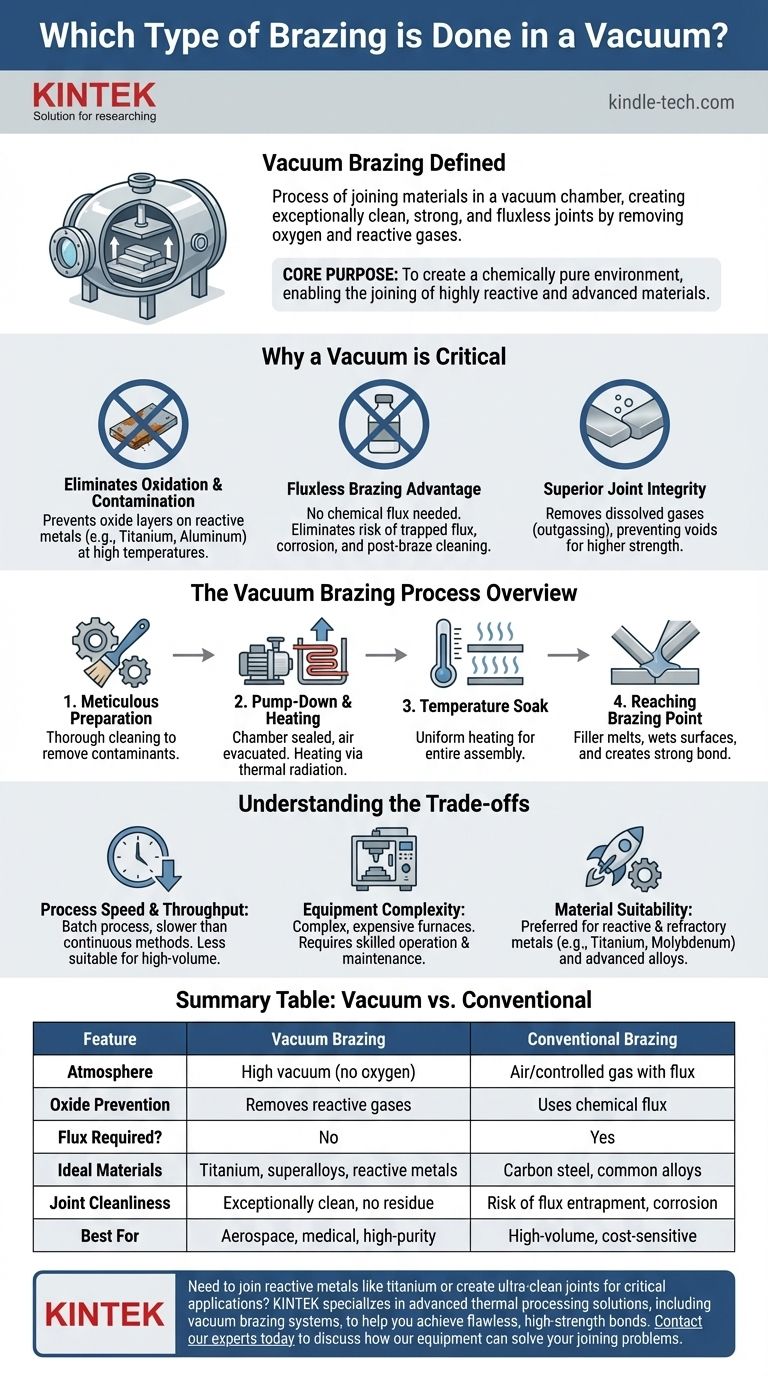
The process of brazing performed inside a vacuum chamber is known as vacuum brazing. This is a high-purity joining method where components are heated and joined using a filler metal in an environment nearly devoid of air. By removing oxygen and other reactive gases, the process prevents oxidation of the assembly, creating exceptionally clean and strong joints without the need for chemical fluxes.
The core purpose of vacuum brazing is not just to join parts, but to create a chemically pure environment. By removing air, the vacuum prevents oxidation, enabling the joining of highly reactive and advanced materials that would be impossible to process with conventional methods.

Why a Vacuum is the Critical Ingredient
Using a vacuum fundamentally changes the brazing environment. Instead of fighting against atmospheric contaminants with chemicals, you simply remove them from the equation.
Eliminating Oxidation and Contamination
At brazing temperatures, most metals react readily with oxygen. This creates oxide layers that prevent the filler metal from wetting and flowing properly, leading to a weak or failed joint.
A vacuum furnace evacuates these reactive gases. This protective, controlled atmosphere is essential when working with materials like titanium, aluminum, and nickel-based superalloys, which are highly susceptible to oxidation.
The Advantage of Fluxless Brazing
Conventional brazing methods require a chemical flux to dissolve oxides and protect the metal surfaces. However, flux can become trapped in the joint, causing corrosion and creating a potential failure point.
Vacuum brazing is a fluxless process. The clean environment means no flux is needed, which results in cleaner joints and eliminates the need for aggressive post-braze cleaning to remove corrosive flux residue.
Superior Joint Integrity
Heating in a vacuum also helps to remove dissolved volatile substances from the base metals, a process known as outgassing. This prevents gas pockets and voids from forming within the joint, leading to higher strength and structural integrity.
The Vacuum Brazing Process: An Overview
The vacuum brazing cycle is a precise, multi-stage process that prioritizes thermal uniformity and environmental purity.
Meticulous Preparation and Cleaning
Like any brazing process, success begins with cleanliness. Components undergo thorough cleaning using methods like vapor degreasing to remove any oils or contaminants that could interfere with the braze.
The Furnace Cycle: Pump-Down and Heating
Once loaded, the furnace chamber is sealed and a vacuum pump removes the air. Heating is accomplished through thermal radiation from elements made of materials like molybdenum or graphite, as convection is not possible in a vacuum.
Temperature Soak for Uniformity
The heating cycle often includes a "soak" at an intermediate temperature. This allows the entire assembly, including thick and thin sections, to reach a uniform temperature before proceeding to the final brazing heat.
Reaching the Brazing Point
The temperature is then raised to the filler metal's melting point. The vacuum environment ensures the molten filler metal wets the surfaces cleanly and is drawn into the joint by capillary action, creating a strong metallurgical bond.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum brazing is not a universal solution. It involves clear trade-offs against other methods like atmosphere-controlled or gas-shielded brazing.
Process Speed and Throughput
Vacuum brazing is a batch process. A single furnace cycle can take several hours, making it slower than continuous methods like gas-shielded brazing. This makes it less suitable for high-volume, low-cost production.
Equipment and Operational Complexity
Vacuum furnaces are complex and expensive pieces of equipment. They require careful maintenance and skilled operators to manage the precise control of vacuum levels and temperature profiles throughout the cycle.
Material Suitability
This is where vacuum brazing excels. It is the preferred—and often the only—method for joining reactive metals (titanium, zirconium), refractory metals (molybdenum, niobium), and advanced alloys used in aerospace and high-tech applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct brazing process depends entirely on your material, application requirements, and production goals.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of carbon steel parts: Conventional atmosphere brazing is likely more cost-effective and faster.
- If your primary focus is joining reactive metals like titanium or superalloys for aerospace: Vacuum brazing is the only viable method to prevent material degradation and ensure a reliable joint.
- If your primary focus is creating exceptionally clean, void-free joints for medical or scientific instruments: The fluxless, high-purity environment of vacuum brazing is essential for meeting the most stringent quality standards.
Ultimately, selecting vacuum brazing is a decision to prioritize material integrity and joint quality above all else.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Vacuum Brazing | Conventional Brazing |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere | High vacuum (no oxygen) | Air or controlled gas with flux |
| Oxide Prevention | Removes reactive gases | Uses chemical flux |
| Flux Required? | No | Yes |
| Ideal Materials | Titanium, superalloys, reactive metals | Carbon steel, common alloys |
| Joint Cleanliness | Exceptionally clean, no residue | Risk of flux entrapment and corrosion |
| Best For | Aerospace, medical, high-purity applications | High-volume, cost-sensitive production |
Need to join reactive metals like titanium or create ultra-clean joints for critical applications?
KINTEK specializes in advanced thermal processing solutions, including vacuum brazing systems and consumables, to help you achieve flawless, high-strength bonds without oxidation or flux contamination. Our expertise ensures your lab or production facility can meet the most demanding quality standards for aerospace, medical, and high-tech components.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our vacuum brazing equipment and support can solve your most challenging joining problems.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do automated precision furnaces influence Zr1Nb structural evolution? Master Hydrogenation and Polygonization
- Why is vacuum important for deposition of thin films? The Key to Purity and Control in Thin Film Coating
- How does a vacuum drying oven contribute to the preparation of cathodes for all-solid-state batteries? Pure Electrodes
- What role do industrial-grade high-temperature sintering furnaces play in the final formation of Lanthanum Zirconate?
- How is a high-vacuum or atmosphere sintering furnace utilized for nanocrystalline stainless steel thermal stability?
- What is the function of a vacuum furnace? Achieve High-Purity, Contamination-Free Thermal Processing
- What is the vacuum annealing process? Achieve Superior Material Purity and Stress Relief
- What is the function of a high-temperature vacuum annealing furnace? Optimize Your Zr2Al3C4 Coating Formation



















