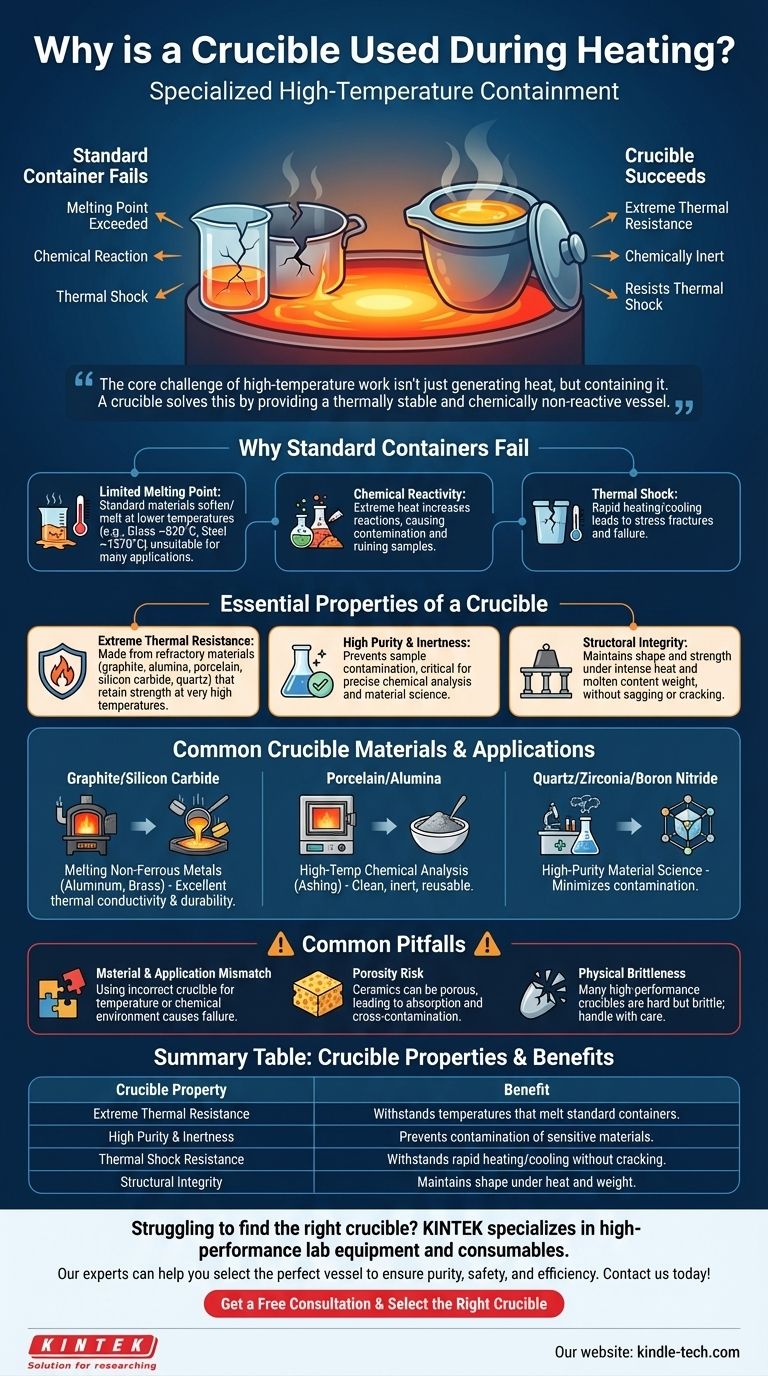
In short, a crucible is used during heating because it is a specialized container engineered to withstand extreme temperatures that would melt or destroy standard vessels. Its purpose is to safely hold materials, like metals or chemical compounds, as they are heated, melted, or chemically altered without breaking, melting, or contaminating the contents.
The core challenge of high-temperature work isn't just generating heat, but containing it. A crucible solves this by providing a thermally stable and chemically non-reactive vessel, ensuring the integrity of both the sample and the process.
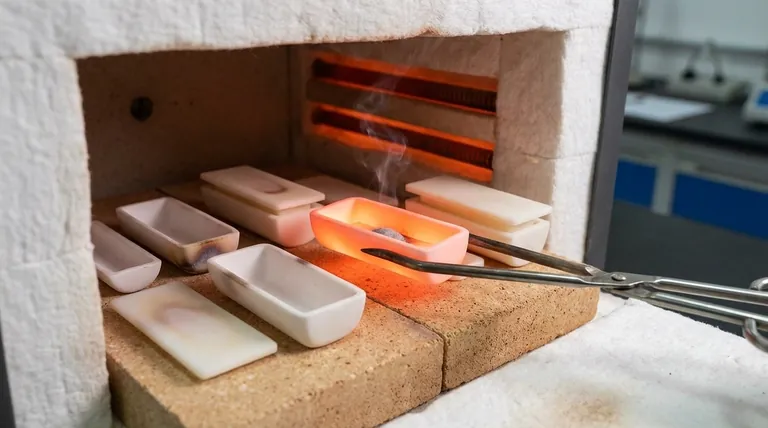

Why a Standard Container Fails
To understand the crucible's role, we must first consider why an ordinary container, like a glass beaker or a steel pot, is unsuitable for many high-temperature applications.
Limited Melting Point
The most obvious limitation is the melting point. A standard borosilicate glass beaker softens around 820°C (1508°F), and steel melts around 1370°C (2500°F). These temperatures are far too low for melting materials like copper (1084°C), iron (1538°C), or silica (1710°C).
Chemical Reactivity
Even if a container doesn't melt, extreme heat dramatically increases the rate of chemical reactions. A hot metal pot could react with its contents, introducing impurities and ruining the sample. A crucible is selected for its chemical inertness at high temperatures.
Thermal Shock
Rapidly heating or cooling a standard container causes it to expand or contract unevenly, leading to stress fractures and catastrophic failure. Crucibles are made from materials specifically chosen for their ability to resist this thermal shock.
The Essential Properties of a Crucible
A crucible is not defined by a single material but by a set of critical properties. The choice of crucible material depends entirely on the specific process it will be used for.
Extreme Thermal Resistance
This is the primary characteristic. Crucibles are made from refractory materials—substances that retain their strength at very high temperatures. Common materials include graphite, alumina, porcelain, silicon carbide, and quartz. Each has a different maximum operating temperature.
High Purity and Inertness
The crucible must not become part of the experiment. For applications in metallurgy or material science, preventing contamination from the container is critical. Materials like high-purity alumina or quartz are used when the final product's chemical composition must be precise.
Structural Integrity
A crucible must remain physically stable and strong even when incandescent. It cannot sag, warp, or crack under the combined stress of intense heat and the weight of its molten contents.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
While essential, using a crucible is not without its challenges. Understanding these limitations is key to successful high-temperature work.
Material and Application Mismatch
Using the wrong crucible for the job is the most common mistake. For example, using a porcelain crucible in a process that requires a temperature above its limit will cause it to fail. Likewise, melting a reactive metal in a crucible it can corrode will destroy both the sample and the equipment.
The Risk of Porosity
Some ceramic crucibles can be slightly porous. This can lead to the absorption of molten material, causing cross-contamination between different batches or weakening the crucible's structure over time.
Physical Brittleness
Many high-performance ceramic crucibles are extremely hard but also very brittle. Dropping one or subjecting it to mechanical impact can easily cause it to shatter. They require careful handling.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct crucible is a critical decision based entirely on the intended application.
- If your primary focus is melting common, non-ferrous metals like aluminum or brass: A clay-graphite or silicon carbide crucible offers excellent thermal conductivity and durability for furnace use.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature chemical analysis (like ashing a sample): A porcelain or alumina crucible provides a clean, inert, and reusable option suitable for most laboratory muffle furnaces.
- If your primary focus is high-purity material science or melting reactive metals: A specialized, high-purity vessel made of quartz, zirconia, or pyrolytic boron nitride is necessary to minimize contamination.
Ultimately, a crucible is more than just a bowl; it is a critical piece of technical equipment engineered to provide stability in an environment of extreme heat.
Summary Table:
| Crucible Property | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Extreme Thermal Resistance | Withstands temperatures that melt standard containers (e.g., glass, steel). |
| High Purity & Inertness | Prevents contamination of sensitive materials like metals or chemicals. |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Can withstand rapid heating or cooling without cracking. |
| Structural Integrity | Maintains shape and strength under intense heat and weight of molten contents. |
Struggling to find the right crucible for your specific high-temperature application? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including a wide range of crucibles made from materials like alumina, quartz, graphite, and silicon carbide. Our experts can help you select the perfect vessel to ensure purity, safety, and efficiency in your processes—whether you're melting metals, conducting chemical analysis, or developing new materials. Contact us today to discuss your needs and enhance your lab's capabilities!
Get a Free Consultation & Select the Right Crucible
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Custom Machined and Molded PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer with PTFE Crucible and Lid
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- What role does an Alumina Crucible play in the high-temperature solid-state synthesis of Na3OBr? Ensure Sample Purity
- Why is the use of high-purity alumina crucibles necessary for NMC powders? Ensure Purity in Cathode Synthesis
- What are the advantages of selecting an alumina crucible for TGA? Ensure High-Precision Thermal Analysis Data
- Why is a high-purity alumina crucible preferred for high-temperature oxidation? Ensure Unmatched Data Integrity
- Why are high-purity alumina crucibles used for LATP? Preserve Purity and Conductivity in Sintering



















