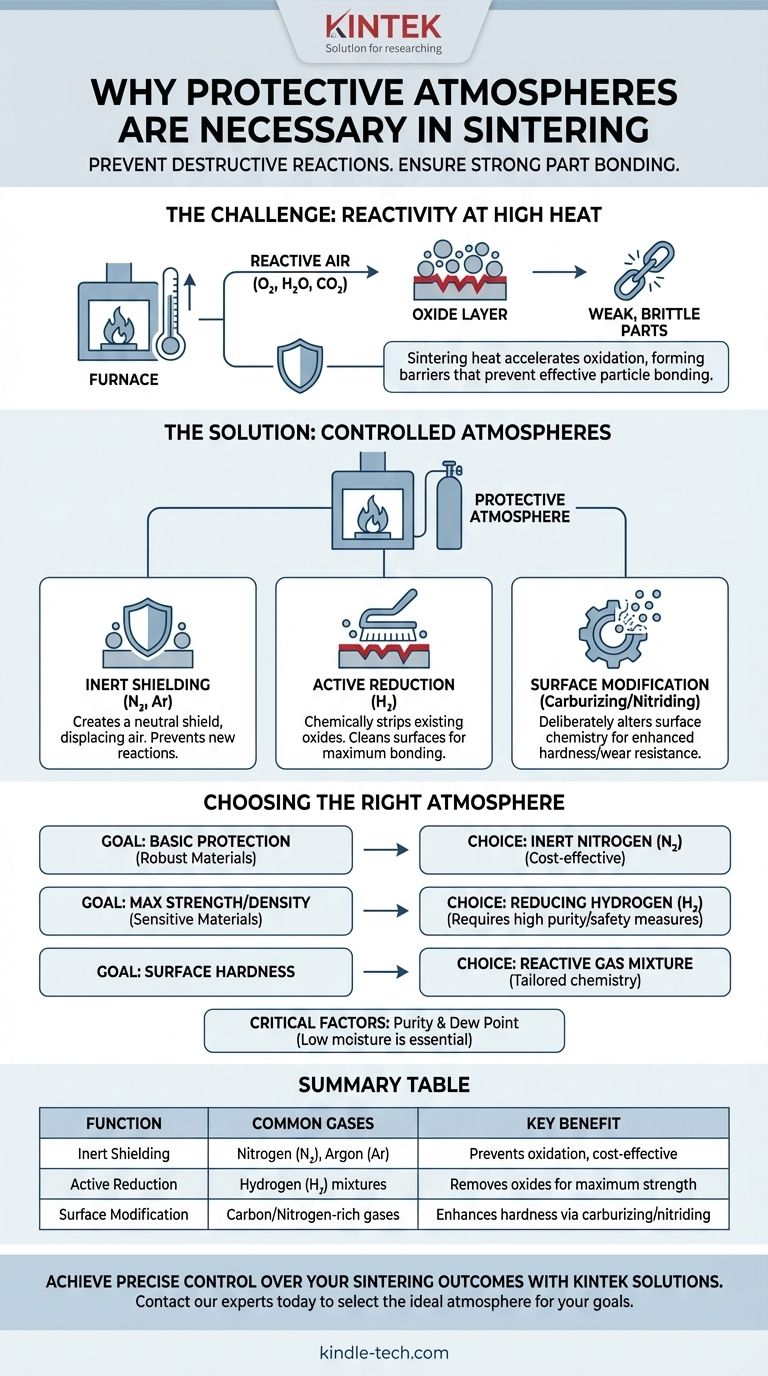
In short, protective atmospheres are necessary in sintering to prevent destructive chemical reactions, primarily oxidation, that occur at high temperatures. This controlled environment ensures that metal powder particles can bond together effectively, which is the entire goal of the process.
Sintering requires immense heat to fuse material particles, but that same heat makes those particles highly vulnerable to chemical attack from the surrounding air. A protective atmosphere replaces the reactive air with a controlled gas, acting as a chemical shield that either prevents these reactions or guides them to a desired outcome.
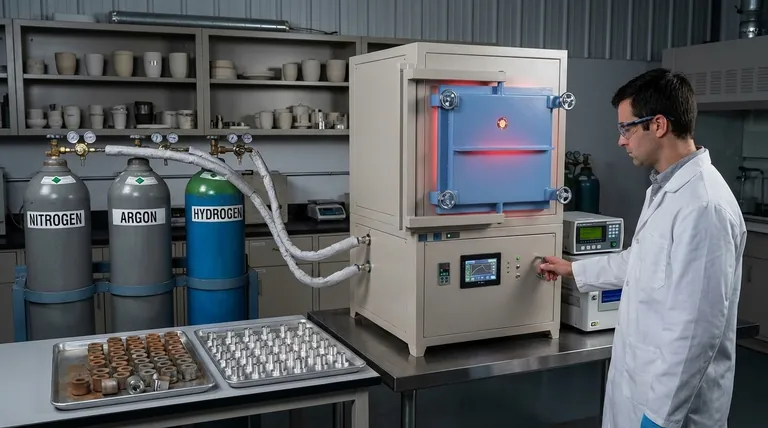

The Fundamental Challenge: Reactivity at High Temperatures
Sintering operates on a simple principle: heat a compacted powder until the particles bond and densify. However, the high temperatures required also dramatically accelerate chemical reactions, creating a significant engineering challenge.
The Primary Enemy: Oxidation
Most industrial sintering involves metal powders. When heated, these metals will readily react with any oxygen present in the atmosphere.
This reaction, called oxidation, forms a thin, hard, ceramic-like layer (an oxide) on the surface of each powder particle.
This oxide layer acts as a barrier, physically preventing the metal surfaces from making direct contact and fusing. The result is a weak, brittle part that has failed to sinter properly.
Beyond Oxygen: Other Contaminants
While oxygen is the main concern, other components of air can also be detrimental. Water vapor (humidity) and carbon dioxide are both potent oxidizing agents at sintering temperatures and must be removed or displaced to protect the material.
How Protective Atmospheres Solve the Problem
A protective atmosphere works by replacing the ambient, reactive air in the furnace with a gas or gas mixture that is either non-reactive or has a specific, desirable reactivity.
The Principle of Inertness: Creating a Shield
The simplest approach is to use an inert gas, most commonly Nitrogen (N₂) or Argon (Ar).
These gases do not chemically react with the material being sintered, even at high temperatures. They work by simply displacing the oxygen and moisture, creating a neutral "shield" around the parts.
The Principle of Reduction: Actively Cleaning Surfaces
A more powerful approach involves a reducing atmosphere, which typically contains Hydrogen (H₂).
Hydrogen not only prevents new oxidation but can also actively reverse it. It chemically strips oxygen atoms from any existing oxide layers on the powder surfaces, turning them into water vapor (H₂O) which is then flushed from the furnace.
This "cleaning" action ensures a pristine metallic surface, which is critical for achieving maximum density and strength in the final part, especially with easily oxidized materials.
Deliberate Reactions: Modifying the Surface
Sometimes, the goal isn't just to protect the surface but to intentionally change it. Specific gas mixtures can be used to diffuse elements into the material's surface.
For example, an atmosphere rich in carbon (a carburizing atmosphere) can be used to create a hard, wear-resistant steel surface on a part. Similarly, a nitrogen-rich atmosphere can be used for nitriding. In these cases, the atmosphere becomes a key part of the material's design.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right atmosphere is a balance of technical requirements, safety, and cost. There is no single "best" atmosphere for all applications.
Inert vs. Reducing Atmospheres
An inert atmosphere like pure Nitrogen is safe, relatively low-cost, and effective for preventing oxidation in less-sensitive materials.
A reducing atmosphere containing Hydrogen is more effective for creating high-purity, high-density parts, but it introduces the cost and safety complexities of handling a flammable gas.
The Critical Role of Purity and Dew Point
The effectiveness of any protective atmosphere hinges on its purity. Even a Nitrogen atmosphere can become oxidizing if it contains too much moisture or trace oxygen.
The dew point of the gas is a critical measure of its moisture content. A low dew point indicates a very dry gas, which is essential for preventing unwanted reactions during the high-temperature sintering cycle.
Cost and System Complexity
Pure Argon provides the most inert shield but is significantly more expensive than Nitrogen. Hydrogen systems require sophisticated flow controls, safety interlocks, and burn-off systems, increasing the initial investment and operational complexity of the furnace.
Selecting the Right Atmosphere for Your Goal
Your choice of atmosphere depends directly on the material you are working with and the final properties you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is basic oxidation prevention for robust materials (like some copper alloys): An inert Nitrogen atmosphere is often the most cost-effective and sufficient choice.
- If your primary focus is maximum density and strength for sensitive materials (like stainless steels or tungsten): A reducing atmosphere containing Hydrogen is necessary to clean surface oxides and ensure strong metallic bonding.
- If your primary focus is enhancing surface hardness and wear resistance: A reactive atmosphere designed for carburizing or nitriding is required to achieve the desired surface chemistry.
Ultimately, controlling the furnace atmosphere is equivalent to controlling the fundamental chemistry of your process, giving you direct command over the final quality of the sintered component.
Summary Table:
| Function | Common Gases Used | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Inert Shielding | Nitrogen (N₂), Argon (Ar) | Prevents oxidation, cost-effective |
| Active Reduction | Hydrogen (H₂) mixtures | Removes existing oxides for maximum strength |
| Surface Modification | Carbon/Nitrogen-rich gases | Enhances hardness via carburizing/nitriding |
Achieve precise control over your sintering outcomes. The right protective atmosphere is critical for part density, strength, and surface properties. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing solutions for all your laboratory sintering needs. Let our experts help you select the ideal atmosphere for your material and goals. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your process and ensure high-quality results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
People Also Ask
- What is the role of an atmosphere-controlled tube furnace in Cu-Mo sintering? Achieve High-Purity Densification
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes
- Can nitrogen be used for brazing? Key Conditions and Applications Explained
- What gases are used in inert atmospheres? Choose the Right Gas for Non-Reactive Environments
- What is an example of an inert atmosphere? Discover the Best Gas for Your Process



















