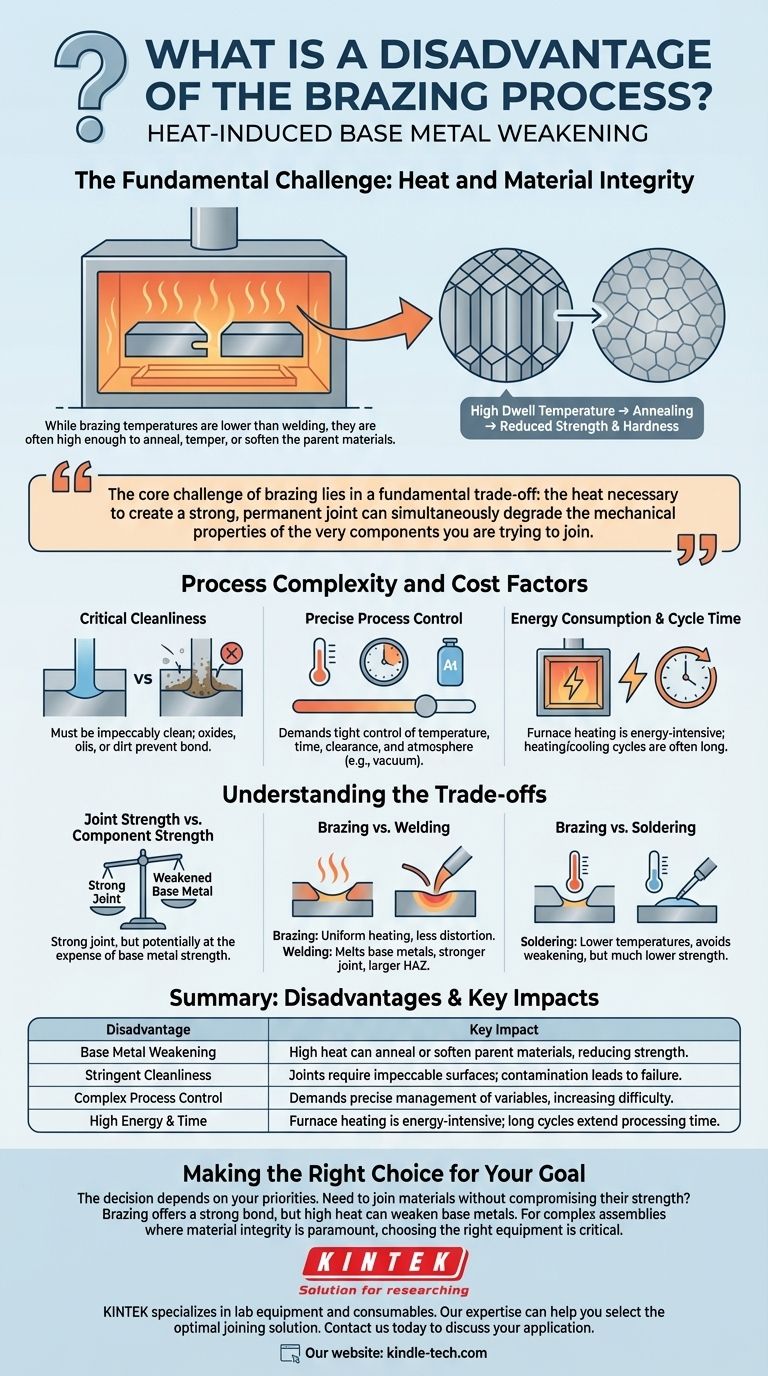
A primary disadvantage of the brazing process is the potential for the high heat required to weaken or otherwise negatively alter the metallurgical properties of the base metals being joined. While brazing temperatures are lower than welding, they are often high enough to anneal, temper, or soften the parent materials, which can compromise the overall strength of the finished assembly.
The core challenge of brazing lies in a fundamental trade-off: the heat necessary to create a strong, permanent joint can simultaneously degrade the mechanical properties of the very components you are trying to join.

The Fundamental Challenge: Heat and Material Integrity
To understand the disadvantages, we must first look at how the process works. Brazing relies on heat to achieve a bond, and this heat has consequences.
How Brazing Works
Brazing uses a filler metal (an alloy with a lower melting point than the base metals) to join two closely fitted surfaces. The assembly is heated to a temperature above the filler's melting point but below the base metals' melting point.
The molten filler is then drawn into the gap between the components via capillary action, creating a strong, permanent metallurgical bond upon cooling.
The Unintended Consequence: Reduced Material Hardness
The key issue is that this required temperature, known as the dwell temperature, is often high enough to act as a heat treatment process on the base materials.
For many metals, especially those that have been hardened through work-hardening or previous heat treatments, this exposure to high temperatures can cause annealing, a process that softens the metal and reduces its strength and hardness.
Process Complexity and Cost Factors
Beyond the primary issue of material softening, brazing presents several other practical challenges that contribute to its overall cost and difficulty.
The Critical Need for Cleanliness
Brazing joints are highly sensitive to contamination. For the filler metal to flow properly and bond with the base metals, the surfaces must be impeccably clean.
Any oxides, oils, or dirt will prevent the capillary action and result in a weak or failed joint. This necessitates intensive and often costly pre-cleaning steps.
Precise Process Control is Non-Negotiable
Brazing is not a forgiving process. It demands tight control over essential parameters, including temperature, time, joint clearance, and atmosphere (e.g., in vacuum brazing).
Failure to precisely manage these variables can lead to incomplete joint filling, erosion of the base metal, or other critical defects. This high technical requirement adds to its complexity.
Energy Consumption and Cycle Time
Heating an entire assembly to brazing temperature, often done in a furnace, is an energy-intensive process.
Furthermore, the heating and controlled cooling cycles can be quite long, extending the overall processing time and limiting throughput compared to faster joining methods like spot welding.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No joining process is perfect. The disadvantages of brazing must be weighed against its unique advantages to make an informed decision.
Joint Strength vs. Component Strength
The primary trade-off is clear: you gain a strong, clean, and continuous joint, but potentially at the expense of the base metals' original strength. This is unlike mechanical fasteners, which do not alter the material at all.
Brazing vs. Welding
Welding melts the base metals themselves, often creating a stronger joint but also causing significant localized stress, distortion, and a larger heat-affected zone (HAZ) that can also weaken the material. Brazing's uniform heating often results in far less distortion, a key advantage for complex or precision assemblies.
Brazing vs. Soldering
Soldering is a similar process but uses much lower temperatures and lower-strength filler metals. It avoids the issue of weakening the base metals but produces a joint with significantly lower mechanical strength.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use brazing depends entirely on your project's specific priorities and constraints.
- If your primary focus is maximum component strength: You must account for potential heat-induced softening of the base metals or choose an alternative low-temperature joining process.
- If your primary focus is joining complex shapes with minimal distortion: Brazing is an excellent choice, but you must be prepared for the stringent process controls and cleaning requirements.
- If your primary focus is creating leak-proof, continuous joints: Brazing provides superior performance compared to mechanical fastening, justifying its higher process complexity.
By understanding these inherent trade-offs, you can confidently determine if brazing is the optimal solution for your specific engineering challenge.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| Base Metal Weakening | High brazing heat can anneal or soften the parent materials, reducing their original strength and hardness. |
| Stringent Cleanliness | Joints require impeccably clean surfaces; any contamination leads to weak or failed bonds. |
| Complex Process Control | Demands precise management of temperature, time, and atmosphere, increasing technical difficulty. |
| High Energy & Time | Furnace heating is energy-intensive, and controlled cooling cycles extend processing time. |
Need to join materials without compromising their strength?
Brazing offers a strong, clean bond, but its high heat can weaken your base metals. For complex assemblies where material integrity is paramount, choosing the right equipment and process is critical.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our expertise can help you select the optimal joining solution for your specific materials and project goals, ensuring performance and reliability.
Contact us today to discuss your application and discover how we can support your success. Get in touch via our contact form.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the basic construction and temperature control mechanism of a laboratory tube furnace? Master Precision Heating for Your Lab
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis



















