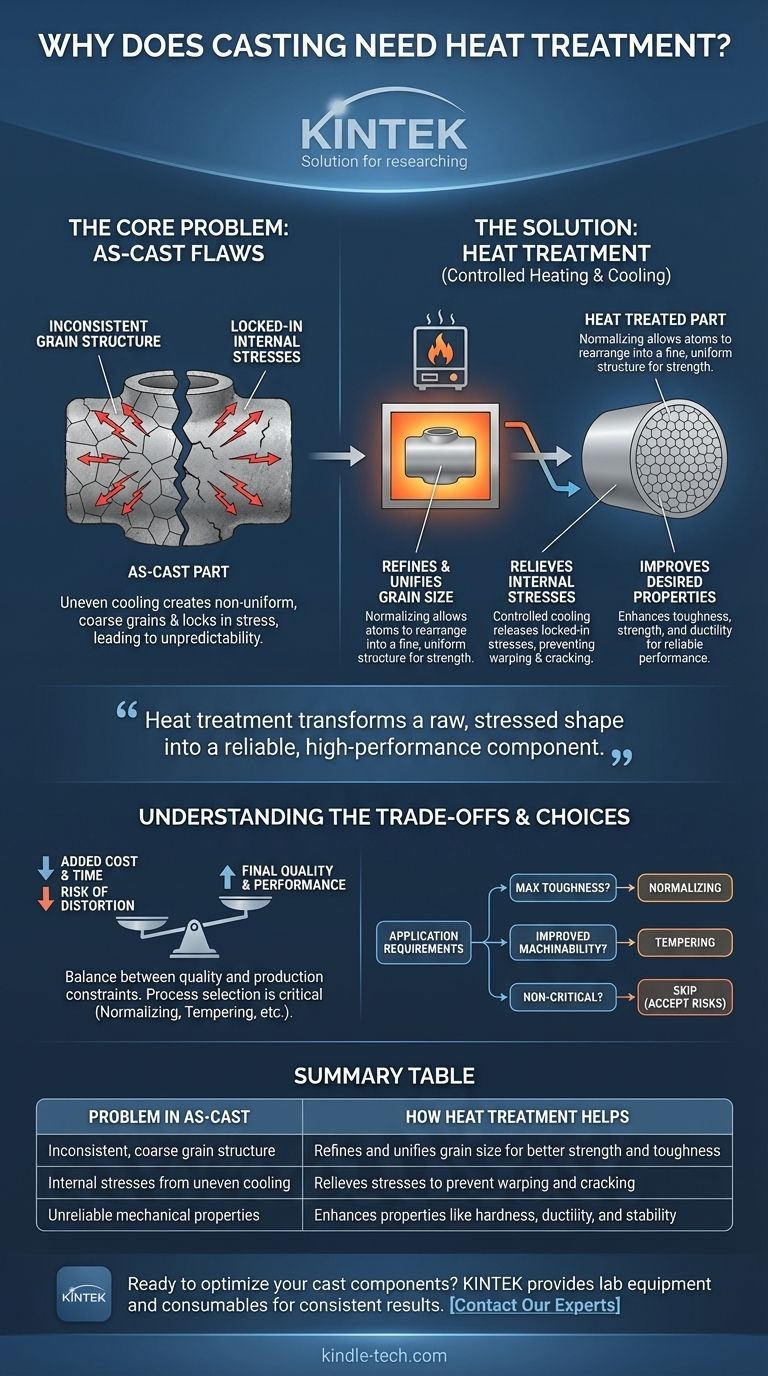
Simply put, a metal casting needs heat treatment to correct the structural imperfections and internal stresses created during the casting process. Through controlled heating and cooling, heat treatment refines the metal's internal grain structure to improve critical properties like strength, toughness, and dimensional stability, making the part suitable for its intended application.
The casting process creates an object's shape, but it leaves behind an inconsistent and stressed internal structure. Heat treatment is the essential refining step that transforms this raw shape into a reliable, high-performance engineering component.

The Core Problem: Why As-Cast Parts Are Flawed
A metal part fresh from its mold, known as an "as-cast" part, is rarely ready for service. The uncontrolled cooling inherent in the casting process introduces significant internal flaws that compromise its performance.
Inconsistent Grain Structure
As molten metal solidifies and cools in a mold, different sections cool at different rates. Thicker sections cool slowly, while thinner sections cool rapidly.
This uneven cooling creates a non-uniform and often coarse grain structure throughout the part. Coarse grains typically result in lower strength and toughness.
Locked-In Internal Stresses
The same uneven cooling process that affects grain structure also locks significant internal stresses into the material.
These stresses can cause the part to warp or crack over time, sometimes even before it is put into service. They also make the component brittle and unpredictable under load.
Unreliable Mechanical Properties
Because of the inconsistent grain structure and internal stresses, an as-cast part has unpredictable and unreliable mechanical properties.
One area of the casting might be harder and more brittle, while another might be softer. This lack of uniformity is unacceptable for most engineering applications, from automotive components to aircraft parts.
How Heat Treatment Corrects Casting Flaws
Heat treatment is a highly controlled process designed to reverse the negative effects of uncontrolled cooling. It fundamentally reorganizes the metal's internal structure at a microscopic level.
It Refines and Unifies Grain Size
Processes like normalizing involve heating the steel to a specific temperature above its critical point and holding it there.
This allows the atoms to rearrange into a much finer, more uniform grain structure. As the references note, this process achieves a consistent "pearlitic structure" that significantly refines the grain size.
It Relieves Internal Stresses
By heating the entire component uniformly and then allowing it to cool in a controlled manner (such as in open air for normalizing), the locked-in stresses are released.
This stress relief makes the part dimensionally stable and dramatically reduces the risk of cracking or distortion later in its service life.
It Improves Desired Properties
The ultimate goal of heat treatment is to enhance the physical properties of the casting.
A refined grain structure directly leads to increased toughness and strength. Other treatments, like tempering, can be used after an initial hardening process to increase ductility and reduce brittleness, achieving a precise balance of properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While essential for performance, heat treatment is not without its considerations. It represents a balance between final quality and production constraints.
Added Cost and Time
Heat treatment requires specialized furnaces, significant energy consumption, and additional processing time. This adds to the overall cost and lead time of producing the final part.
Risk of Distortion
Heating a part to high temperatures can cause it to warp or distort, especially with complex geometries or thin-walled components. This requires careful furnace loading, support, and process control to mitigate.
Process Selection Is Critical
There is no one-size-fits-all heat treatment. Using the wrong process can be worse than using none at all. The choice between normalizing, annealing, quenching, or tempering depends entirely on the specific metal alloy and the desired final properties of the component.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to apply heat treatment and which type to use is driven by the part's final application requirements.
- If your primary focus is on maximum toughness and stress relief for a final part: Normalizing is a critical step to create a strong, stable, and reliable steel component.
- If your primary focus is on improving machinability after a hardening process: Tempering is a necessary secondary treatment to reduce brittleness and restore some ductility.
- If your primary focus is on cost-reduction for non-critical applications: You may choose to skip heat treatment, but you must accept the inherent risks of internal stress, potential brittleness, and inconsistent mechanical properties.
Ultimately, heat treatment is the crucial process that elevates a metal casting from a simple shape into a predictable and dependable engineered component.
Summary Table:
| Problem in As-Cast Parts | How Heat Treatment Helps |
|---|---|
| Inconsistent, coarse grain structure | Refines and unifies grain size for better strength and toughness |
| Internal stresses from uneven cooling | Relieves stresses to prevent warping and cracking |
| Unreliable mechanical properties | Enhances properties like hardness, ductility, and stability |
Ready to optimize your cast components with precise heat treatment? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for metallurgical processes, helping you achieve consistent, high-performance results. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why is deposition technology an amazing scientific advancement? Unlock Atomic-Level Material Engineering
- How can we reduce the toxicity of carbon nanotubes? Strategies for Safer Applications
- What is the difference between sputtering and PLD? Sputtering vs. PLD for Thin Film Deposition
- How are polymers used in the sintering process? Master Porosity and Strength with Expert Techniques
- How long does heat treatment of steel take? From Minutes to Days for Your Project
- What are the limitations of magnetron sputtering? Key Trade-offs in Thin Film Deposition
- What are the factors that affect the quality of heat treatment? Mastering Temperature, Atmosphere, and Process Control
- What is the standard heat treatment process? A Framework to Achieve Your Desired Material Properties



















