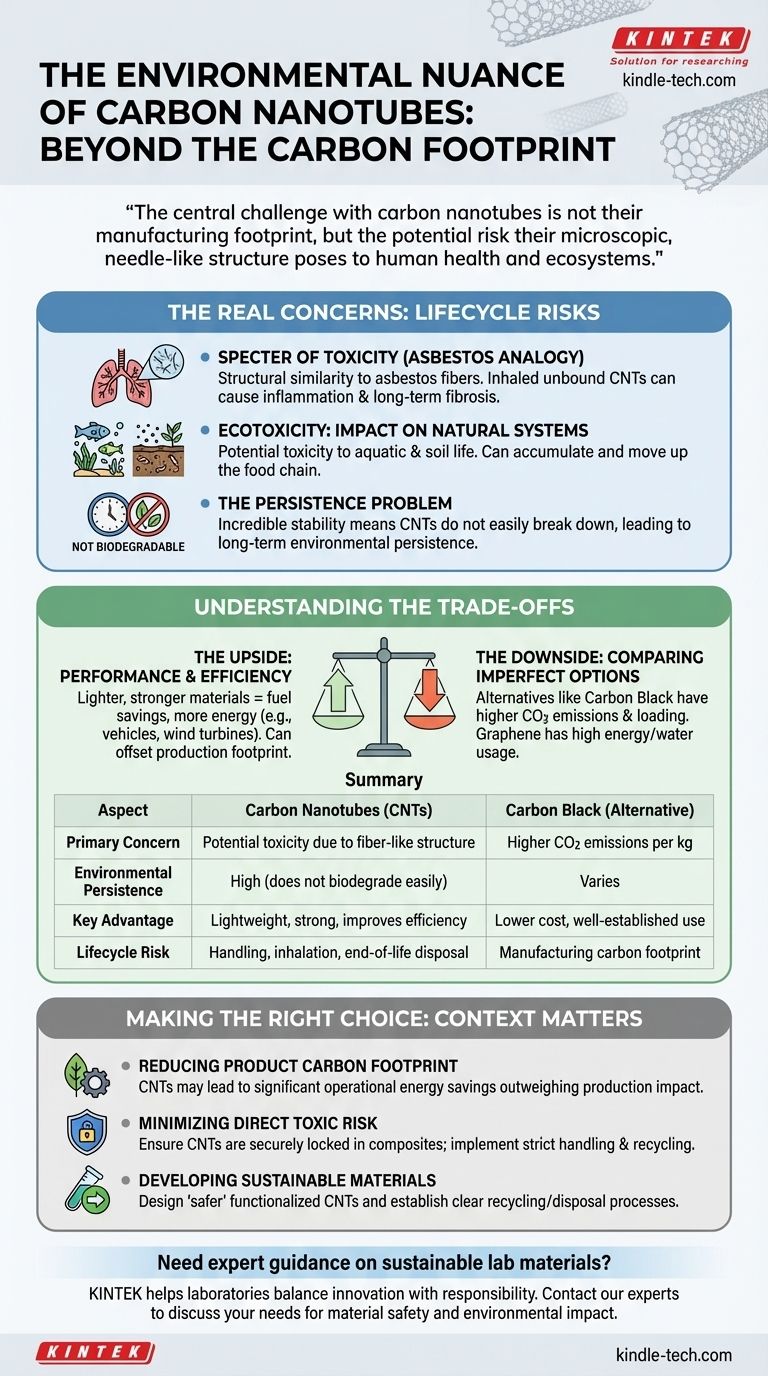
The environmental case against carbon nanotubes (CNTs) is highly nuanced. While the manufacturing of CNTs can be less carbon-intensive than common alternatives like carbon black, the primary environmental and health concerns are not about CO2. The focus of the debate is on the potential toxicity of the nanotubes themselves due to their unique physical structure and their persistence in the environment.
The central challenge with carbon nanotubes is not their manufacturing footprint, but the potential risk their microscopic, needle-like structure poses to human health and ecosystems. This creates a critical trade-off between their performance benefits and their lifecycle safety.

Beyond the Carbon Footprint: The Real Concerns
To understand the environmental and health questions surrounding CNTs, we must look beyond the factory and consider the material's entire lifecycle, from handling to end-of-life disposal.
The Specter of Toxicity: The Asbestos Analogy
The most significant concern with certain types of CNTs is their structural similarity to asbestos fibers. Materials that are long, thin, and durable (a high aspect ratio) can be difficult for the body's immune system to clear from the lungs.
If inhaled in sufficient quantities, these fibers can cause inflammation, scarring (fibrosis), and other serious long-term health effects. This risk is primarily associated with airborne, unbound CNTs, such as those that might be encountered in manufacturing or processing facilities without proper safety protocols.
Ecotoxicity: Impact on Natural Systems
When CNTs enter the environment, they can have adverse effects on ecosystems. Their small size and high surface area mean they can interact with organisms in unique ways.
Studies have shown potential toxicity to aquatic life, such as fish and algae, as well as to soil organisms. The concern is that these materials could accumulate in the environment and move up the food chain, with long-term consequences that are not yet fully understood.
The Persistence Problem: A Question of Biodegradability
Carbon nanotubes are prized for their incredible strength and stability. This durability, however, is a double-edged sword.
Because they do not break down easily, CNTs can persist in the environment for very long periods. This lack of biodegradability raises questions about their long-term accumulation in soil, water, and biological systems.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect. The decision to use CNTs involves weighing their significant advantages against their potential risks, especially when compared to the alternatives.
The Upside: Lighter, Stronger, More Efficient
The primary driver for using CNTs is their revolutionary properties. Adding a small amount of CNTs to a polymer can dramatically increase its strength while reducing its weight.
This enables the creation of lighter airplanes and vehicles that burn less fuel, more durable wind turbine blades that generate more energy, and more efficient batteries. These applications offer substantial positive environmental impacts that can offset the material's own footprint.
The Downside: Comparing Imperfect Options
While CNTs have potential toxicity risks, their alternatives are not without their own environmental baggage. As the reference data indicates, traditional materials like carbon black require higher loading percentages in composites and have higher CO2 emissions per kilogram.
Similarly, other advanced materials like graphene face their own production challenges, including high energy consumption, significant water usage, and the use of harsh chemicals. The choice is rarely between a "dirty" material and a "clean" one, but between different sets of technical and environmental trade-offs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "right" decision depends entirely on the context of the application and the priority of the user. Responsible use requires a full lifecycle assessment.
- If your primary focus is reducing the carbon footprint of an end-product: CNTs may be an excellent choice, as their use can lead to significant energy savings that far outweigh their production impact.
- If your primary focus is minimizing direct toxicological risk: You must ensure CNTs are securely locked within a composite matrix and implement strict handling protocols during manufacturing and end-of-life recycling.
- If your primary focus is developing sustainable materials: The goal should be to design "safer" CNTs (e.g., through surface functionalization to reduce toxicity) and establish clear processes for recycling or safely disposing of CNT-enabled products.
Ultimately, harnessing the power of carbon nanotubes responsibly requires a diligent focus on managing their entire lifecycle, from safe production to controlled end-of-life handling.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) | Carbon Black (Alternative) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Concern | Potential toxicity due to fiber-like structure | Higher CO2 emissions per kg |
| Environmental Persistence | High (does not biodegrade easily) | Varies |
| Key Advantage | Lightweight, strong, improves product efficiency | Lower cost, well-established use |
| Lifecycle Risk | Handling, inhalation, end-of-life disposal | Manufacturing carbon footprint |
Need expert guidance on selecting sustainable lab materials?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables, helping laboratories like yours make informed decisions about material safety, performance, and environmental impact. Whether you're researching nanomaterials or developing next-generation composites, our solutions ensure precision, safety, and compliance.
Let us help you balance innovation with responsibility. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Tube
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Centrifuge Tubes
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is Boron Nitride used in RRDE? Enhance Precision with Superior Insulating and Protective Material
- How do porcelain boats and quartz tubes function in CVD of BN? Optimize Your Boron Nitride Coating Efficiency
- What is the function of a BN inner liner in a graphite mold during Flash Sintering? Master Precise Current Control
- What are the strengths of brazing? Achieve Strong, Clean, and Precise Metal Joining
- What is the function of the ceramic tube in a DBD plasma jet? Enhancing Stability for Delicate Material Treatment



















